Leakage monitoring sensor layout optimization method under urban water supply network semi-supervised condition
A technology for monitoring sensors and urban water supply, applied in instruments, computer parts, calculations, etc., can solve problems such as can not be ignored, no longer applicable, unknown location of local leakage, etc., to improve efficiency and effectiveness, and achieve good results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
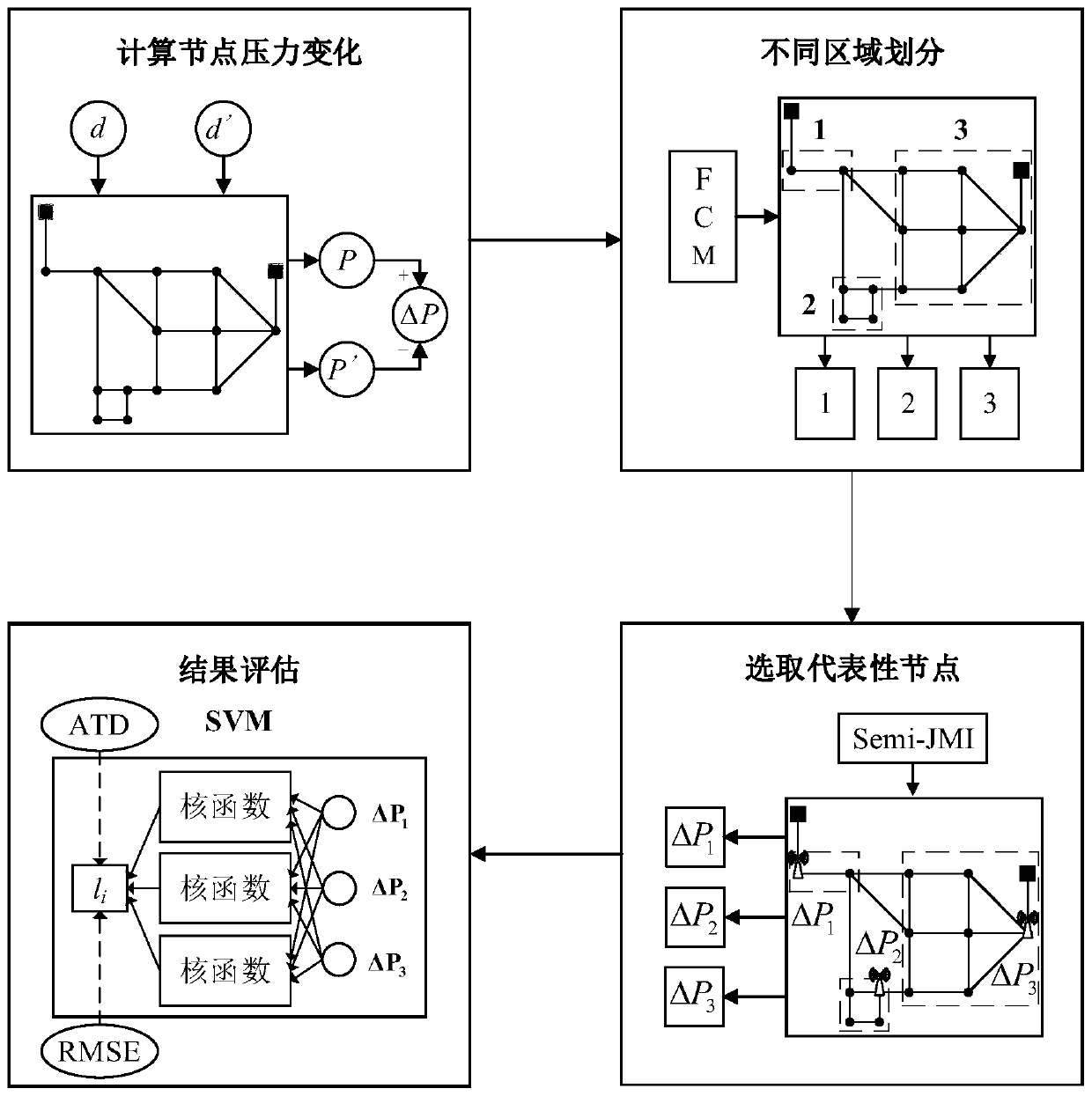
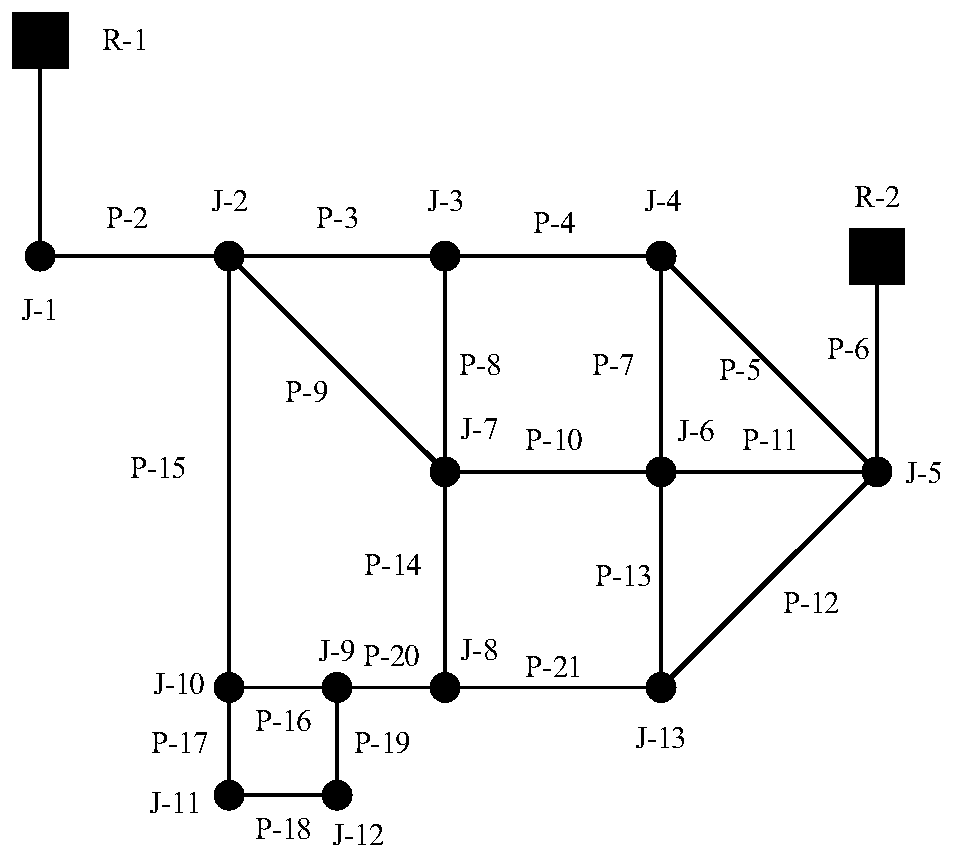
[0094] Such as image 3 As shown, the water supply network 1 is composed of 2 reservoirs, 13 nodes and 21 pipelines, and the average daily water demand is about 874 liters / second.
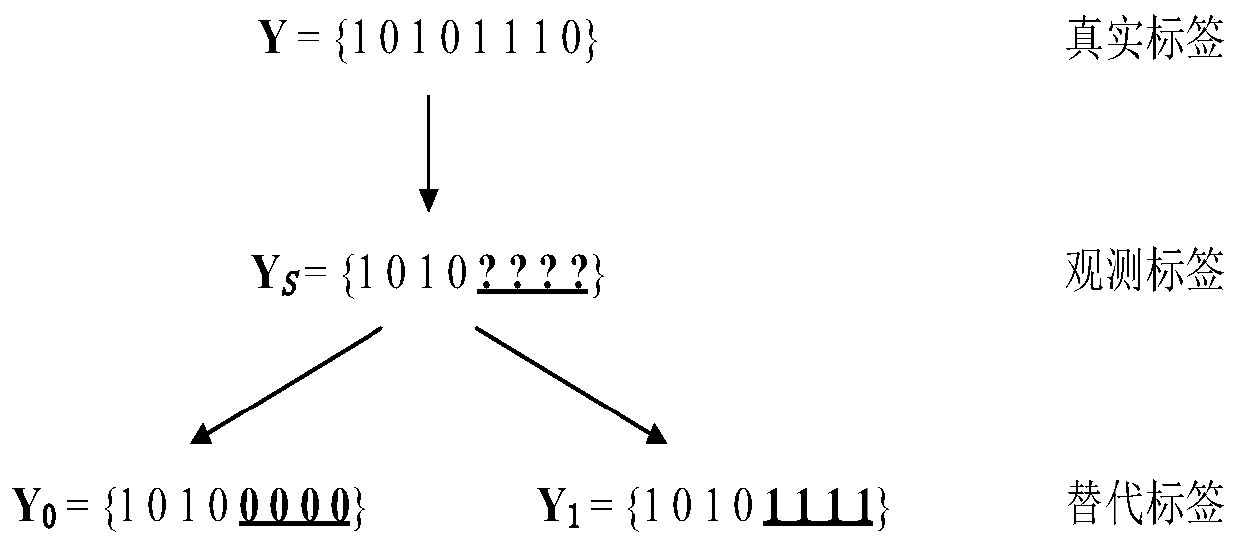
[0095] Although there is no specific standard on the amount of leakage, it should be ensured that the abnormal pressure value caused by the leakage is significantly different from the normal pressure value. In addition, it should be noted that the maximum leakage cannot be set too large, otherwise the water supply network will not work in the EPANET software. In this case, the node leakage is set to 3% of the total average water demand, ranging from 19L / s to 37L / s, and added to each node in turn at an interval of 2L / s to form 13 data sets, each data set 10 leak situations. Then the water supply network 1 is divided into three regions according to the FCM algorithm. The ultimate goal of the sensor layout optimization problem is to select the most representative nodes from each region to deploy pr...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the water supply network 2 has a water tank, 23 nodes and 34 pipes. The total average water demand per day is about 282L / s, and the node leakage is set to 2% of the total average water demand, ranging from 3L / s to 8L / s, with an interval of 1L / s and added to each node in turn, similar to Example 1 Similarly, the FCM algorithm is used to cluster the areas belonging to the same area, and then semi-JMI is used to select monitoring nodes from each area. The results of the two semi-supervised methods are summarized in Table 4.
[0109] Table 4 Optimization results of two semi-supervised strategies in water supply network 2 sensor layout
[0110]
[0111] As shown in Table 4, different datasets lead to different node combinations and computation times. Finally, the selected node combination for method 1 is {1, 2, 5, 6} and for method 2 is {1, 4, 5, 18}. The average calculation time of method 1 is 2.141s. Method 2 is 1.539 times longer than M...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com