Interference control method and device, message sending method and device, message forwarding method and device, communication equipment and system
A technology of interference control and transmission method, which is applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of propagation distance extension, uplink signal interference, propagation delay exceeding the guard gap, etc., and achieve beneficial effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035]Under certain weather conditions, the low density at higher altitudes in Earth's atmosphere causes a decrease in the refractive index, bending the signal toward Earth. In this case, the signal can propagate in the higher index layer, ie the atmospheric duct, due to the reflection and refraction encountered at the boundary of the low index material. This phenomenon is called atmospheric ducting, and in the atmospheric ducting mode of propagation, radio signals experience less attenuation and are able to travel over distances far greater than normal radiation. Atmospheric ducting phenomenon usually occurs in the spring-summer transition period and summer-autumn transition period in inland areas and winter in coastal areas, and its affected frequency ranges from about 0.3GHz to 30GHz.
[0036] At present, in a TDD (Time Division Duplexing, Time Division Duplexing) network configured with the same uplink and downlink transmission directions, guard gaps are used to avoid cros...
Embodiment 2
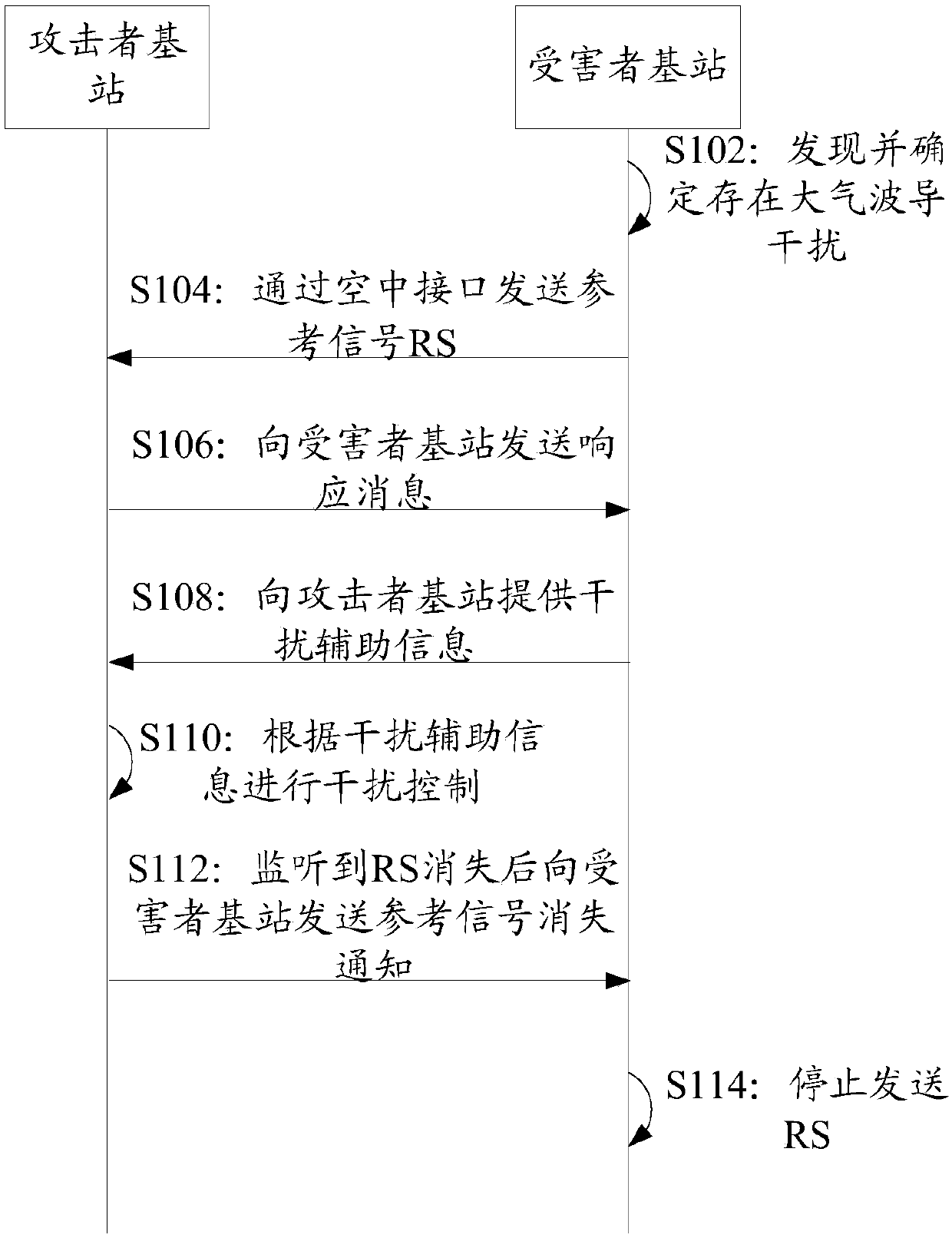
[0097] This embodiment will introduce the process of sending response messages on the attacker node side in the atmospheric waveguide interference control scheme in combination with the previous embodiments. Please refer to Figure 8 :
[0098] S802: The base station of the attacker performs reference signal monitoring.
[0099] In an example of this embodiment, after receiving the message notification from the network management, the group center node of the attacker node group may instruct the base stations in the group to monitor the atmospheric waveguide interference. The attacker base station monitors the atmospheric waveguide interference after receiving the monitoring instruction from the group center node, so as to determine whether it can monitor the reference signal sent by the victim base station.
[0100] In other examples of this embodiment, each base station of the attacker node group can monitor the reference signal without being notified and triggered by the g...
Embodiment 3
[0121] This embodiment will continue to introduce the process of sending response messages on the attacker node side in the atmospheric waveguide interference control scheme in combination with the previous embodiments. The difference from Embodiment 2 is that the response messages in this embodiment are not sent by the attacker base station itself. , but sent by the group center node of the attacker node group, see Figure 9 :
[0122] S902: The group central node obtains the monitoring result of the reference signal by the base stations in the node group.
[0123]In an example of this embodiment, after receiving the message notification from the network management, the group center node of the attacker node group may instruct the base stations in the group to monitor the atmospheric waveguide interference. After receiving the monitoring instruction from the group center node, the attacker base station monitors the atmospheric waveguide interference, and reports the monitori...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com