A distribution network fault line selection method based on Min's distance of characteristic frequency band convergence
A technology of distribution network faults and characteristic frequency bands, which is applied in the direction of fault location and fault detection according to conductor type, can solve the problems of extended power outage time, operation overvoltage and resonance overvoltage distribution network impact, etc., and achieve the goal of improving accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
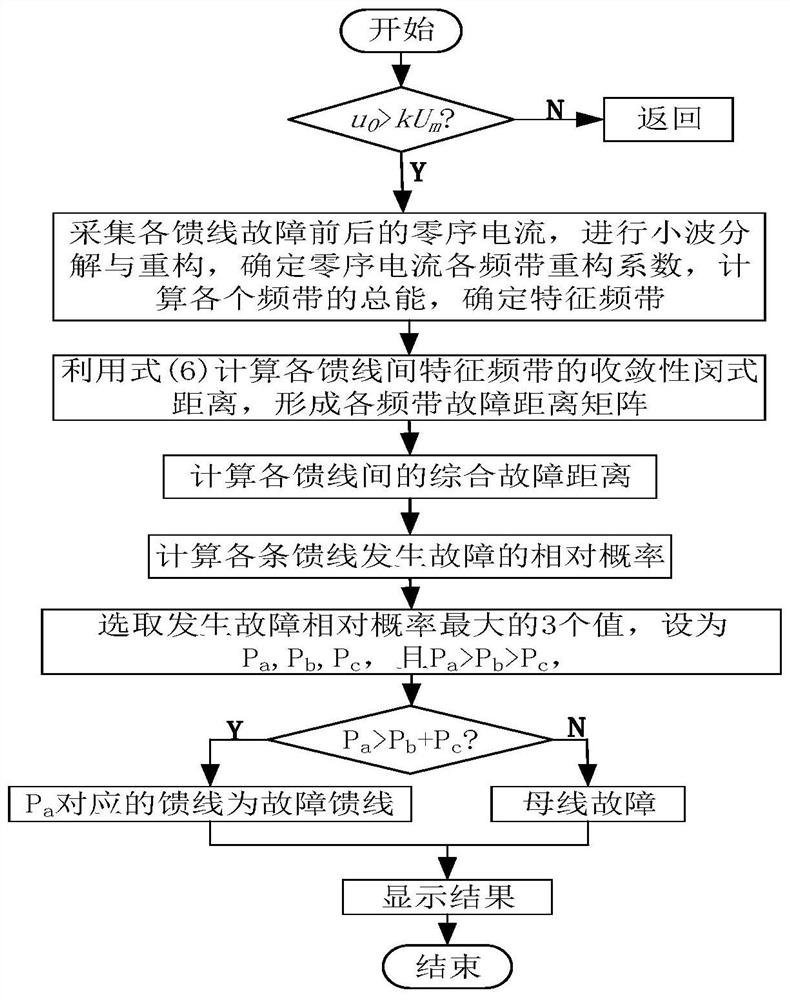
[0041] Embodiment 1: A method for fault line selection of distribution network based on characteristic frequency band convergence Min's distance, including the following steps: when a single-phase grounding fault occurs in the distribution network, the zero-sequence current data of each feeder is collected. The zero-sequence current in the window uses wavelet transform to calculate the total energy of each feeder in each frequency band, determines the characteristic frequency band according to the energy and maximum principle, calculates the convergent Min's distance of the characteristic frequency band between each feeder, and forms the fault distance matrix of the characteristic frequency band , using the fault distance matrix of the characteristic frequency band to calculate the comprehensive fault distance between each feeder, obtain the relative probability of single-phase grounding fault on each feeder according to the comprehensive fault distance between the feeders, and ...
