Device and method for recycling phosphorus-containing wastewater in vacuum system of vacuum rectification of yellow phosphorus
A vacuum rectification and vacuum system technology, applied in vacuum distillation, fractionation, etc., can solve the problems of production system fluctuations, high production pressure, high processing costs, etc., and achieve the effect of ensuring continuous normal operation and normal and stable negative pressure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
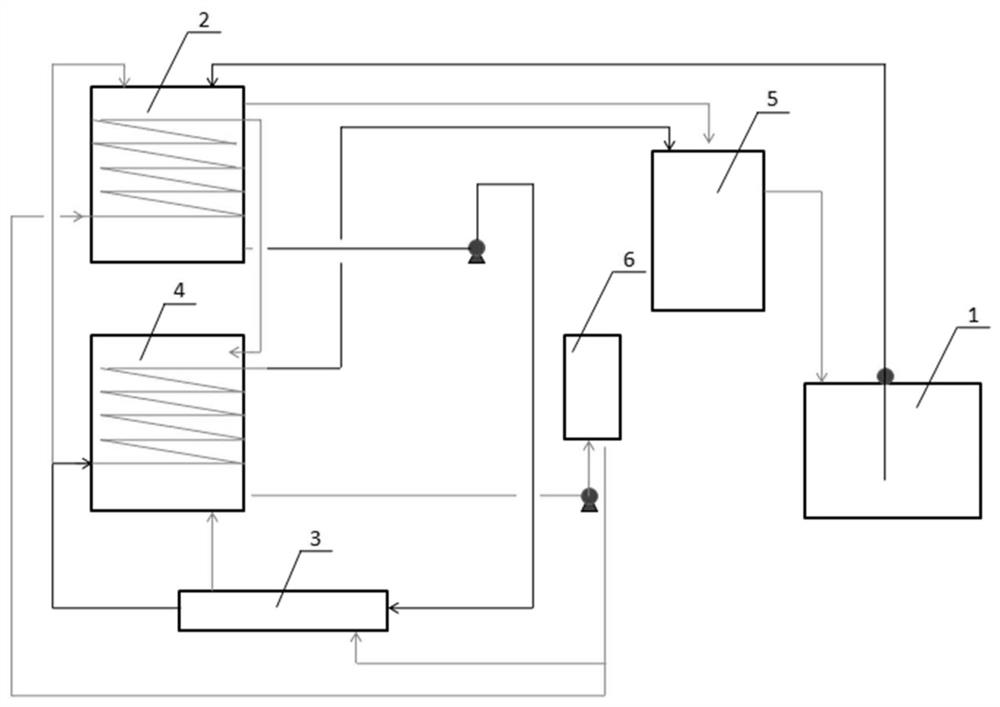
[0036] Such as figure 1 A yellow phosphorus decompression rectification vacuum system is shown as a device for treating phosphorus-containing wastewater. The device includes a phosphorus-containing wastewater collection tank 1, a cold water tank 2, a cold water tank 4, a heat exchanger 3, a water chiller 6, and a vacuum water tank. 5. Phosphorus-containing waste water collection tank 1 is connected to cold water tank 1 2; cold water tank 1 2 is connected to heat exchanger 3, heat exchanger 3 is connected to cold water tank 2 4, cold water tank 2 4 is connected to vacuum water tank 5, and vacuum water tank 5 Together with the phosphorus-containing wastewater collection tank 1, a circulation pipeline is formed.
[0037] Cold water tank one 2 is also connected with cold water tank two 4, and cold water tank two 4 is connected with chiller 6, and chiller 6 is connected with cold water tank one 2, and cold water tank one 2 is connected with cold water tank two 4 to form a circulati...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The method for recycling phosphorus-containing wastewater using the device of Example 1 (see the appendix to the description for the device corresponding to the method) figure 1 ), the specific steps are:
[0043] (1) Send the wastewater in the phosphorus-containing wastewater collection tank 1 to the cold water tank-2;
[0044] (2) Turn on the delivery pump from the cold water tank 1 to the heat exchanger 3, and cool the cold water by 25°C in the heat exchanger 3;
[0045] (3) Part of the cooling water cooled by the heat exchanger 3 enters the coil of the cold water tank 2 4 and is cooled to 12°C again; part of it enters the cold water tank 1 2, which can reduce the phosphorus-containing wastewater from the phosphorus-containing wastewater collection tank to 32°C;
[0046] (4) The cooling water in the cold water tank 2 enters the chiller 6 through the transfer pump to cool down by 12°C. After cooling, part of it enters the heat exchanger 3 as the cooling water for th...
Embodiment 3
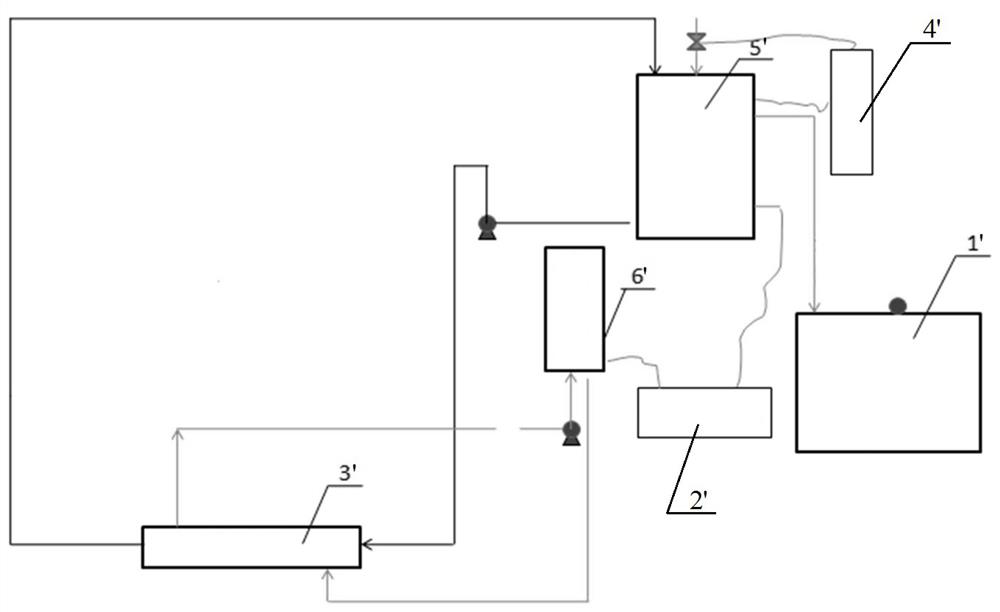
[0051] Embodiment 3 (the corresponding device of this method is shown in the description attached figure 1 )
[0052] (1) Send the wastewater in the phosphorus-containing wastewater collection tank to the cold water tank one;
[0053] (2) Turn on the transfer pump from the second cold water tank to the heat exchanger, and cool the cold water by 25°C in the heat exchanger;
[0054] (3) The second cooling water of the cold water tank is sent to the chiller, the parameters are set, the set temperature is 15°C, and the refrigerant outlet water is 15°C for cooling;
[0055] (4) Open the valve on the cooling water delivery pipe, pass part of the cooling water of the chiller into the tube heat exchanger, and then into the second cold water tank; the other part enters the first coil of the cold water tank, and then returns to the second cold water tank;
[0056] (5) Phosphorus-containing waste water in the cold water tank is cooled by the internal coil, enters the heat exchanger, open...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com