Fingerprint indoor positioning method based on binary k-means
An indoor positioning and k-means technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problem of poor selection and positioning of the initial clustering center, and achieve the effect of improving accuracy and positioning accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
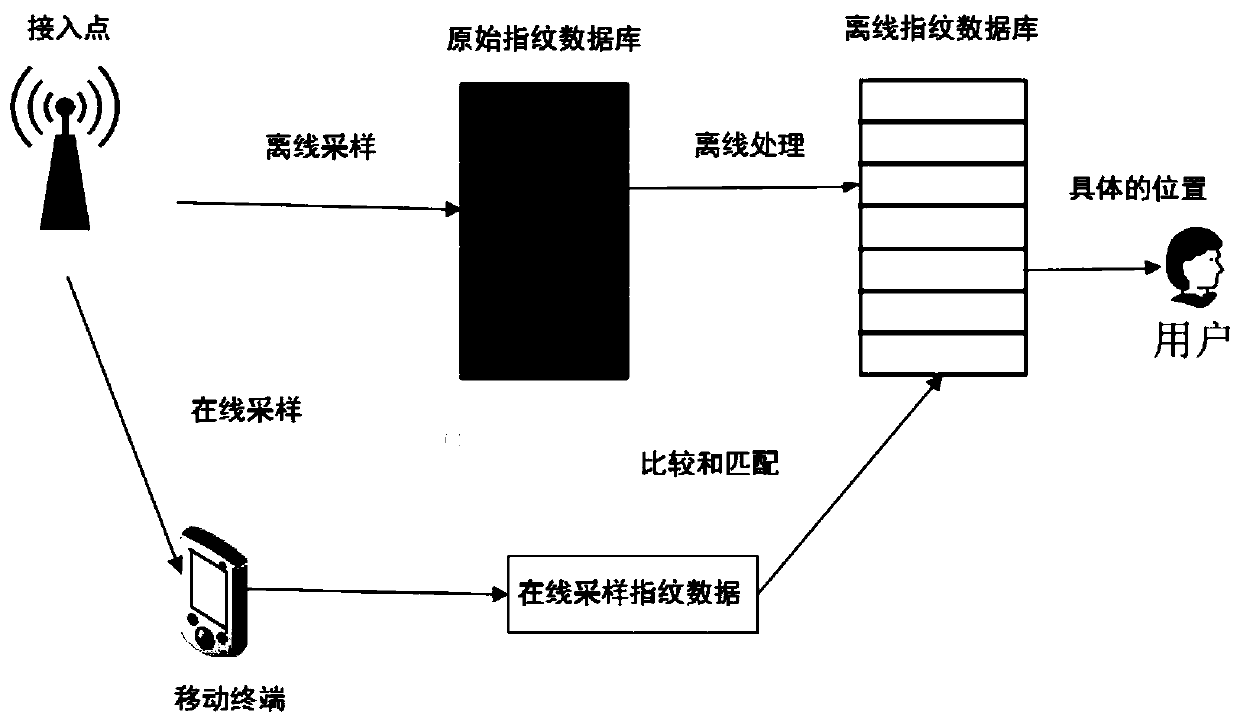
[0036] In the existing indoor positioning methods, in order to have a better positioning effect, it is often necessary to lay a large number of sensors specially used for positioning in the positioning area, which will lead to waste; when the positioning environment does not change, the positioning effect is better. However, when there are people walking around in the positioning area or obstacles increase or decrease, the positioning accuracy cannot be guaranteed, and the practicability is poor. In some positioning methods, clustering algorithms are used, such as k-means algorithm, so that the positioning results strongly depend on the initial cluster centers of k clusters, so that when the initial cluster centers are not selected properly, the positioning effect is very poor .
