Binary coding addressing method and addressing device
A binary code and addresser technology, applied in the field of binary coded addressing method and addresser, can solve the problem of low efficiency of binary coded addressing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
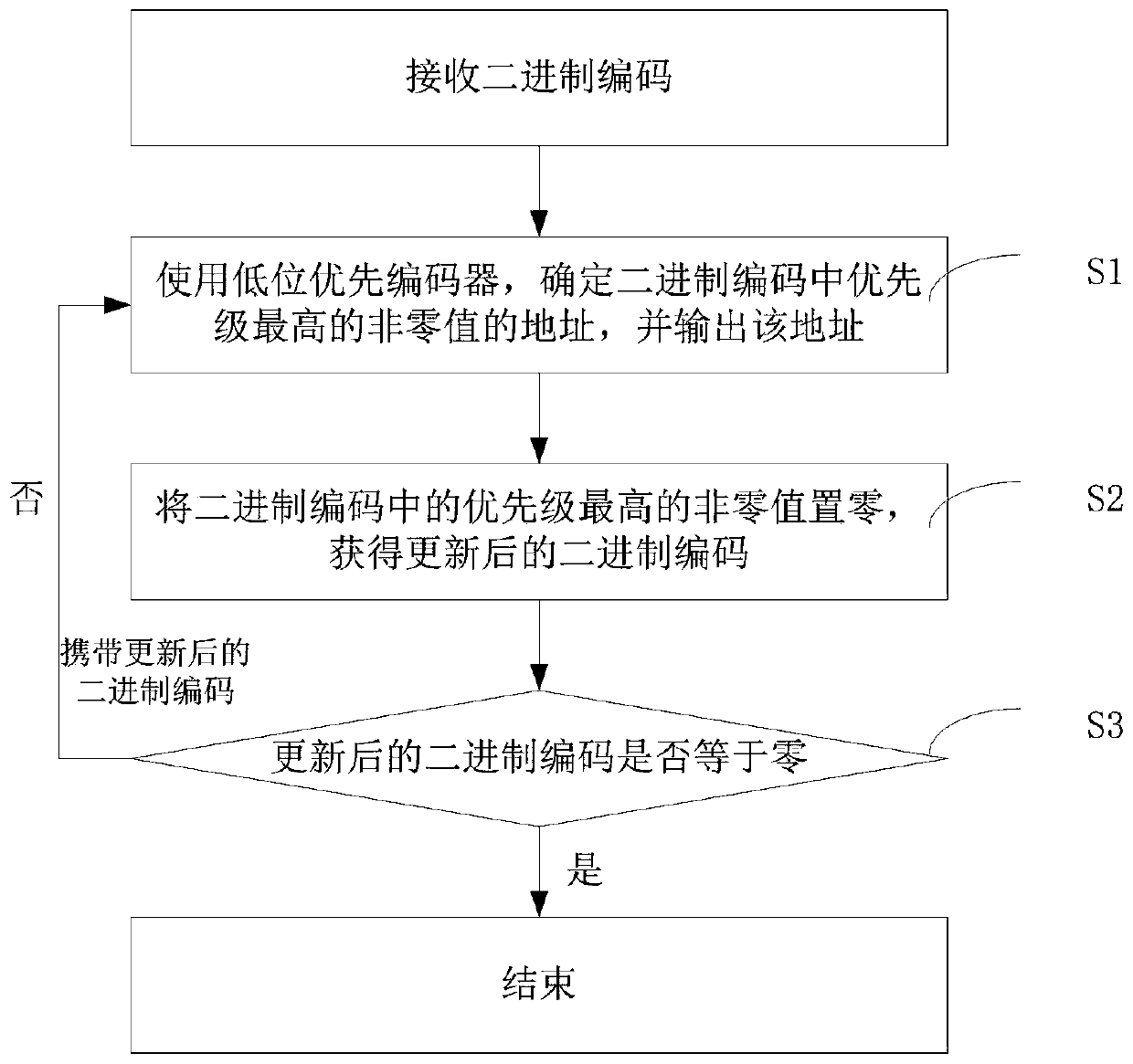
[0029] see figure 1 , this embodiment takes the low-order first encoder as an example to describe the addressing method of the binary code provided by this embodiment. Specifically, the method provided in this embodiment determines addresses of all non-zero values of the binary code by performing the following steps S1-S3 after receiving the binary code.
