Plane two-freedom-degree parallel mechanism
A two-degree-of-freedom, two-plane technology, applied to manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as limited range of motion, many structural parts, and many hinge points, so as to ensure operational stability and modular scalability , to achieve the effect of flexible manufacturing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
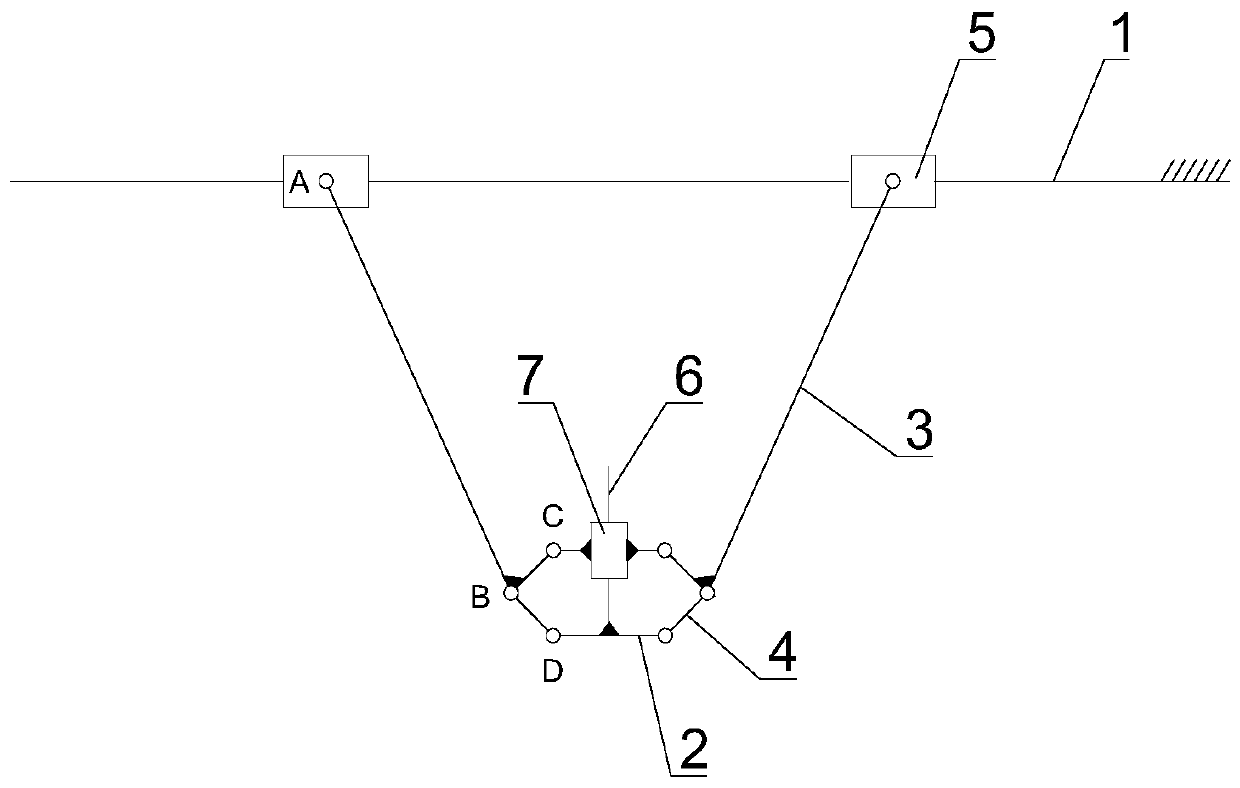
[0027] see figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a planar two-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism, which includes a fixed guide rail 1 , a tool flange 2 , two members 3 and two connecting rods 4 .
[0028] The fixed guide rail 1 is provided with two driving sliding blocks 5 which respectively constitute moving pairs. The fixed guide rail 1 is fixed and the two driving sliding blocks 5 are independently driven by motors to move linearly along the fixed guide rail 1 . The moving pair can be slider guide rail, V-type guide rail roller, roller guide rail, linear bearing or dovetail groove guide rail slide table, and the driving mode can be belt drive, sprocket drive, rack and pinion drive or lead screw drive.
