Self-adaptive variable-posture bionic mechanical foot
A bionic machine and attitude changing technology, applied in the field of engineering bionics, can solve the problem of not considering the adjustment of motion attitude in detail, and achieve the effects of improving traction performance, reducing intrusion resistance, and changing the ground contact area.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
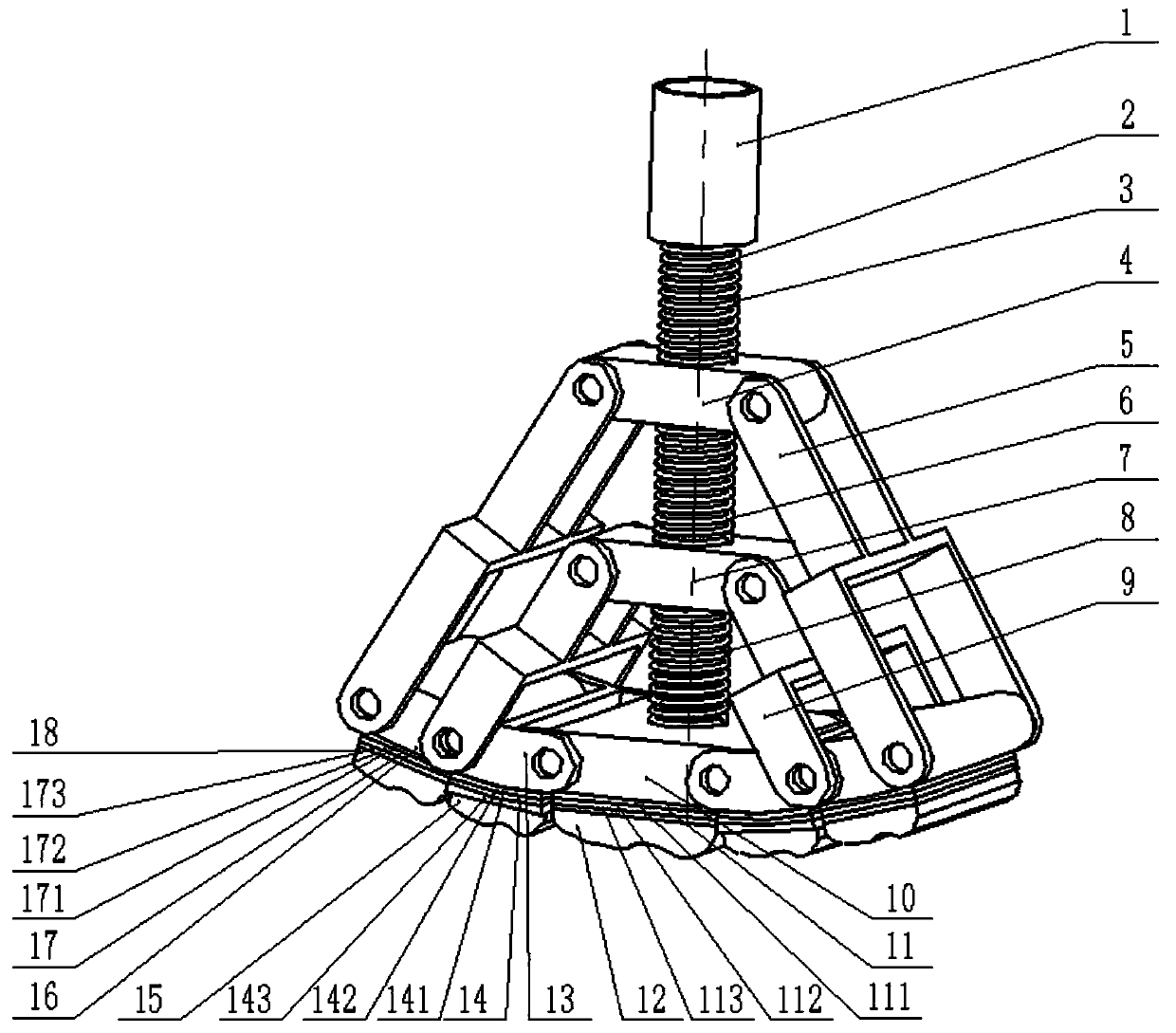
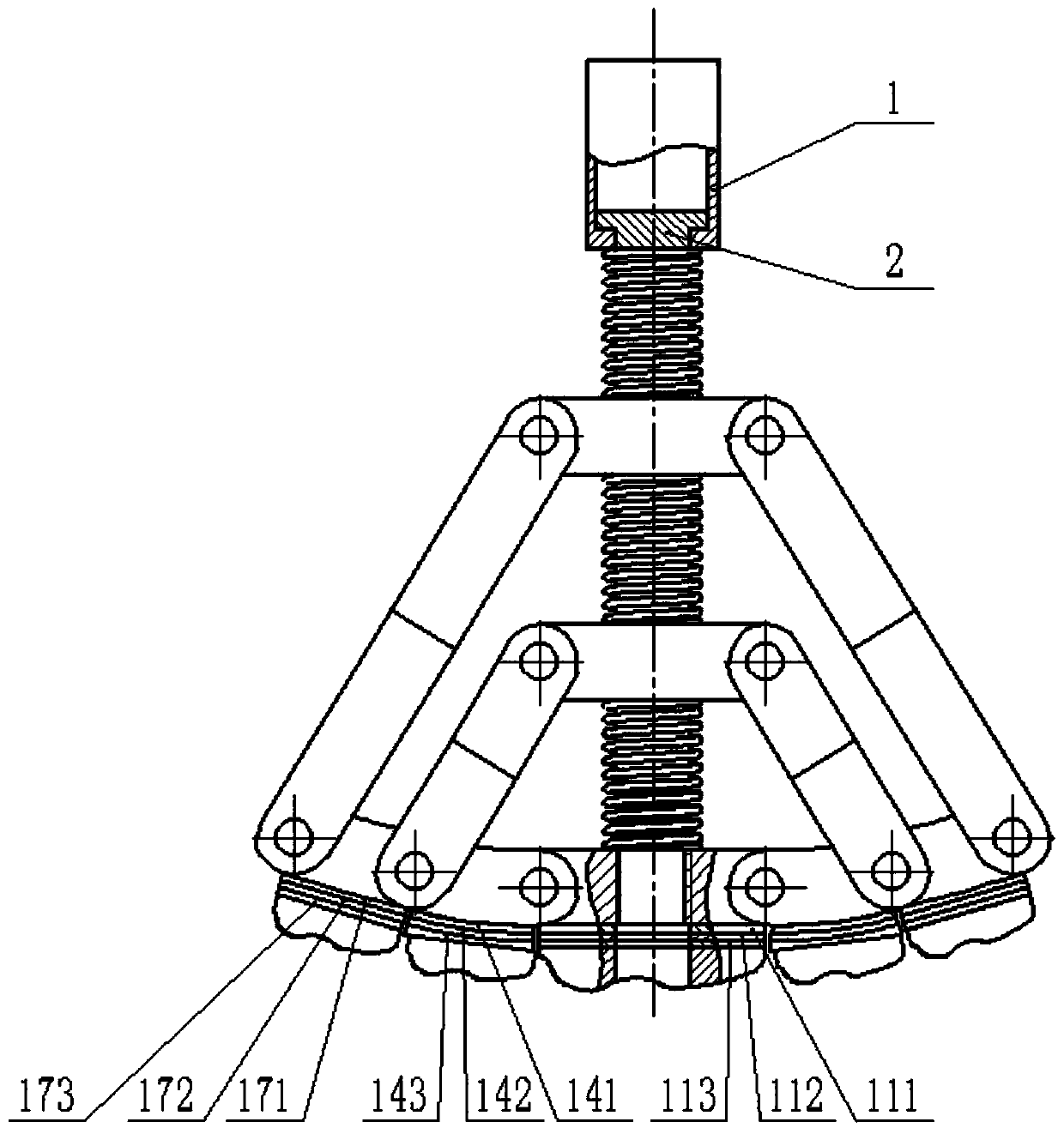
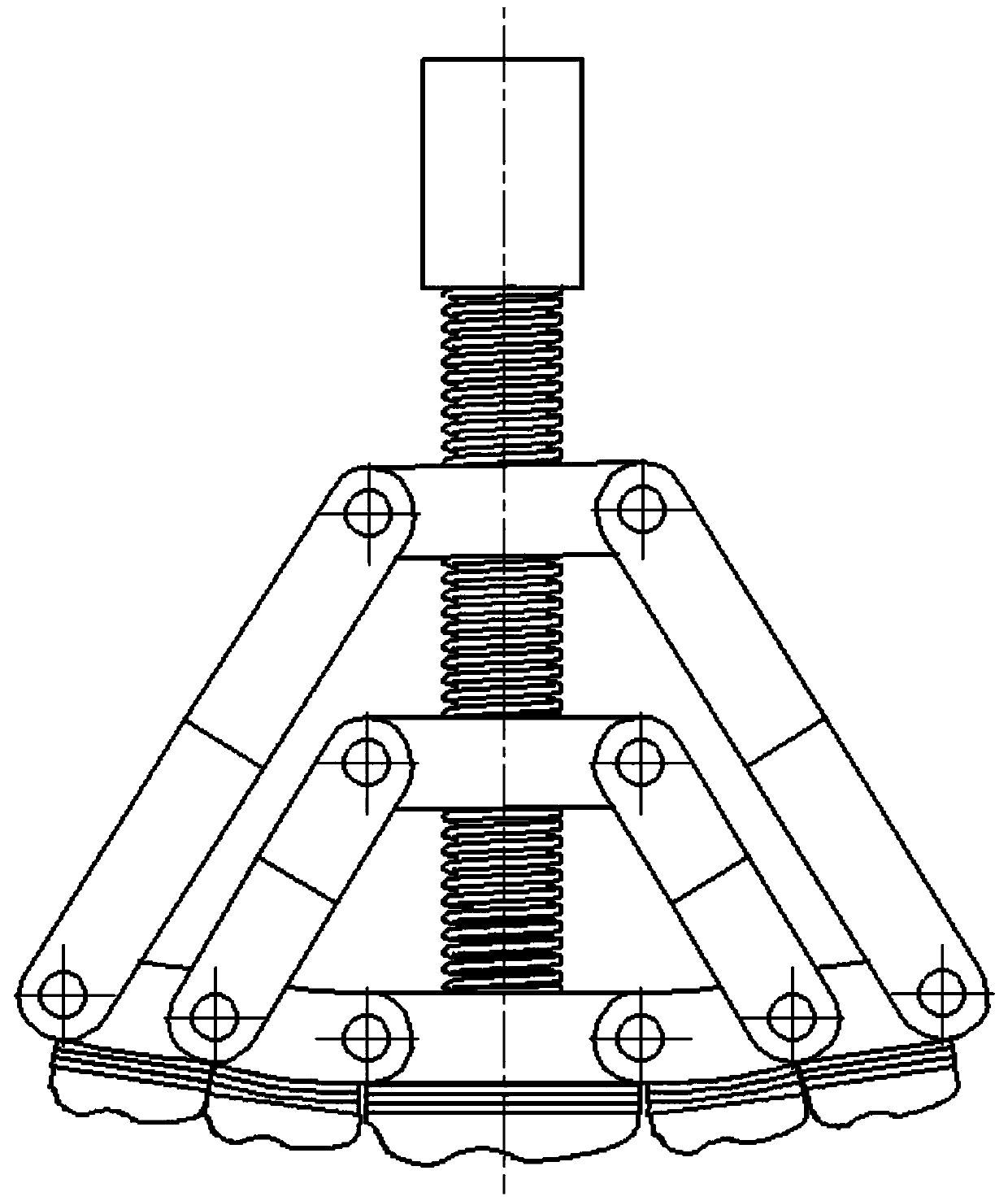
[0024] The following combination Figure 1 to Figure 6 , the specific implementation of the bionic mechanical foot will be described.
[0025] An adaptive posture-changing bionic mechanical foot, comprising a load-bearing rod 1, a guide rod 2, a first slider linkage mechanism, a second slider linkage mechanism, a first toe mechanism, a pair of second toe mechanisms, a on the third toe body. After the guide rod 2 passes through the load-bearing rod 1, the first slider 4 of the first slider linkage mechanism, and the second slider 7 of the second slider linkage mechanism, it is threadedly connected with the first toe mechanism; The second toe mechanism is respectively hinged on the left and right sides of the first toe mechanism; a pair of third toe mechanisms are respectively hinged on the outside of the second toe mechanism on the corresponding side. The ends of the two first connecting rods 5 of the first slider link mechanism are respectively hinged with the third toe mech...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com