[0030] Step S1, using a little bit first encoder to determine the address of the highest priority non-zero value in the binary code, and output the address.
[0031] The priority encoder allows input signals at several input terminals at the same time, and according to the priority order of the input signals, only the signal with the highest priority among the several input signals at the same time is encoded.
[0032] Exemplarily, take an 8-wire-3-wire low-order priority encoder as an example. The encoder has eight input terminals and three output terminals, and can input eight signals at the same time, and gradually red...
Embodiment 2
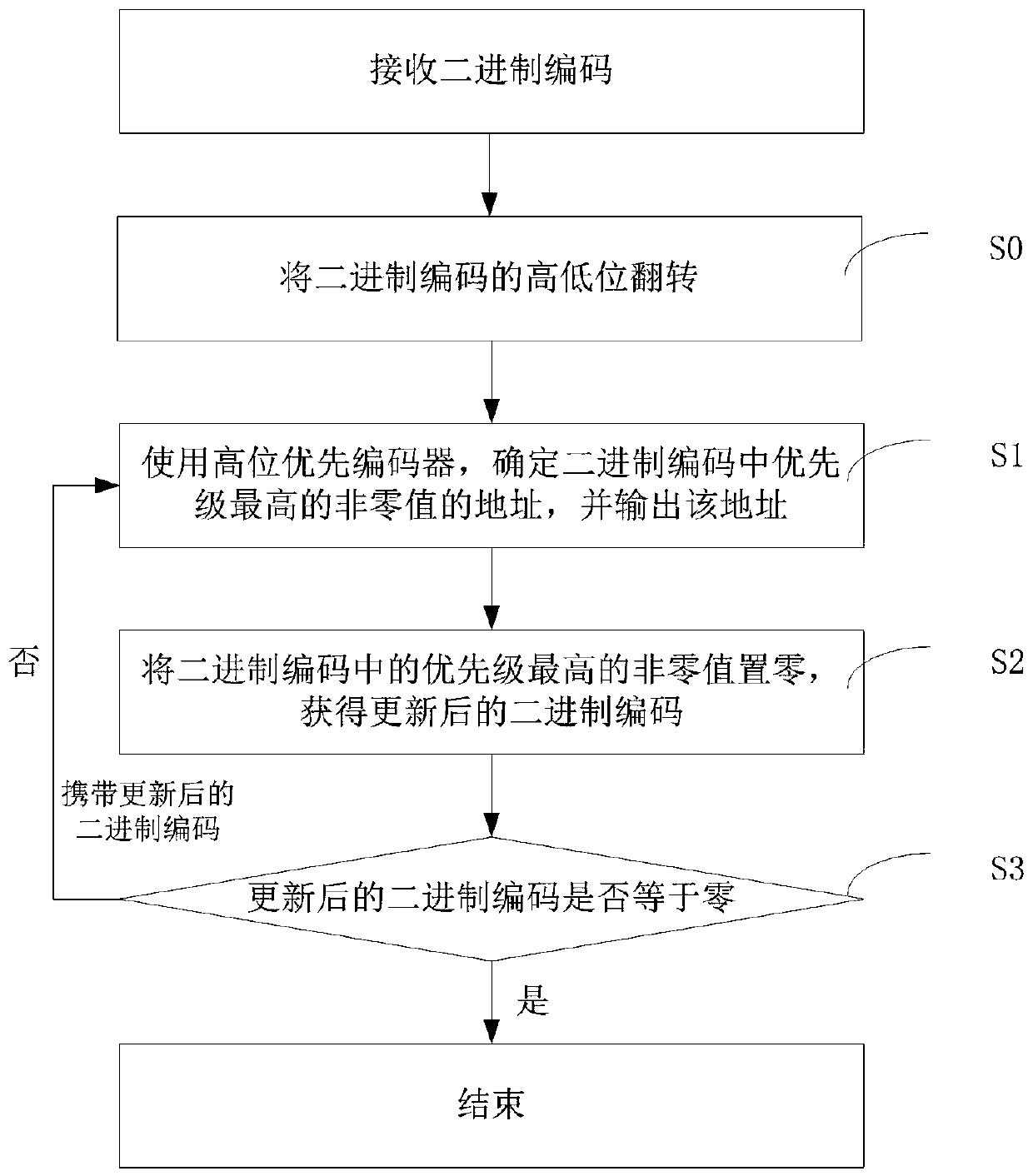
[0060] see figure 2 , this embodiment takes a high-order-first encoder as an example to describe the addressing method of the binary code provided in this embodiment. Specifically, the method provided in this embodiment determines addresses of all non-zero values in the binary code through the following steps S0-S3 after receiving the binary code.
