The method of accurately calculating repeated frozen fusion after the cold area of the cold area of the cold area of the cold area
A technology of repeated freezing and thawing and elastic modulus, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, strength characteristics, material thermal analysis, etc., can solve the problem of not considering the influence of freezing and thawing cycles on the frost heaving force of surrounding rocks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Embodiment 1. Calculation of frost heaving force of surrounding rock based on elastic theory.
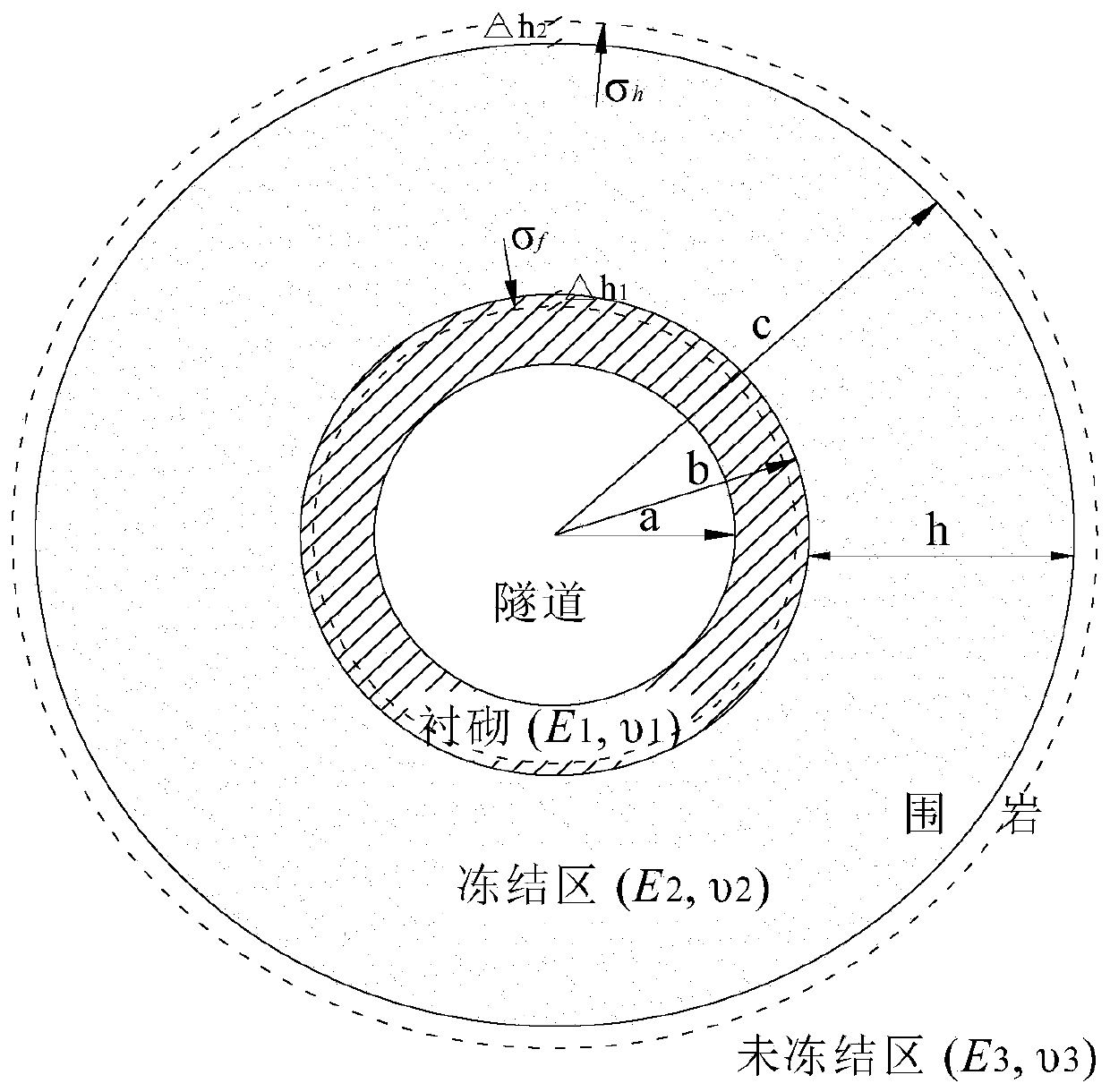
[0084] Computational models such as figure 1 , in order to simplify the problem, firstly, the frozen zone and unfrozen zone in the tunnel lining and surrounding rock are regarded as a stress system composed of three axisymmetric elastic bodies in complete contact with each other, in which the tunnel is a circle located in an infinite mountain a, b, and c are respectively the inner diameter of the lining, the inner diameter of the frozen zone (also known as the outer diameter of the lining), and the outer diameter of the frozen zone, and the following assumptions are made: (1) The