Path planning method through collaboration of multiple underwater robots
An underwater robot, path planning technology, applied in three-dimensional position/channel control and other directions, can solve problems such as long optimization time, limited operation ability, and uneven path.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
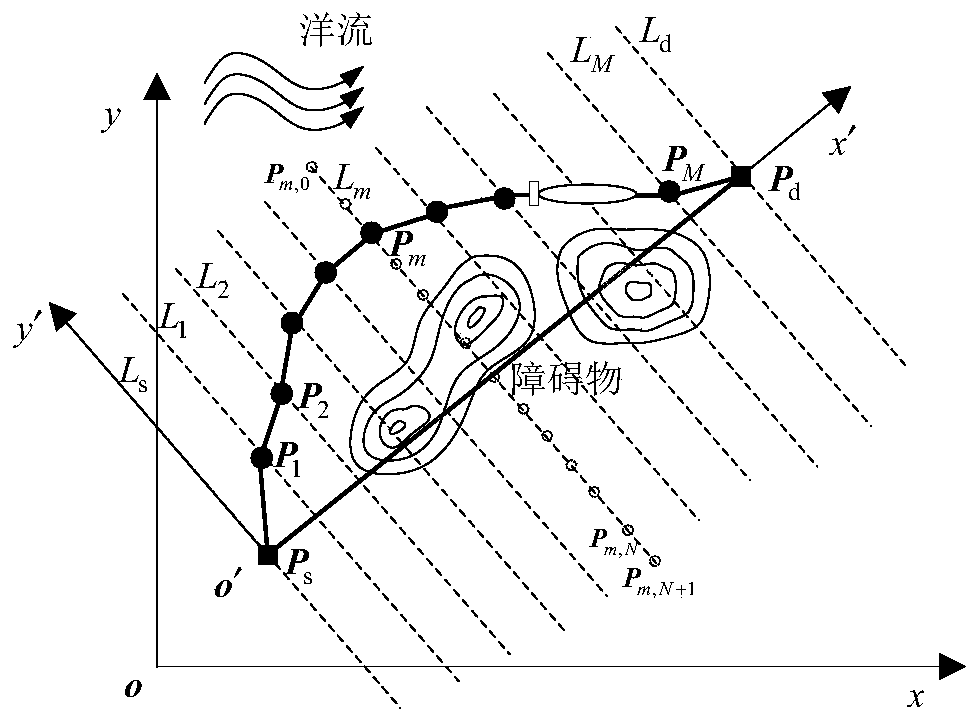
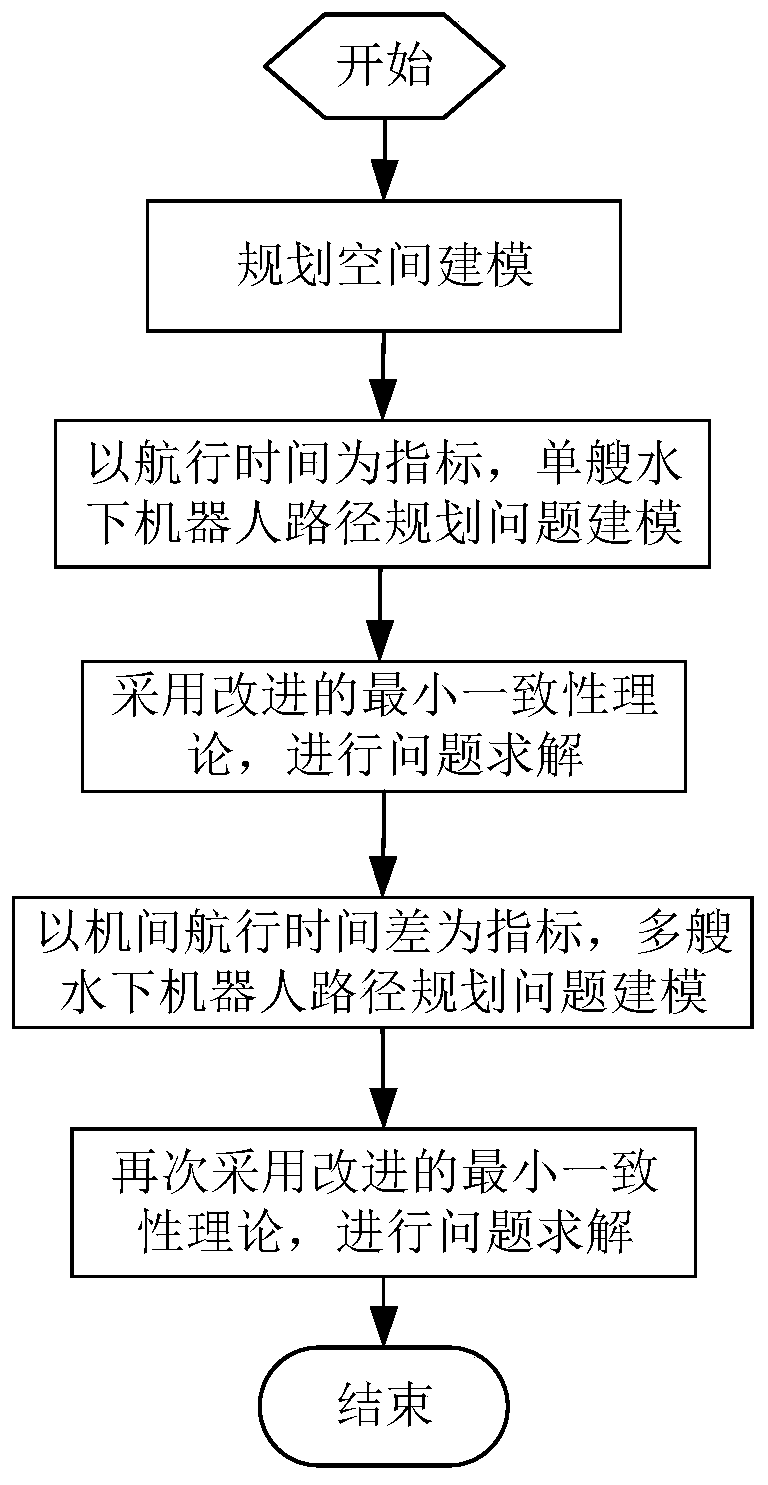
[0098] Before multiple underwater robots sail in formation or perform tasks such as saturation attacks, they often need to reach (assemble) the desired target point at the same time. At this time, it is necessary to consider the time constraints of simultaneous arrival to plan the path of multiple robots. This embodiment will