High-throughput screening system for breeding high-nucleic-acid yeast and application
A nucleic acid yeast, high-throughput technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, to achieve the effect of broad market prospects, huge economic value, and avoiding the problem of transgenic
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1: Construction of reporter plasmid YEp-Hyg B-yeGFP
[0041] 1. Construction of plasmid YEp-Hyg B containing hygromycin B resistance gene
[0042] (1) Construction of hygromycin B resistance gene expression cassette
[0043] Using the plasmid YEp-CH as a template, using the primer Sal I-pJ-TEF1-F
[0044] (5'-CATTTCCCCGAAAAGTGCCACCTGACGTCGACATGGAGGCCCAGAATACC-3') and pJ-TEF1-Nco I-R (5'-CCTCCATGGCAGTATAGCGACCAGCATTC-3') amplified about 1500bp hygromycin B gene expression cassette Sal with Sal I and Nco I restriction sites For I-TEF1p-Hyg B-TEF1t-NcoI, PCR amplification conditions were pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3 min, denaturation at 95°C for 45 s, annealing at 52°C for 15 s, extension at 72°C for 1.5 min, 30 cycles, and final extension at 72°C for 5 min.
[0045] (2) Construction of plasmid YEp-Hyg B containing hygromycin B resistance gene
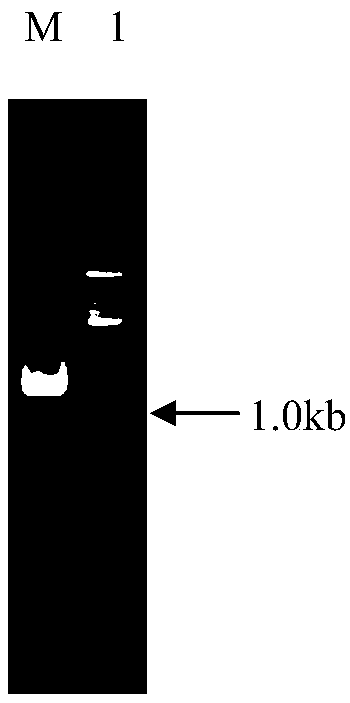
[0046] Use Sal I and Nco I to digest plasmid YEplac195 and hygromycin B gene expression cassette Sal I-TEF1p-HygB...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2: Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae host cells containing reporter plasmids
[0069] 1. Transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae host cells with reporter plasmid
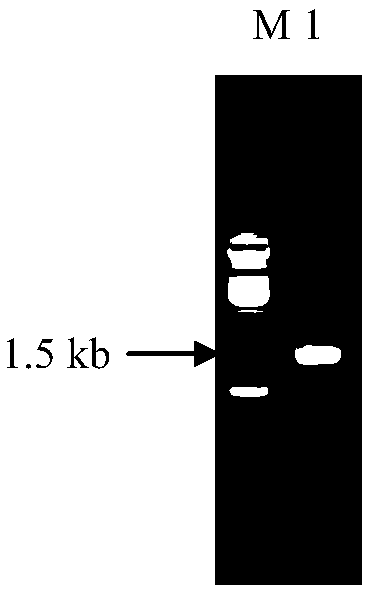
