Method and network for sending multiple signals
A signal and layered network technology, applied in the direction of network synchronization, multiplexing communication, multiplexing multiple codes, etc., can solve the problems of inefficiency, asymmetry, increase the length of the duty cycle, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
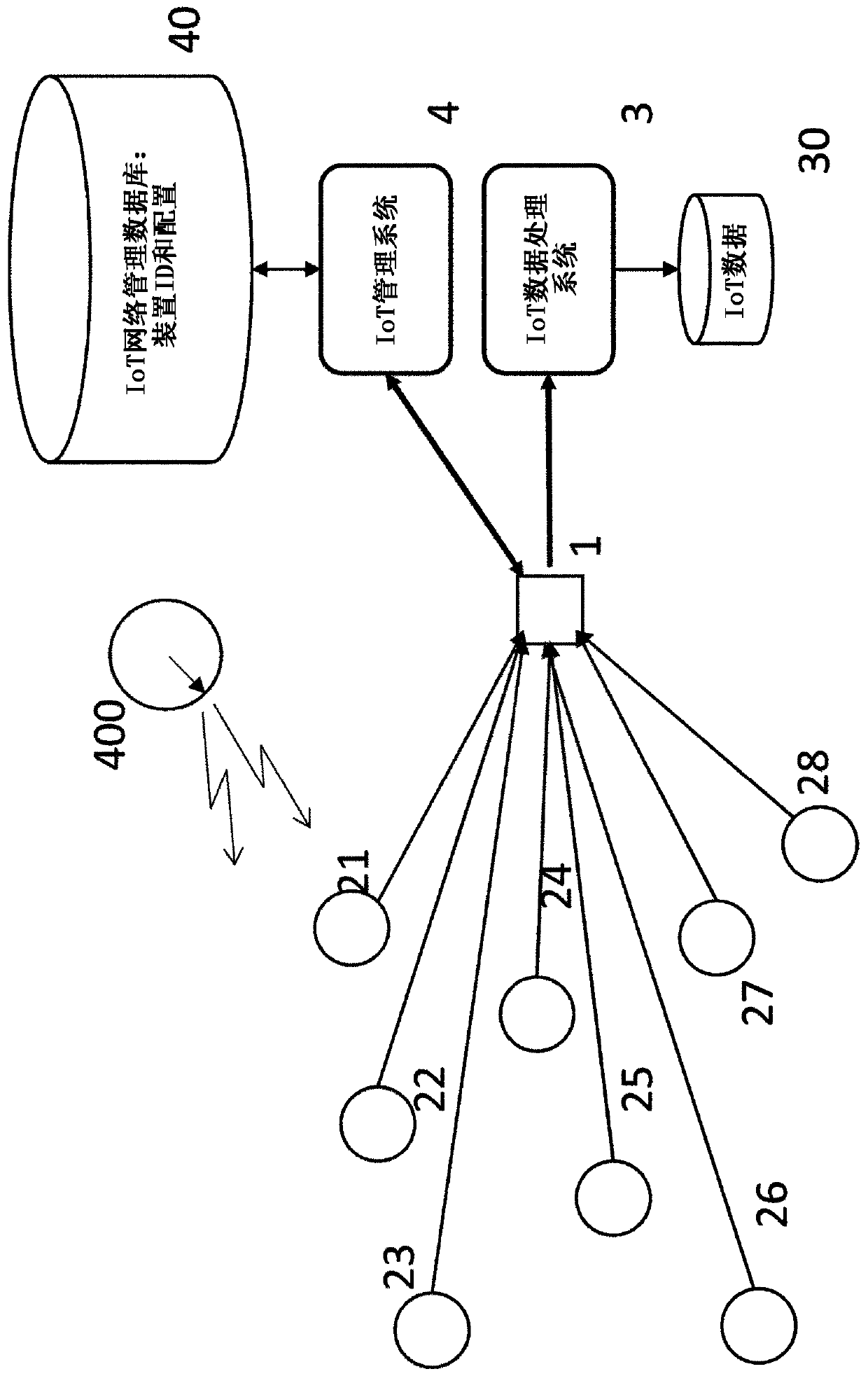
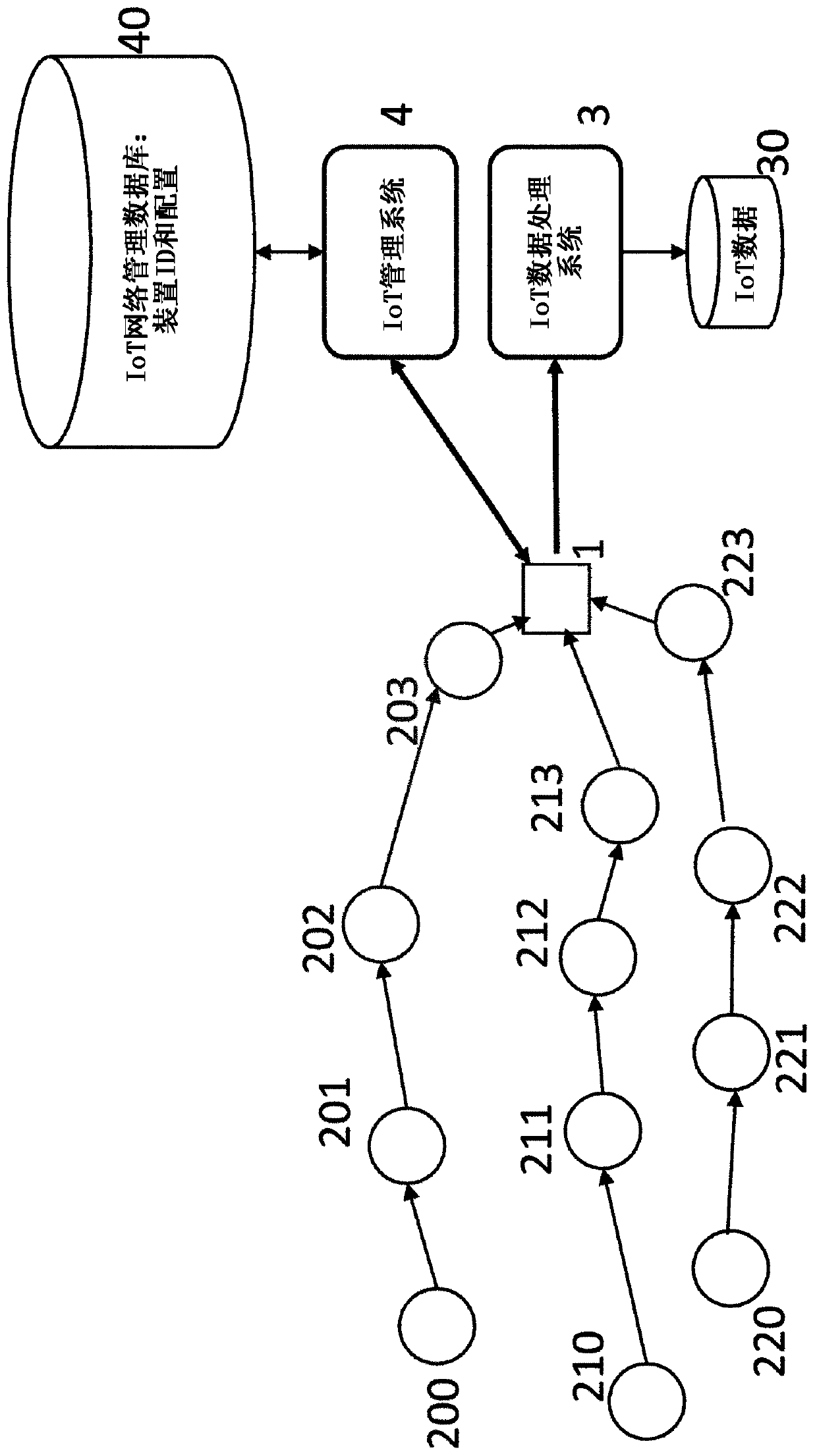
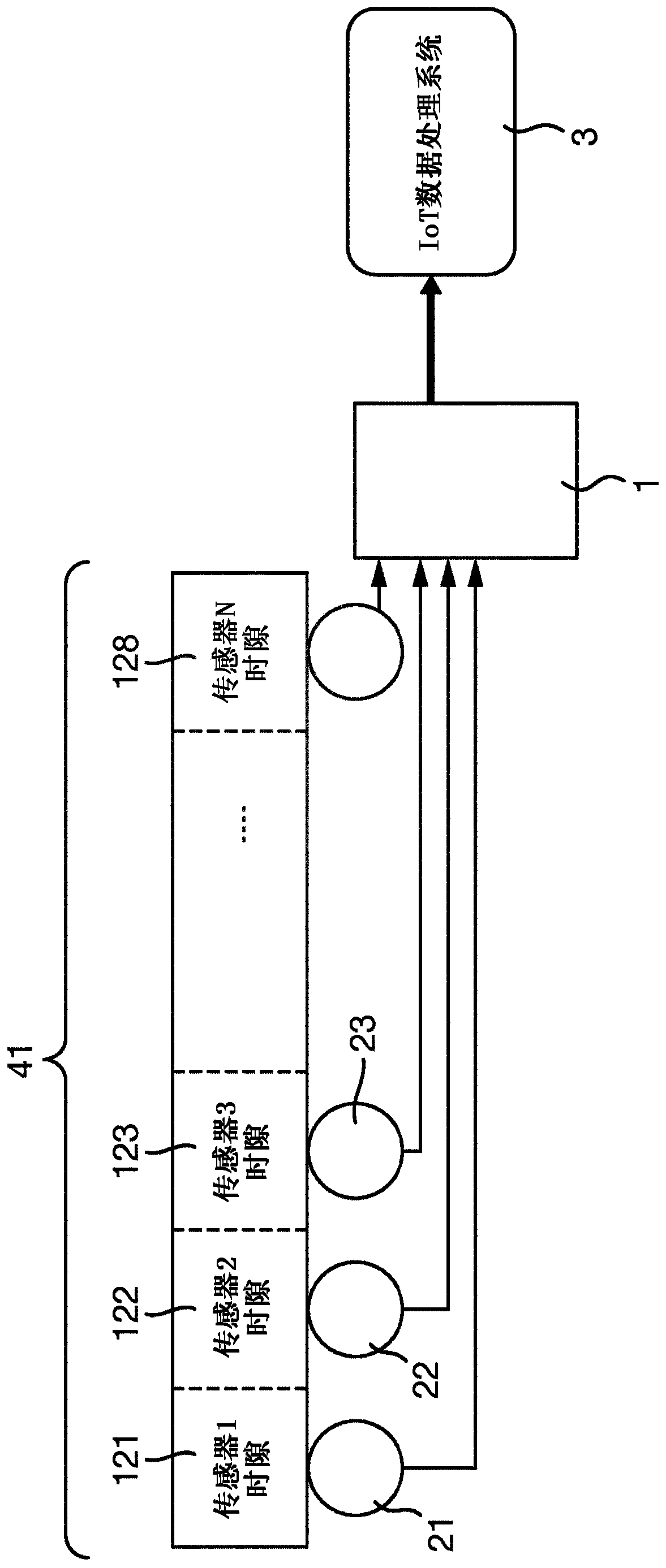
[0041] figure 1 and figure 2 Two simplified network architectures are shown, simplified for illustrative purposes. Due to the limited battery power used by the sensors, and because the sensors typically operate in different frequency bands, use different protocols, and have no Internet connection, the data sent by these sensors often cannot reach the target data processing system directly. Instead, the sensor data is passed to the aggregator / gateway 1 for onward transmission to the target system. exist figure 1 and figure 2 In both, gateway node 1 provides a plurality of sensors 20-29 ( figure 1 ), multiple sensors 200-223 ( figure 2 ) with the data processing system 3 with the database 30 and the management system 4 with the database 40 . The sensors 20 , 200 , etc. send the data they collect to the data processing system 3 and receive control / management instructions from the management system 4 . Such as figure 1 As shown in , data can be transmitted directly betw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com