Packet consistent method for heterogeneous networked multi-agent systems with time-varying delays
A multi-agent system, time-varying time-delay technology, applied in general control systems, control/regulation systems, instruments, etc., can solve problems affecting the convergence speed of the system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
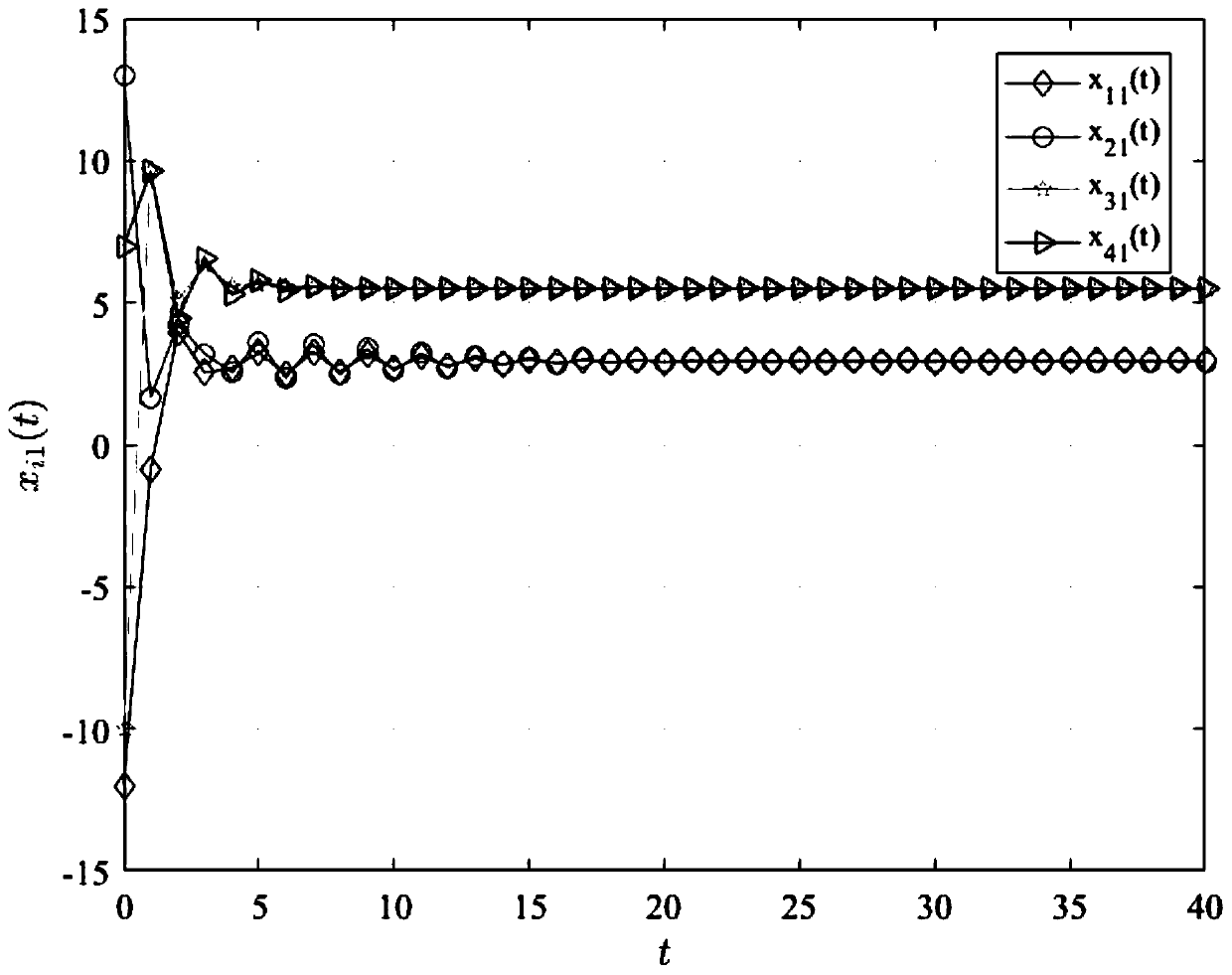
[0071] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 A pair of this embodiment will be described. The method for the group consistency of the heterogeneous networked multi-agent system with time-varying time-delay described in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0072] Step 1. Establishing a discrete-time dynamic model of a heterogeneous networked multi-agent system with time-varying time-delay;
[0073] Step 2, constructing a state observer for the discrete-time dynamic model established in step 1, and performing state prediction;
[0074] Step 3. According to the state prediction of the discrete-time dynamic model of the heterogeneous networked multi-agent system with time-varying time-delay in step 2, design a group consistency control protocol;
[0075] Step 4. According to the group consistency control protocol designed in step 3, a compact expression form of the group state error equation and estimation error equation is obtained;
[0076]...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0078] Specific implementation mode 2: The difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode 1 is that the step 1 is specifically:
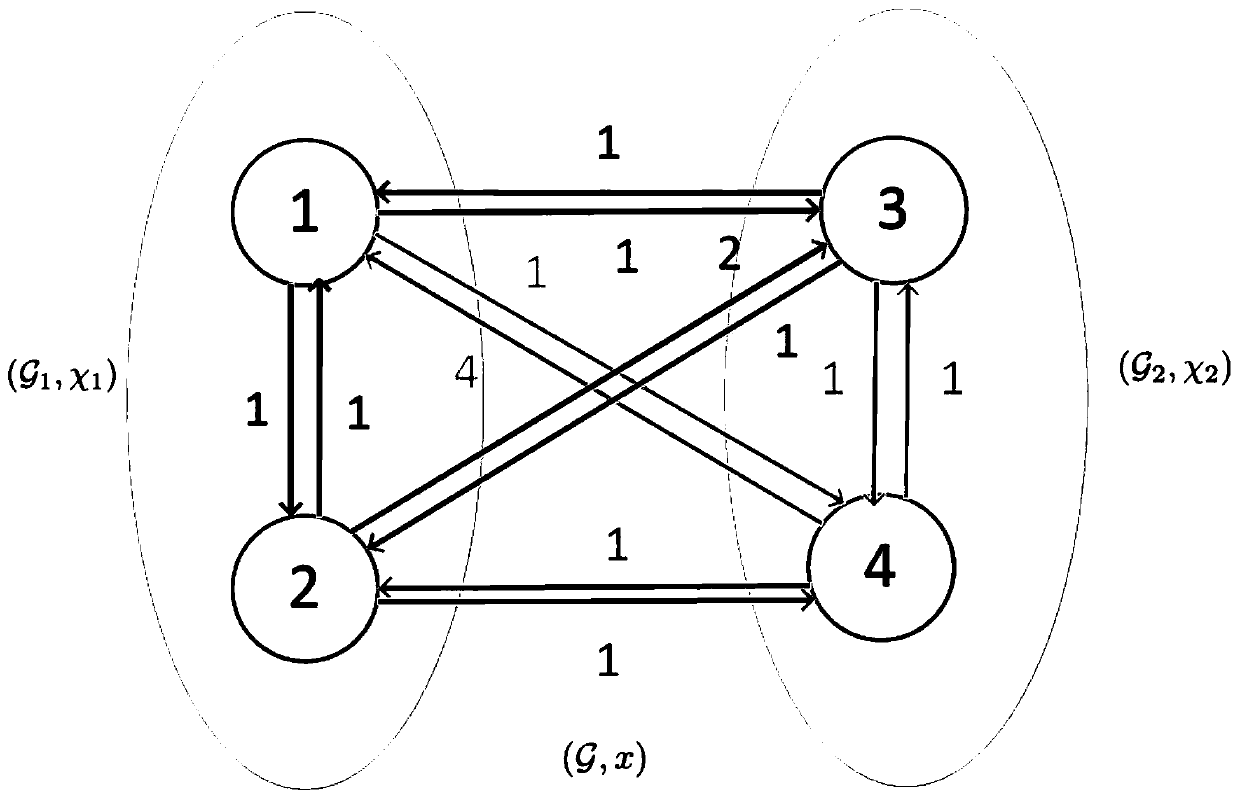
