Algorithms and methods for assessing late clinical endpoints in prostate cancer
A Prostate Cancer, Clinical Outcomes Technology, applied in the field of clinical management options for at-risk prostate cancer patients, to address issues such as inaccurate estimates of individual patient risk and lack of reproducibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0167] Example 1: Risk of Clinical Relapse (CR) and Prostate Cancer Death (PCD) Associated with GPS Results <20
[0168] Two large longitudinal prostate cancer cohorts were analyzed to assess the risk of CR and PCD with GPS 20 units (range 0 to 100). Patient data from E. Klein et al., Eur Urol 66:550-560 (2014) and J. Cullen et al., Eur Urol 68:123-131 (2015) were analyzed to determine a cut-off point with the pre-established GPS of 20 Associated CR and PCD risks. For more details on the baseline characteristics of the patients in this study, see Table 1 of E. Klein et al., Eur Urol 66:550-560 (2014) and Table 1 of J. Cullen et al., Eur Urol 68:123-131 (2015). Table 1.
[0169] Patients were stratified according to the value of GPS (≤20 or >20). Cox regression analysis accounted for group sampling weights. This is due to the fact that the GPS was developed using the Klein standardized hazard ratio (std HR, HR for a 1 standard deviation (SD) change in the covariate) for GP...
Embodiment 2
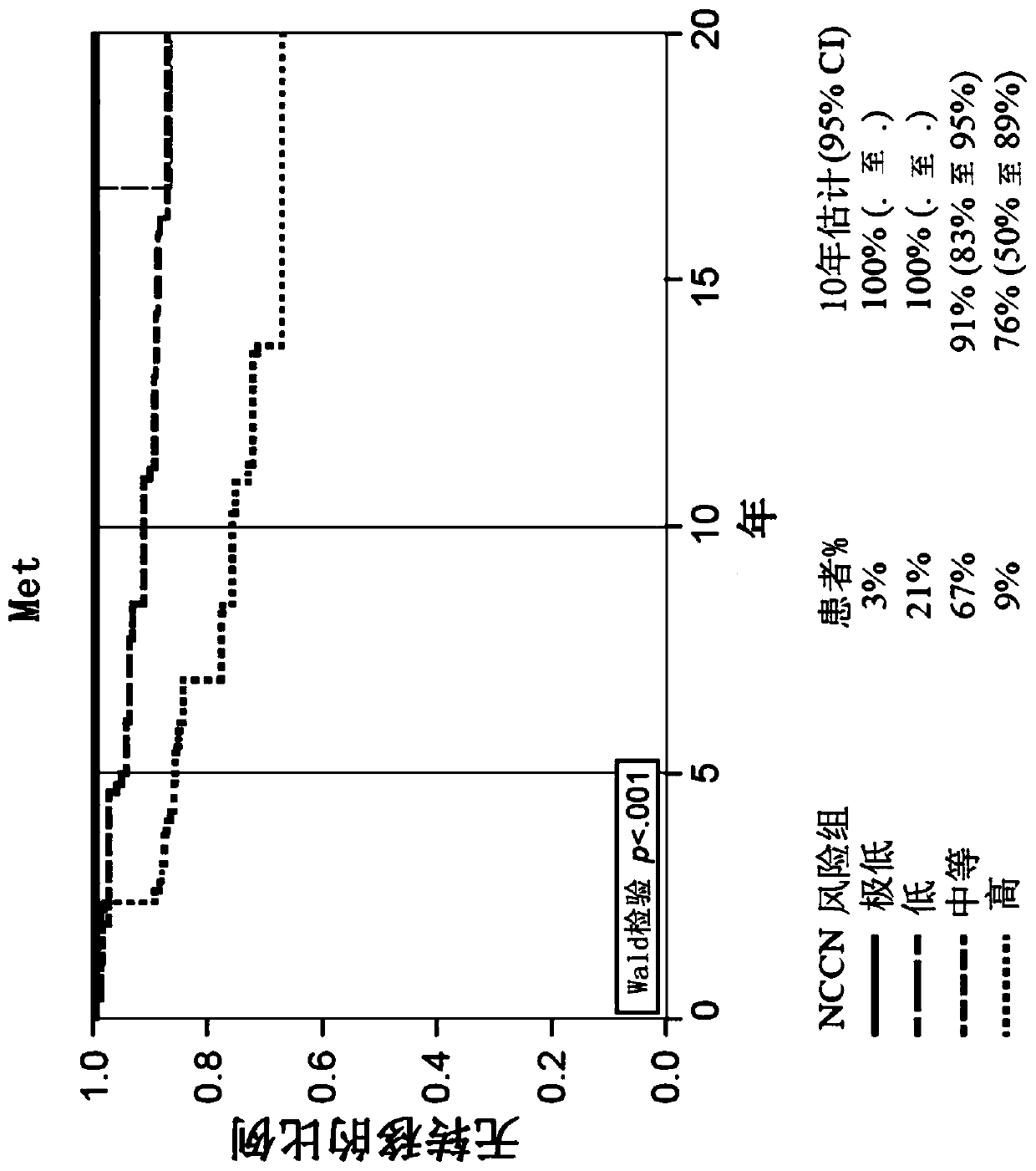
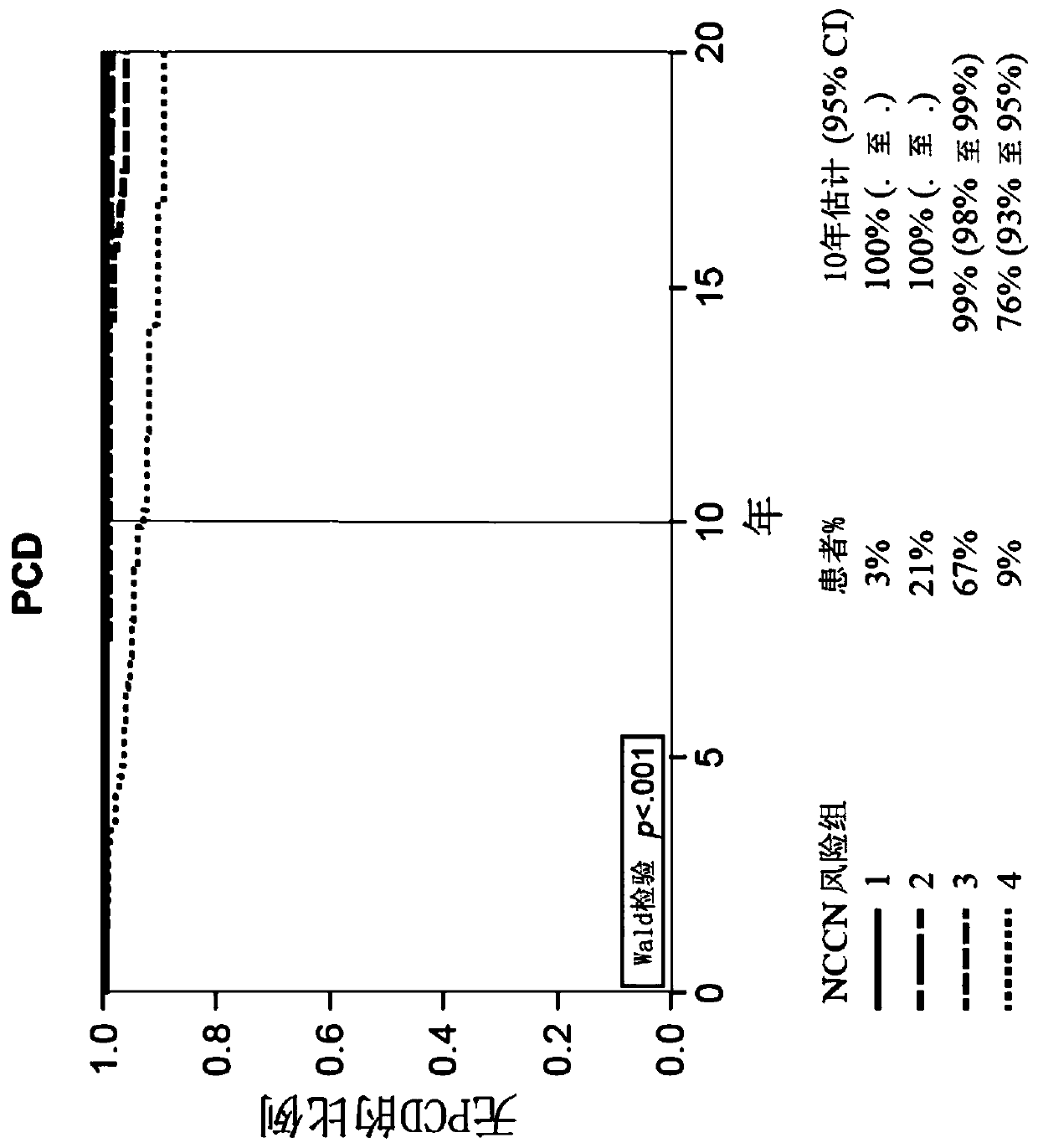
[0173] Example 2: GPS Results ≤40 and >40 and Risk of Distant Metastasis and Prostate Cancer Death in Prostate Cancer Patients
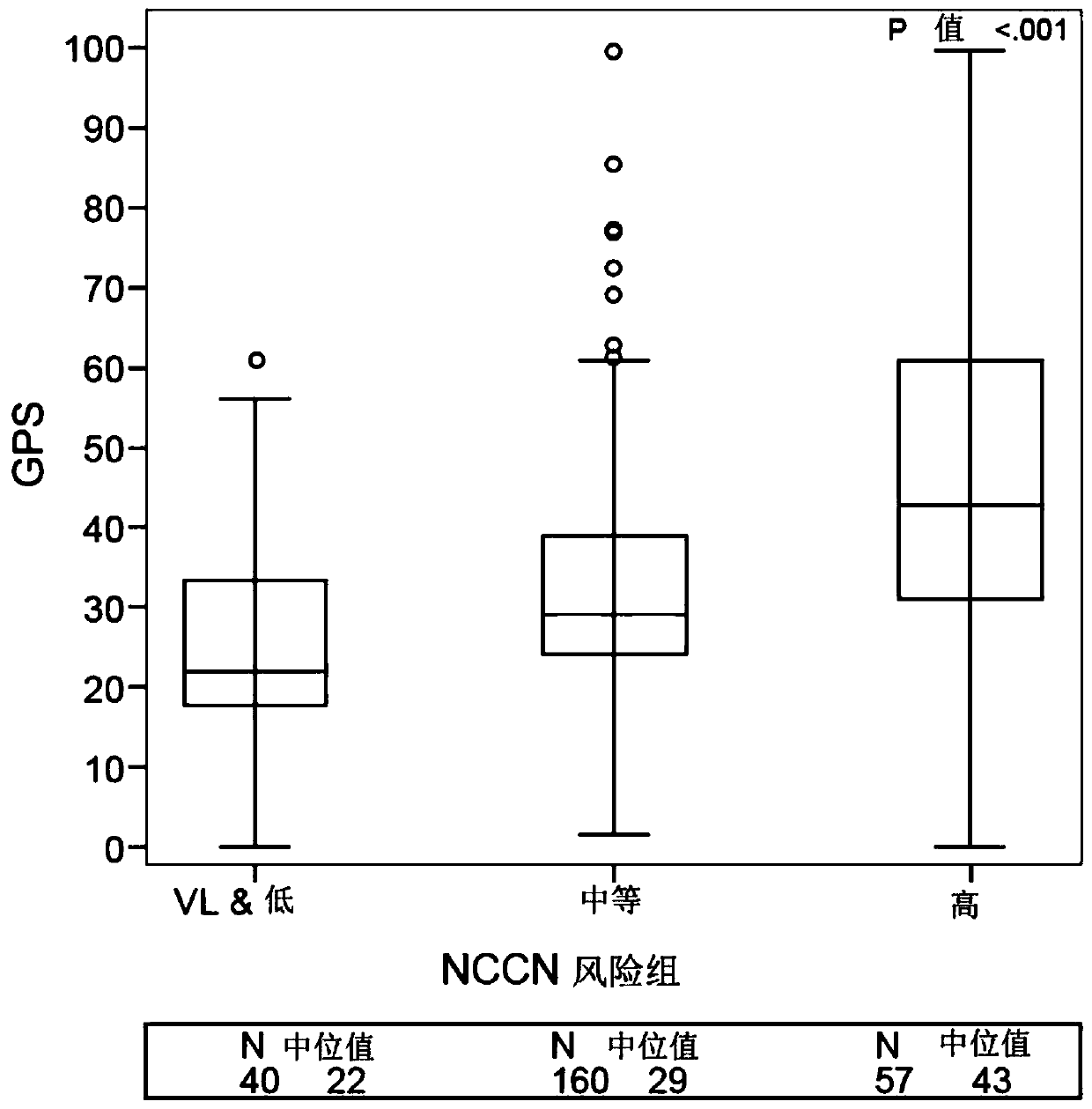
[0174] The initial selection of 259 patients was selected from 6184 men with prostate cancer at very low to high NCCN risk in a large community-based US general health care system from 1995-2010. Specifically, among 6184 eligible patients, 404 patients were selected according to a prespecified group sampling protocol, of whom 334 had available biopsies. Fourteen (4%) were excluded due to clinical ineligibility and 41 (12%) were excluded due to insufficient or incorrect tumor type. Of the remaining 279, 259 (93%) patients had valid GPS results and represented the final evaluable population. The 259 patients included 5 in the very low-risk group, 35 in the low-risk group, 160 in the intermediate-risk group, and 57 in the high-risk group. The table below provides the characteristics of the 259 evaluable patients.
[0175] Table 2
[0176]
[0177...
Embodiment 3
[0205] Example 3: GPS Results ≤40 and >40 and Risk of Clinical Relapse (CR) and Biochemical Relapse (BCR) in Prostate Cancer Patients
[0206] In two other studies, patient data from E. Klein et al., Eur Urol 66:550-560 (2014) and J. Cullen et al., Eur Urol 68:123-131 (2015) were analyzed to consider high How GPS results at or below 40 correlate with BCR and CR in intermediate-risk patients. For more details on the baseline characteristics of patients in these studies, see Table 1 of E. Klein et al., Eur Urol 66:550-560 (2014) and Table 1 of J. Cullen et al., Eur Urol 68:123-131 (2015). Table 1.
[0207] A study of prostate cancer patients from the Cleveland Clinic (Cleveland Clinic, CC) database (described in E. Klein et al., Eur Urol 66:550-560 (2014)) showed that 4.7% of patients in the AUA intermediate risk group with GPS≤40 The RM-adjusted risk of clinical recurrence (CR) within 10 years, while AUA intermediate-risk patients with GPS>40 had a RM-adjusted 10-year CR risk...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com