[0070] The control plasmid YEp-Hyg B and the reporter plasmid YEp-Hyg B-yeGFP were transformed into the yeast strain CGMCC No.9084 (named Y08 in the present invention) with a relatively high nucleic acid content after preliminary screening, and the transformation method used was PEG- LiAc-mediated Saccharomyces cerevisiae transformation method, using YPD plates containing 200mg / L hygromycin B to screen transformants, select transformants, extract plasmids from yeast, and then use primers Sac I-rDNAp-F and URA3-Xho I-R PCR amplification was carried out. The PCR amplification conditions were pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3 min, denaturation at 95°C for 45 s, annealing at 52°C for 15 s, extension at 72°C for 1.5 min, 30 cycles, and final extension at 72°C for 5 min. A band of about 1400bp was a...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3: Utilizing a new high-throughput screening system to screen high-nucleic acid yeast engineered bacteria
[0074] 1. Using ARTP to mutagenize the host cells containing the reporter plasmid
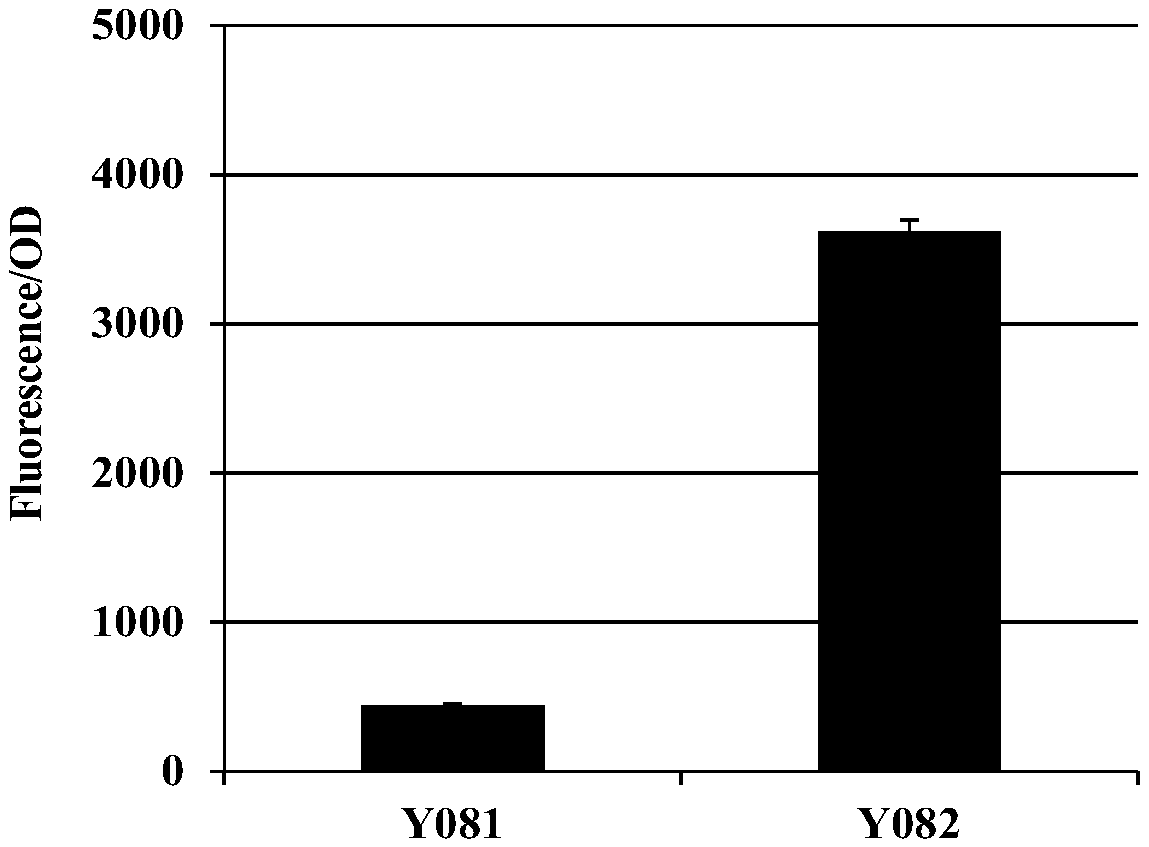
[0075] (1) Strain activation: Saccharomyces cerevisiae industrial strain Y082 expressing a high-throughput screening system was inoculated onto a YPD plate containing 200 mg / L hygromycin B, cultured upside down at 30°C for 2 to 3 days, and then inoculated to a plate containing 200 mg / L In the YPD liquid of hygromycin B, shake culture for 12 to 24 hours, transfer the bacterial liquid to fresh YPD containing 200mg / L hygromycin B to control the bacterial concentration OD 600 ≈0.1, shake culture at 30°C for several hours, control the final concentration of bacteria OD 600 Within ≈1.0, it was used as the starting strain for ARTP mutagenesis.
[0076] (2) ARTP mutagenesis: Take 1 mL of the bacterial liquid, suspend it in a 1.5 mL EP tube, centrifuge at 8000 r / min for 2 min, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com