surrounding rock is a homogeneous and isotropic continuous medium; (2) The stress on the tunnel lining and surrounding rock belongs to the plane strain problem of elastic mechanics; (3) The frozen zone is always in a saturated state; (4) The self-weight of surrounding rock and tunnel lining is not co...
Embodiment 2
[0114] Embodiment 2. Crack initiation criterion and propagation direction of a single microcrack under the action of frost heaving force.
[0115] Because the rock contains many microcracks, the essence of freeze-thaw damage is that the water in the microcracks is frozen into ice at low temperature, resulting in volume expansion, and then the microcracks expand under the action of expansion force, resulting in the deterioration of rock properties. Then when the temperature rises, the ice melts into water, which flows along the expanded microcracks. If the water supply is sufficient and the melting time is long enough, it can be considered that the microcracks will always be in a saturated state. When the temperature drops, the water freezes into ice again, causing the microcracks to expand further and repeating itself. Each freeze-thaw cycle will cause a certain degree of damage to the rock, which is manifested as an increase in the length of microcracks at the micro level, an...
Embodiment 3
[0125] Embodiment 3, the extension length of a single microcrack under the action of frost heaving force.
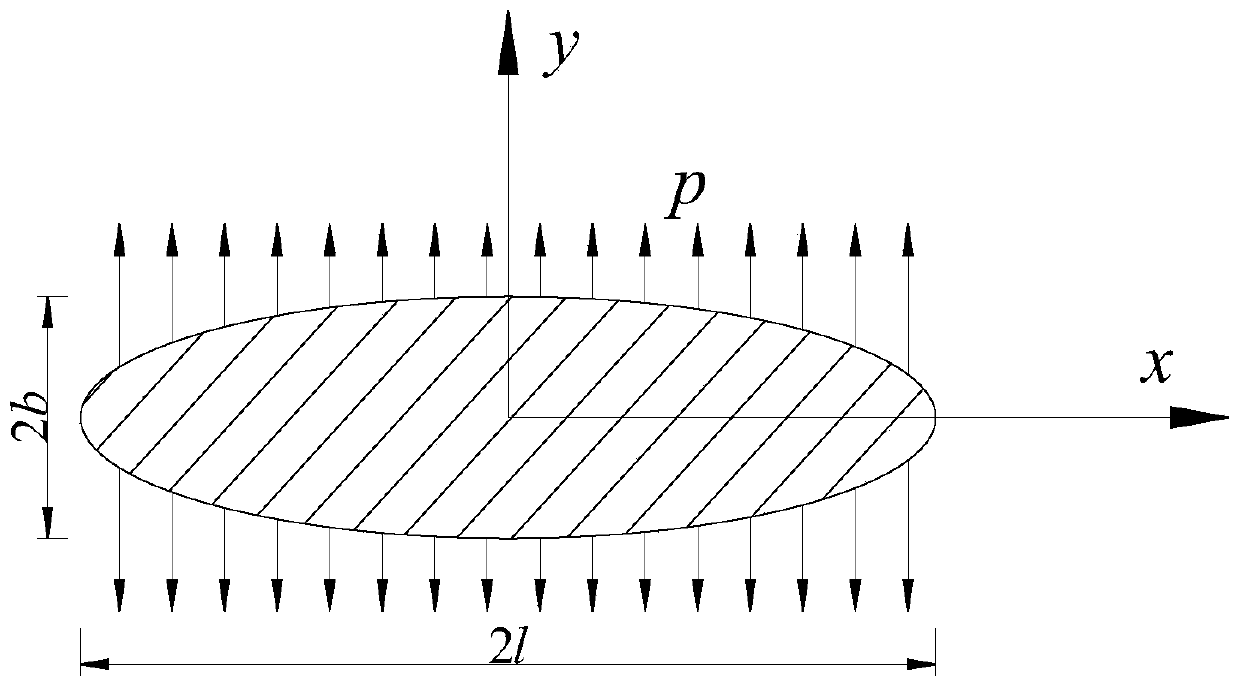
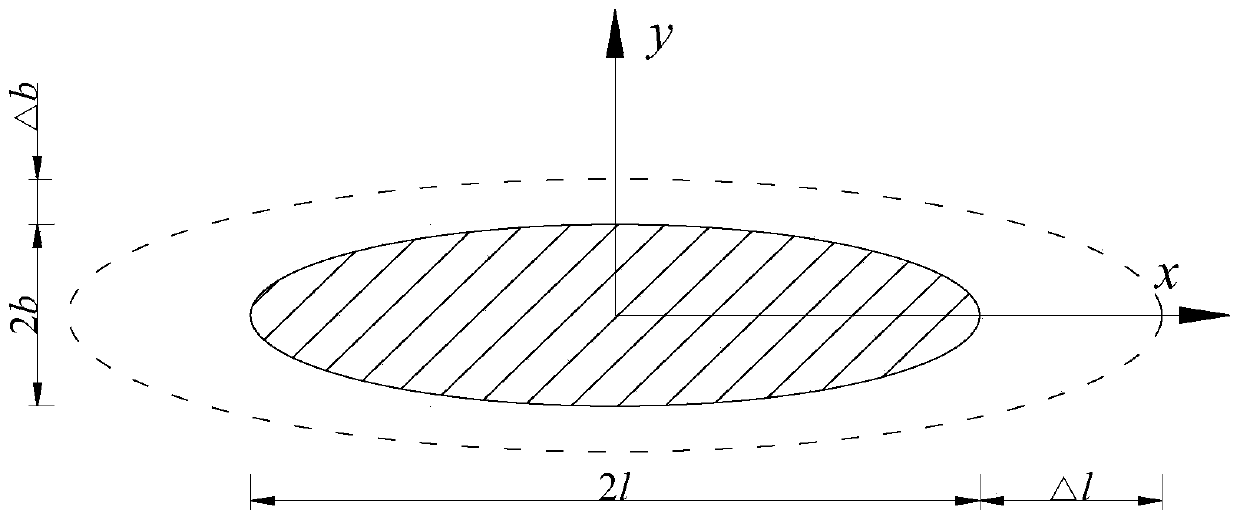
[0126] When frost heaving occurs in the micro-cracks, the inner wall will act with evenly distributed frost-heaving force, and the micro-cracks will expand in the x and y directions accordingly, such as image 3 , the following assumptions are made when studying the growth of micro-cracks frost heave [14]: ① micro-cracks before and after frost heave are plane ellipse, that is, the shape and center position remain unchanged, and only the size changes; ② water migration and rock skeleton deformation are ignored ; ③ The microcracks are always in a saturated state; ④ The microcracks expand stably, and conform to the linear elastic fracture theory.
[0127] According to the Griffith energy release rate theory, when the water in the microcrack freezes into ice, the volume expands, but due to the restraint of the microcrack surface, the ice body generates expansion pressure on ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com