[0079] For a network containing N+M agents N≥2, M≥2; the state of agent i is expressed as x i , i=1,2,…,N+M; each agent is a network A node of , the state of each node can represent the actual physical quantity, such as attitude, position, temperature, voltage, etc. The topology of this networked multi-agent system is a weighted directed graph, is the vertex set, is the edge set, is a non-negative weighted adjacency matrix; the index set of vertices is from vertex v i to vertex v j The directed edge of is denoted as ε ij =(v i ,v j ), j=1,2,…,N+M; corresponding to ε ij The adjacency matrix element a of ij is a non-zero real number, the vertex v i The neighborhood node set of is Laplace matrix Indicates that the element is l ij The (N+M)×(N+M) dimensional matrix, where,
[0080] The weighted ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0086] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 2 is that the specific process of state prediction described in step 2 includes:
[0087] In a networked multi-agent system, agent i can receive information from itself and neighboring agent j, but there is a time-varying delay τ in the communication network ij (t); and is a known bounded function, τ 0 and τ are the lower and upper bounds respectively; the state prediction from time t-τ to time t is:
[0088]
[0089] in, R s is the s-dimensional real number space; it means that based on the information of the agent i until the time t-q, the predicted state of the agent i at the time t-p is obtained, y i (t-τ) represents the output function of the i-th agent at time t-τ, L iDenotes the i-th observer gain matrix, Indicates the predicted output function of the i-th agent at time t-τ, L i Denotes the i-th observer gain matrix.
[0090] Other steps and parameters are the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com