[0029] The tool flange 2 is used to install the external part, and two hinge points D are symmetrically arranged on both sides, and a balance slider 7 is arranged on it. The balance slider 7 moves along the axis perpendicular to the installation plane of the external...
Embodiment 2
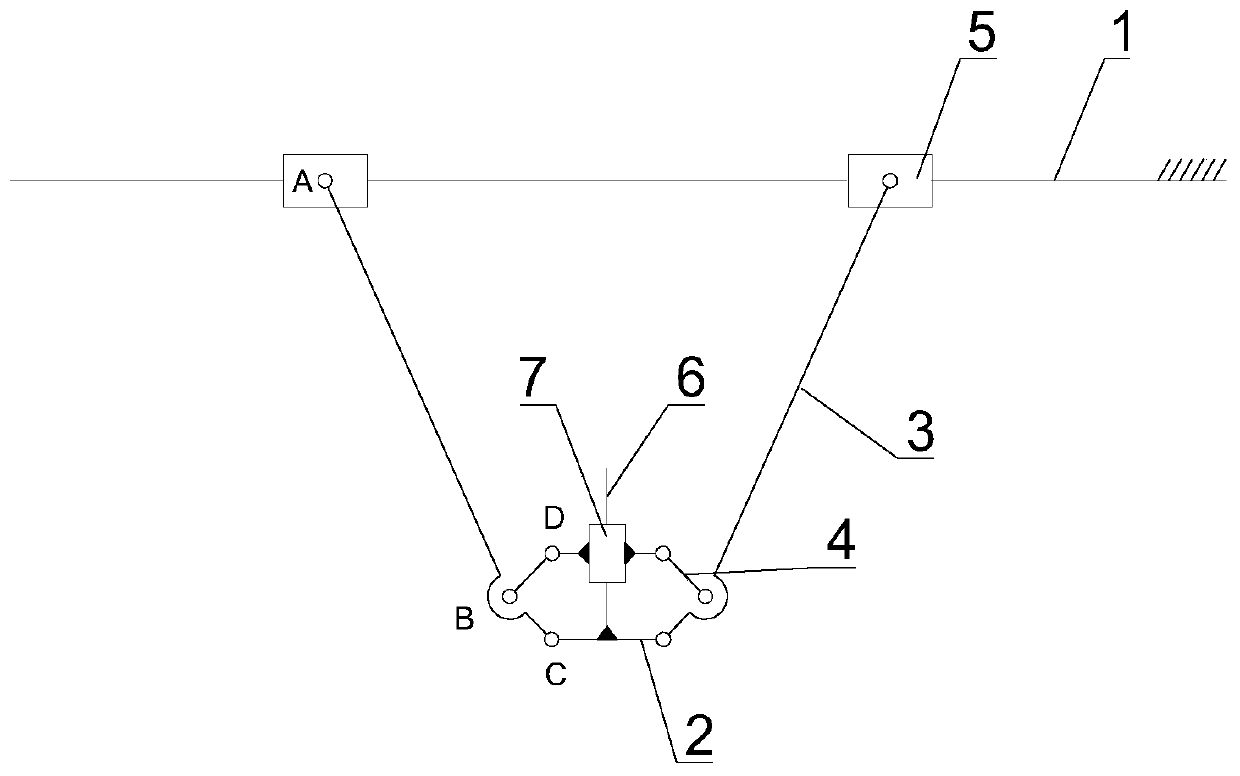
[0040] see figure 2 As shown, this embodiment is the deformation structure of Embodiment 1, the difference is that the balance slider 7 is symmetrically provided with two hinge points D, the hinge point D on the balance slider 7 is hinged with the other end of the connecting rod 4, and the balance The slider 7 is driven by the connecting rod 4 to move along the axis perpendicular to the installation plane of the outer part of the tool flange 2; Under the limit of 7, the installation plane of the external parts of the tool flange 2 always keeps moving in parallel with the fixed guide rail 1.