example 1
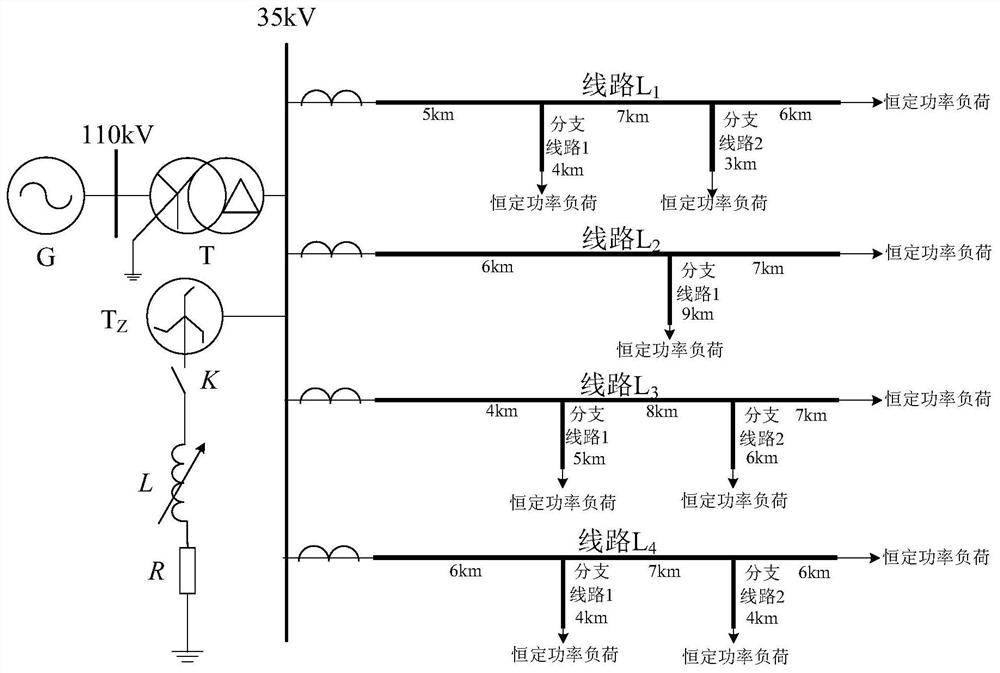
[0065] Example 1: as figure 1 The single-phase-to-ground fault simulation model of the 110kV / 35kV distribution network shown has 4 overhead feeders and all of them contain branch lines. The neutral point of the Z-shaped transformer is grounded through the series resistance of the arc suppression coil. Set feeder L 1 A metallic single-phase grounding fault occurred at the branch line 1 2 kilometers away from the main line, the fault angle was 90°, and the sampling rate was 5kHz. The specific steps of the single-phase-to-ground fault line selection method in the distribution network based on the characteristic frequency band convergence Min's distance in this example are as follows:
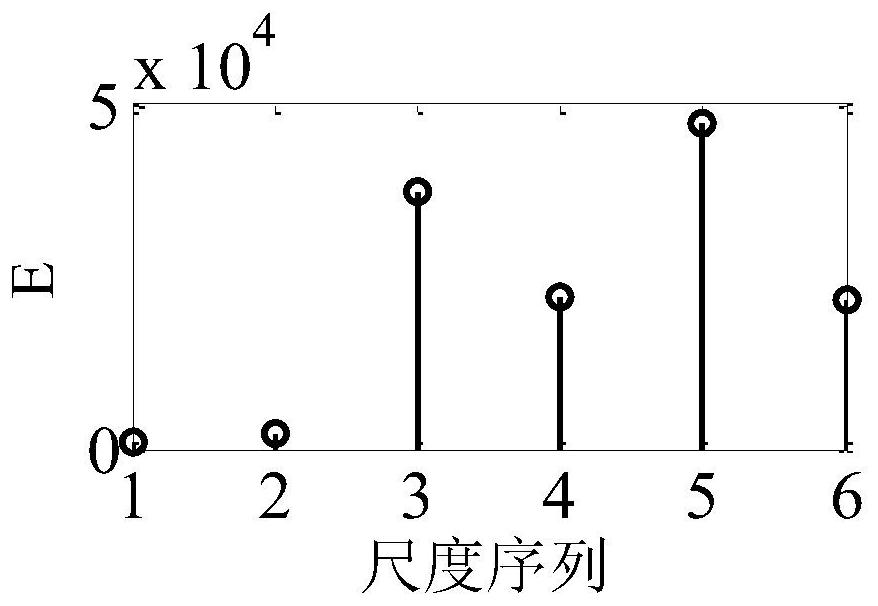
[0066] After the single-phase grounding fault occurs in the resonant grounding system, wavelet transform is used for the zero-sequence current in the 5ms short-time window after each feeder fault, such as image 3 As shown, scale 5 energy sum maximum, according to the energy sum maximum principl...
example 2
[0074] Example 2: 110kV / 35kV resonance grounding system distribution network single-phase grounding fault simulation model is the same as example 1, feeder L 4 A single-phase grounding fault occurs at the branch line 2 3km away from the main line, the grounding resistance is 200Ω, the fault angle is 60°, and the sampling frequency is 5kHz.
[0075] In the same way as Example 1, such as Figure 5 As shown, the energy sum of scale 6 is the largest, and the characteristic frequency band is determined to be 78.125Hz to 156.25Hz, and the characteristic frequency band of the zero-sequence current is as follows Image 6 As shown, calculate the characteristic frequency band fault distance matrix D, the comprehensive fault distance matrix d and the relative probability matrix P between each feeder;
[0076]
[0077] d=[5.36 5.38 5.41 14.07]
[0078] P=[0.18 0.18 0.18 0.46]
[0079] Select the top three with the highest relative probability of single-phase grounding, and they are ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com