An Adaptive Small Cell Clustering Method Based on Many-to-Many Matching
A small cell, self-adaptive technology, applied in transmission monitoring, digital transmission system, data exchange network, etc., can solve problems such as complex mathematical models, large fluctuations in clustering results, irregular layout of small cell base stations, etc., and achieve complexity The effect of low and stable clustering results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] The present invention will be further described below through specific embodiments.
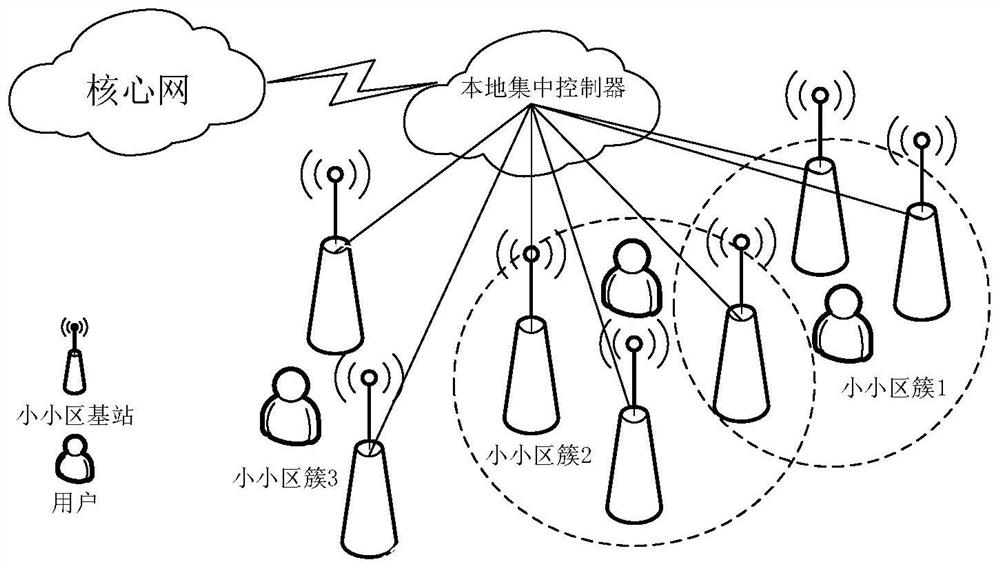
[0040] An adaptive small cell clustering method based on many-to-many matching. When the service quality of the network is not good, it selects small cell clusters for users in the network based on the many-to-many matching clustering algorithm to improve network performance and user experience. The goal of this solution is to match the small cells and users in the UDSN, assign each small cell to one or more users, and at the same time assign each user to one or more small cells.
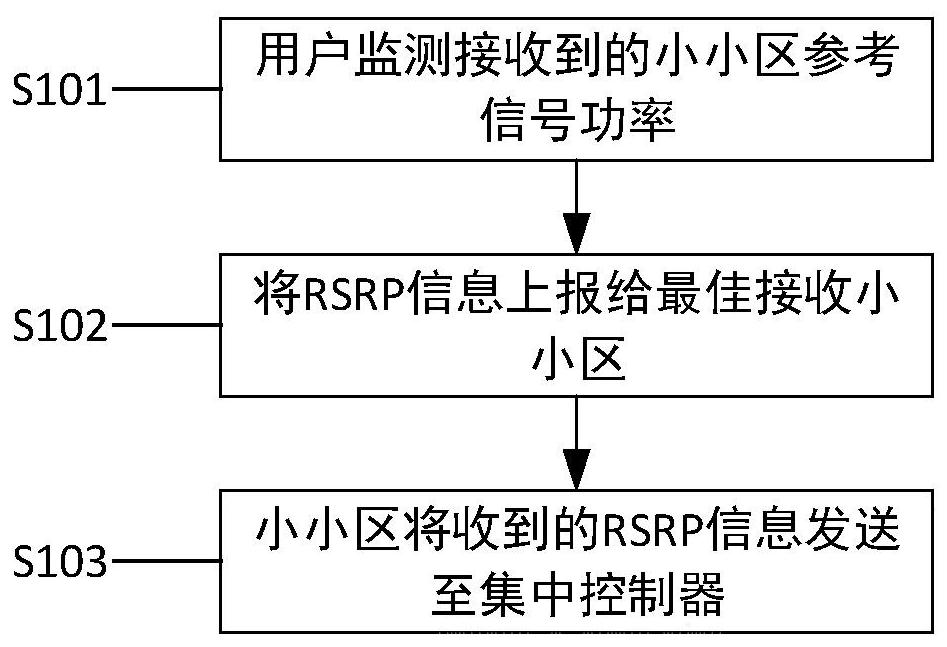
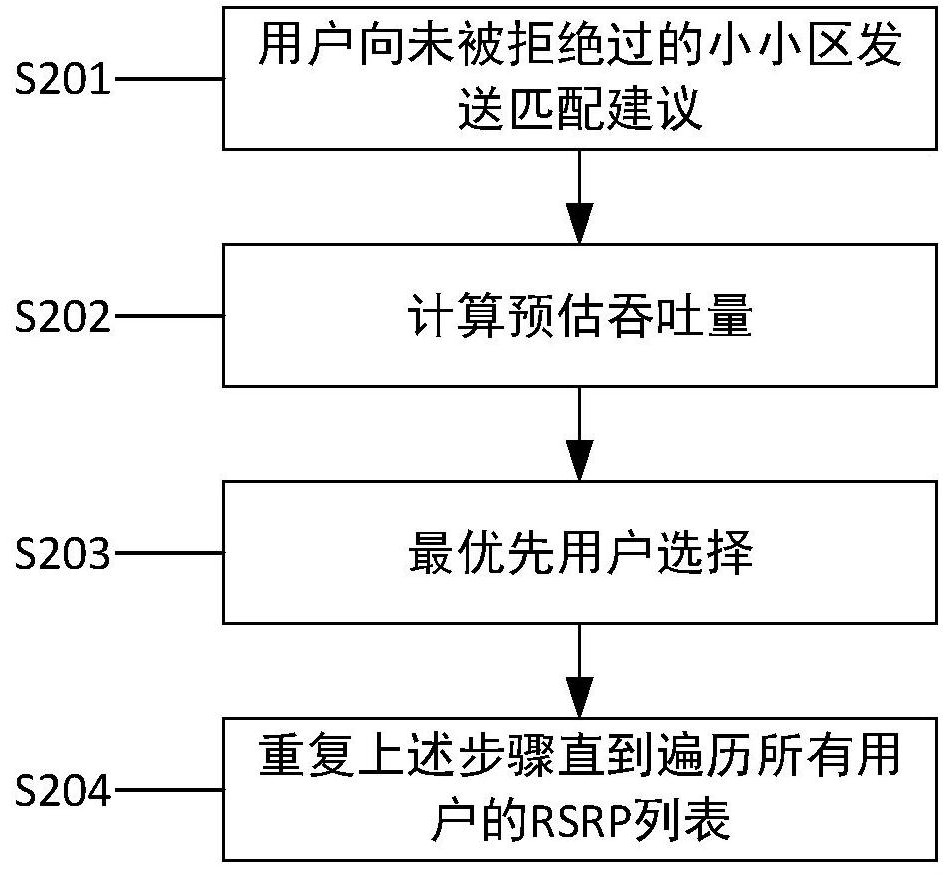
[0041] The centralized controller monitors the quality of service in the network. When the average throughput of network users or the average QoS value of users is lower than the threshold, it executes the clustering algorithm and selects a service small cell for users in the system again. It should be noted that during the execution of the clustering algorithm, the suggestions issued by users or small cell...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com