A method for the simultaneous detection of two HIV DNAs by a DNA-directed color-changing silver nanocluster
A technology of silver nanoclusters and DNA probes, which is applied in the fields of molecular biology and nucleic acid chemistry, can solve the problems of long time-consuming separation and purification of materials, high modification costs, cumbersome operations, etc., and achieve high cost, large emission range, and economical simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Design of fluorescent probes based on color-changing silver nanoclusters
[0047] (1) The design of DNA probe in the present embodiment:
[0048] 1) The DNA probe is composed of two partially complementary ssDNAs, namely cDNA and P strand;
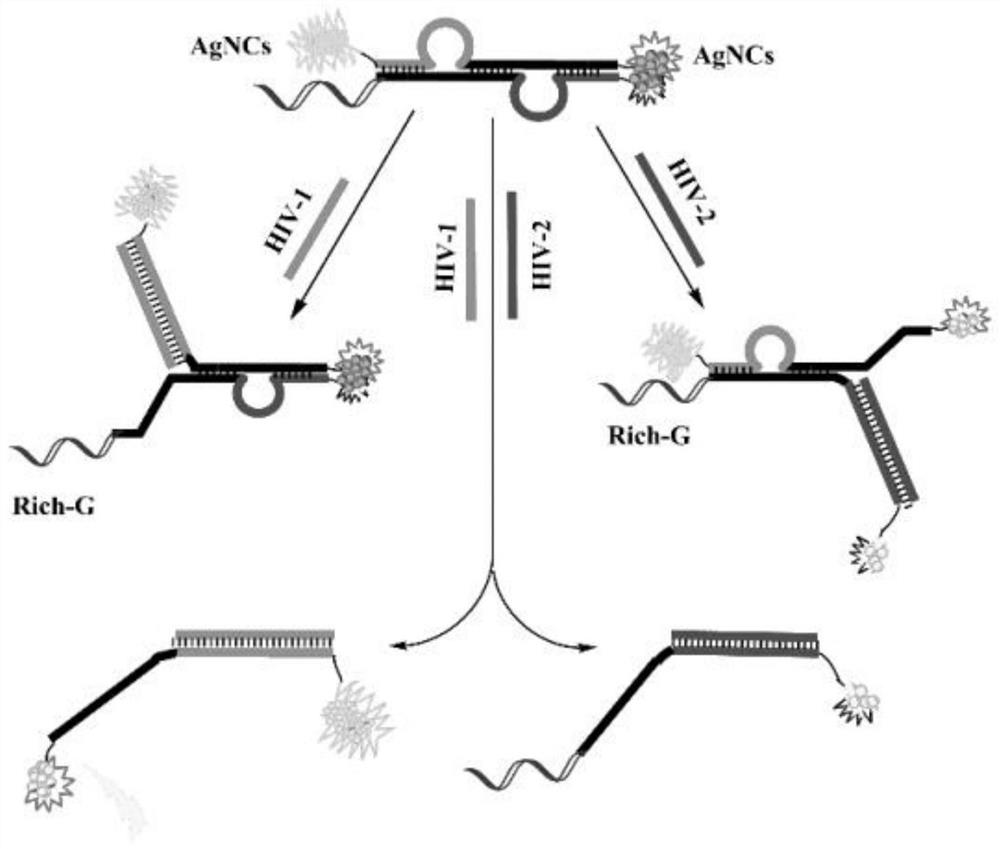
[0049] 2) The cDNA chain is composed of four parts: G-rich sequence, C-rich sequence for synthesizing AgNCs, sequence complementary to HIV-2 sequence and base sequence partially paired with HIV-1 complementary chain;
[0050] 3) The P chain consists of four parts: the sequence of AgNCs capable of synthesizing yellow-green fluorescence, the sequence of AgNCs capable of synthesizing orange-red light, the sequence complementary to the HIV-1 sequence, and the base sequence partially paired with the HIV-2 complementary chain .
[0051] The DNA sequence involved in this embodiment is as figure 2 shown.
[0052] (2) Synthesis of DNA-templated AgNCs:
[0053] 10 μL of Sequence P (500 nM) was dissolved in 170 μL of PBS buffer (20 mM, p...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Validation of the Feasibility of Simultaneously Detecting Two HIV DNAs Using Fluorescent Probes Based on Silver Nanoclusters
[0056]The present invention simultaneously uses luminescent AgNCs with 565nm and 630nm emission peaks as templates to detect HIV-1 and HIV-2, and the working principle is as follows figure 1 .
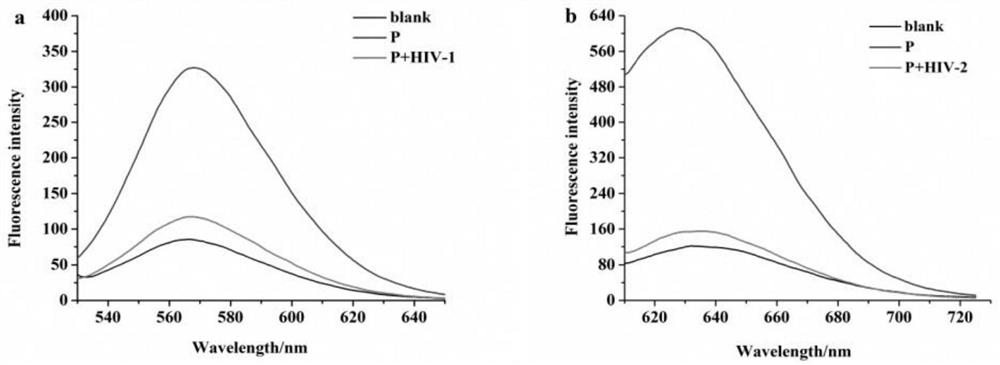
[0057] In this embodiment, we use fluorescence spectroscopy to verify the feasibility of the principle.
[0058] The conditions for fluorescence spectrometry detection are:
[0059] Concentration of analytes: 500nM for HIV-1 and HIV-2
[0060] Instrument: RF-5301PC Fluorescence Spectrophotometer
[0061] Instrument parameters: excitation wavelength: 500nm and 580nm, emission wavelength: 565nm and 630nm, excitation slit: 5nm, emission slit: 5nm
[0062] The specific experimental operation is:
[0063] (1) First, in the absence of target DNA (HIV-1 and HIV-2), mismatch hybridization of 10 μL of P (500 nM) and 10 μL of cDNA solution was dissolved in 15...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Optimization of Experimental Conditions
[0069] (1) Optimization of pH
[0070] Since the pH of the buffer has a certain influence on the synthesis of AgNCs, the pH environment of the experiment must be optimized. We chose five pH values of 6.4, 6.8, 7.0, 7.2, and 7.6 to do a careful optimization. Figure 4 It can be clearly seen that the fluorescence difference obtained is the highest when the pH is 7.0, so in the following experiments, 7.0 is selected as the optimal pH of the system. (I 0 is the fluorescence intensity before adding the target DNA, and I is the fluorescence intensity after adding the target).
[0071] (2) Optimization of the dosage ratio of reagents and DNA templates
[0072] After the pH is determined, a series of optimization work is carried out on the ratio of reagents and DNA templates so that the synthesized AgNCs have the best fluorescence effect. In the experiment, DNA:Ag + : NaBH 4 Proportional usage optimization is shown in the Fig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com