[0061] Step S0, flipping the high and low bits of the binary code.
[0062] For example, when the binary code to be addressed is 10000101, after flipping its high and low bits, 10100001 is obtained.
[0063] It should be noted that, generally, for a binary code, the rightmost binary bit is the lowest bit, and the leftmost binary bit is the highest bit. If the binary code is directly input into the high-order priority encoder, there will be a problem that the priority of the binary bit does not correspond to the priority of the input channel. For example, in the binary code 10000100, 1 with the highest priority is input from t...
Embodiment 3
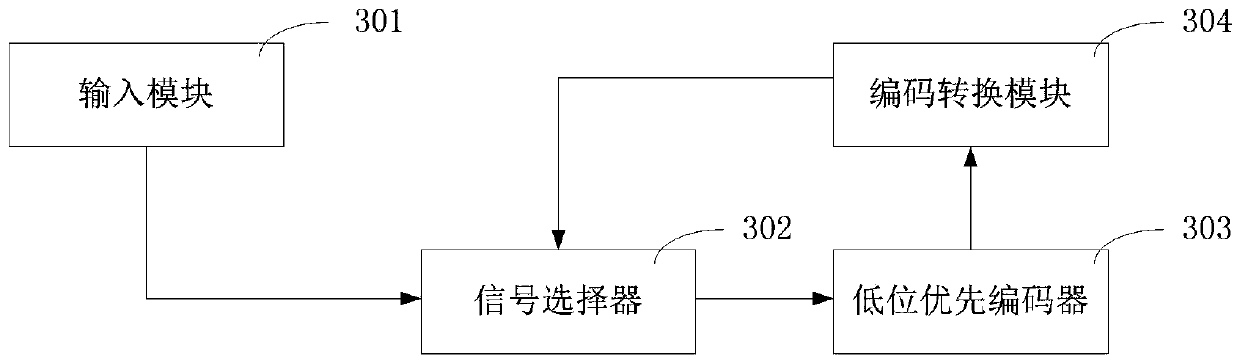
[0091] see image 3 , based on the binary-coded addressing method provided in the above-mentioned embodiment 1, this embodiment provides a binary-coded addresser, the addresser includes an input module 301, a signal selector 302, a low-order-first encoder 303 and an encoding conversion module 304 .
[0092] The input module 301 is configured to receive binary codes.
[0093] The signal selector 302 is configured to input the binary code output by the input module 301 or the updated binary code output by the code conversion module 304 into the low order priority encoder 303 according to a preset selection signal. For example, in the first clock cycle, according to the signal 0, the binary code of the input module 301 is sent to the little bit first encoder 303 . In other clock cycles, according to the signal 1, the binary code of the code conversion module 304 is sent to the low-order first coder 303 .
[0094] The low-order priority encoder 303 is configured to determine th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com