consider the path planning problem of multiple underwater robots when each underwater robot arrives at the terminal at the same time, and apply the above-mentioned path planning method to this embodiment to adjust the planned path so that the estimated arrival time of each underwater robot close to agreement.
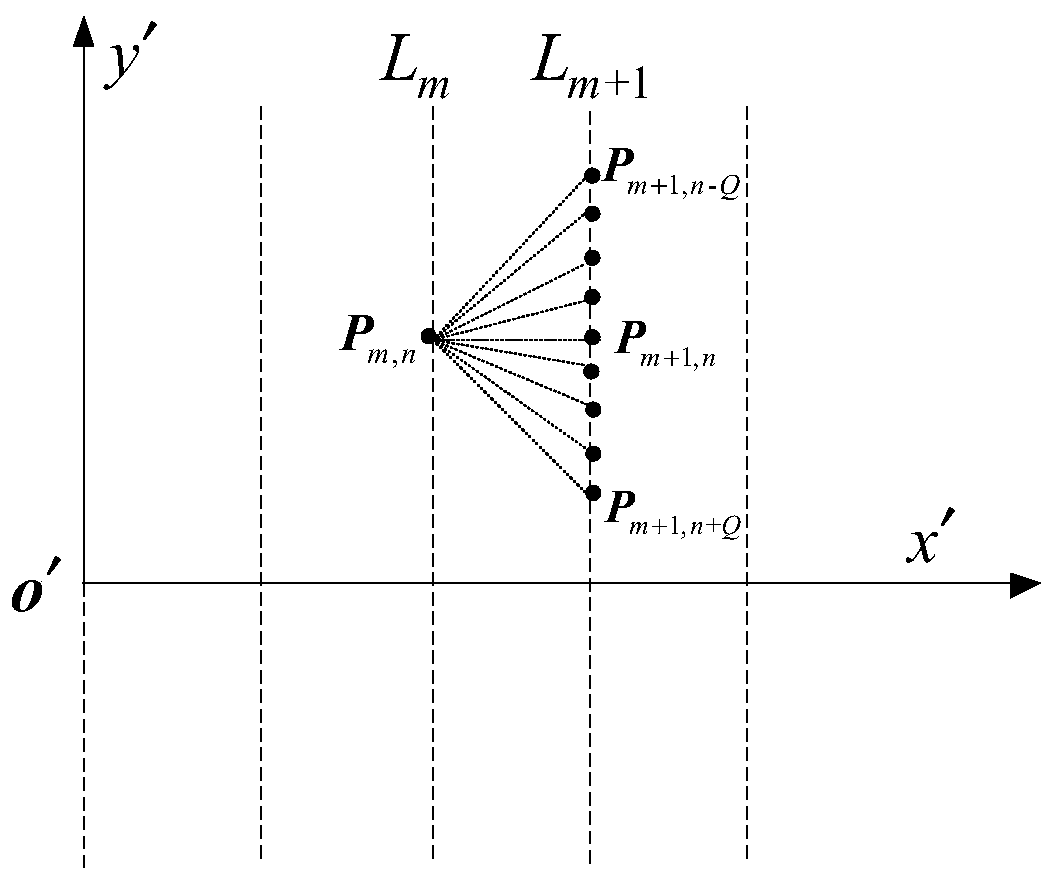
[0099] refer to image 3 As shown, assuming a total of N u Underwater robots work together, specifically taking the path planning problem of the rth underwater robot as an example, in order to minimize the voyage time min T r is an indicator function, with θmax , is a constraint condition, and +∞ is used as a penalty for not satisfying the cons...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com