[0041]As shown in this embodiment, a plane XZ coordinate system is constructed with the second hinge point B as the origin, then the first hinge point A is located in the second quadrant of the XZ coordinate system, and the third hinge point C is located in the XZ coordinate system. In the fourth quadrant, the hinge point D is located in the first quadrant of the XZ coordinate system; t...
Embodiment 3
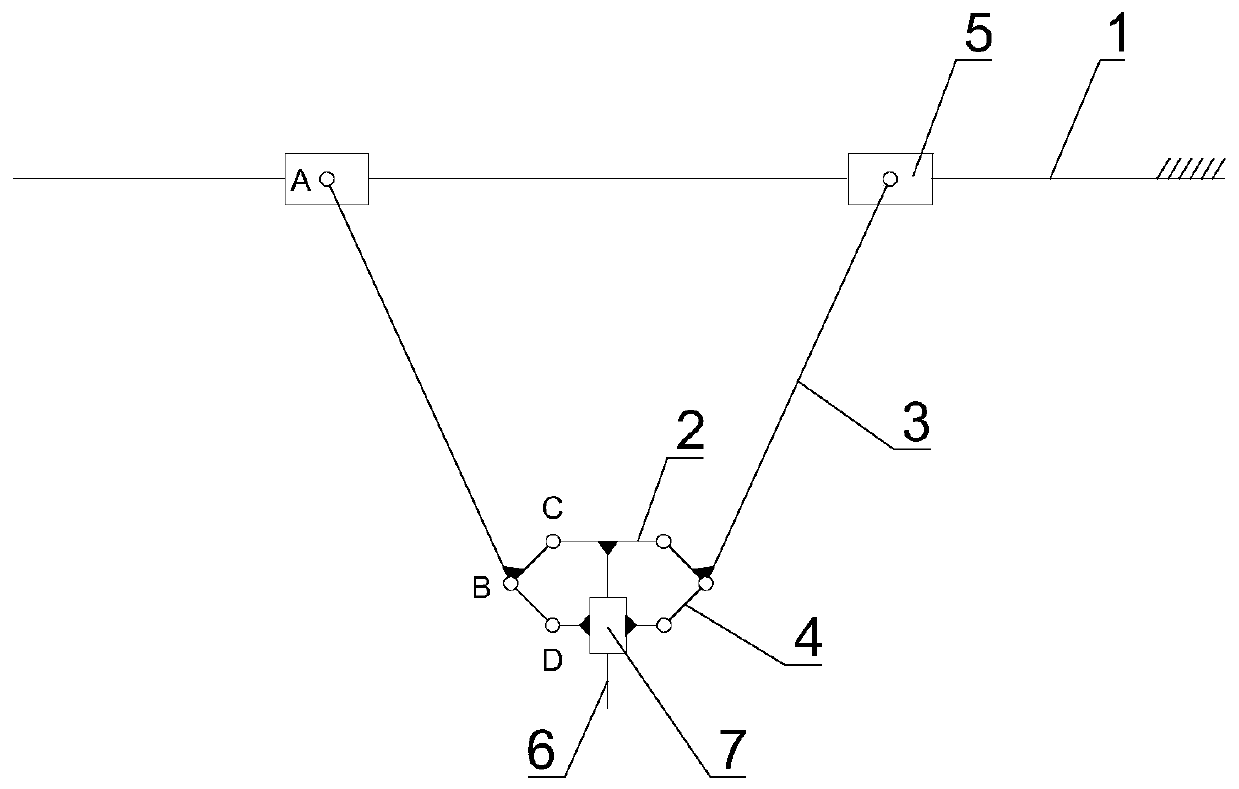
[0043] see image 3 As shown, this embodiment is the deformation structure of Embodiment 1, the difference is that the relative positions of the tool flange 2 and the balance slider 7 are opposite, then the third hinge point C of the member 3 is hinged with the tool flange 2, and the connecting rod 4 The other end is hinged with the balance slider 7. The rest of the structure is the same as that of Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com