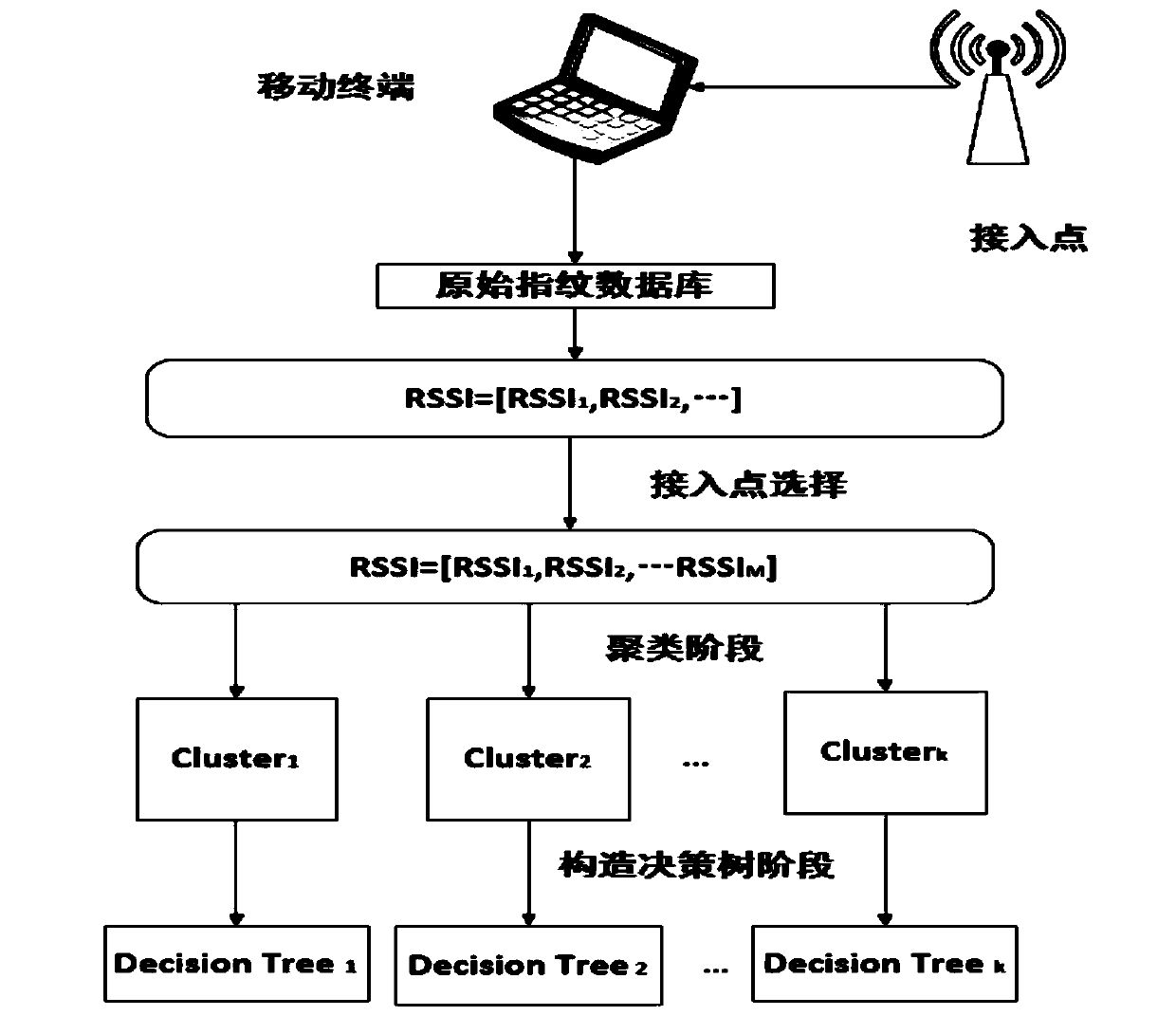
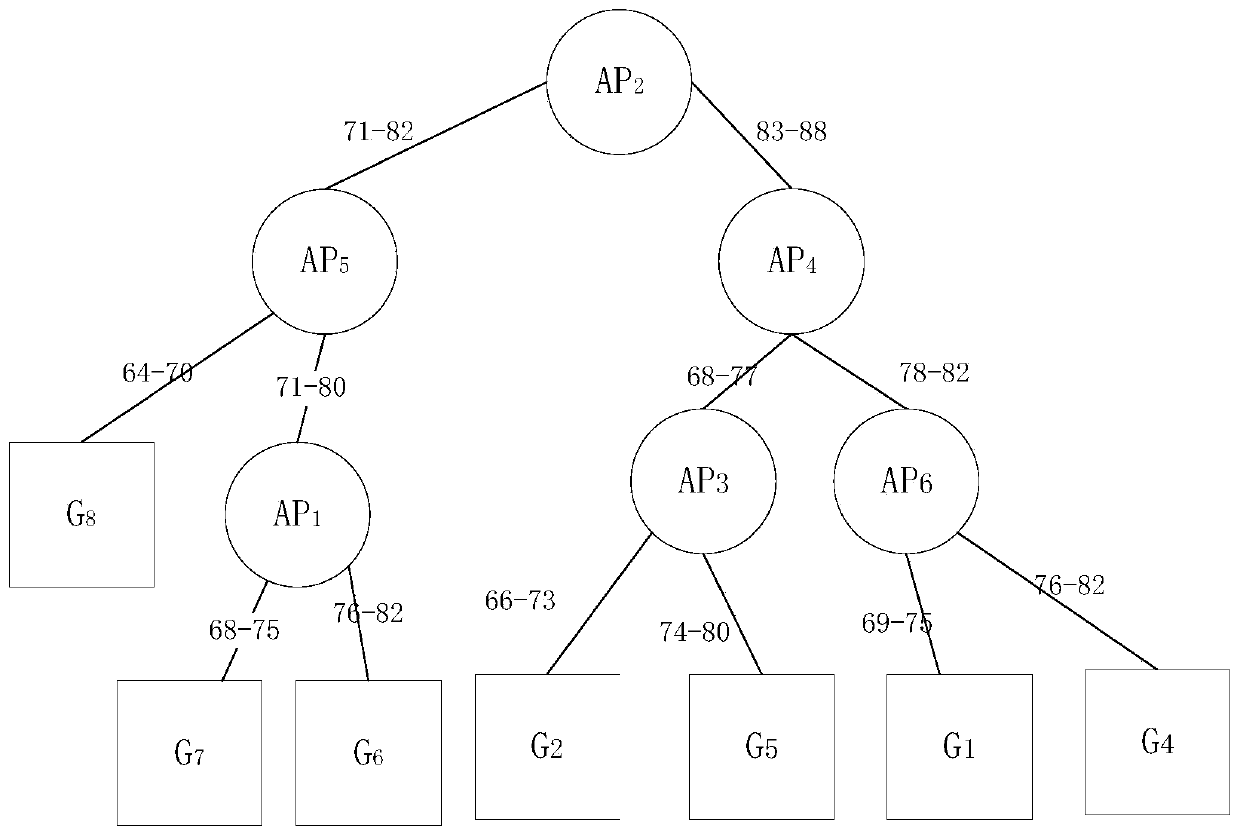
[0037] The invention improves the problems existing in the existing positioning method, and proposes a fingerprint indoor positioning method based on bipartite k-means. see figure 1, the positionin...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The fingerprint indoor positioning method based on the binary k-means is the same as that in embodiment 1, step 1b) selects the m APs that have the greatest impact on the positioning result, and generates a simplified fingerprint library, specifically including the following steps;
[0058] 1b1) The n reference points in the positioning area are denoted as (G 1 ,G 2 ,...G n ), using information theory to select m access points with the largest information gain in the location area. When the access point information is not used, that is, when the received signal strength indication data is not collected, the uncertainty of all reference points is:
[0059]
[0060] In the above formula, G j Indicates the jth reference point, P(G j ) is the proportion of the jth reference area in the positioning area in the positioning environment.
[0061] 1b2) When measured from the i-th access point AP i After receiving the signal strength indication data of , the i-th access ...
Embodiment 3
[0069] The fingerprint indoor positioning method based on dichotomous k-means is the same as embodiment 1-2, and the calculation formula of the cluster center in step 2) is:
[0070]
[0071] All the fingerprint data used in the calculation of the above formula come from the simplified fingerprint library. Among them, N i for cluster C i The number of fingerprint data in N ci for cluster C i The number of reference points in c i for cluster C i center of R jl for cluster C i In the lth fingerprint data collected at the jth reference point, n j for cluster C i The number of fingerprint data of the jth reference point in . In the present invention, the i-th cluster C can be calculated by using the above formula i The cluster center c i , c i Can be used to calculate the cluster C i The sum of squared errors.
[0072] The formula for calculating the sum of squared errors is:
[0073]
[0074] The i-th cluster C can be calculated by using the above formula i ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com