Wearable device control method, wearable device, and computer readable storage medium
A technology of wearable devices and control methods, applied in medical science, telemetry patient monitoring, sensors, etc., can solve problems such as low user experience satisfaction and inability to understand physical conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
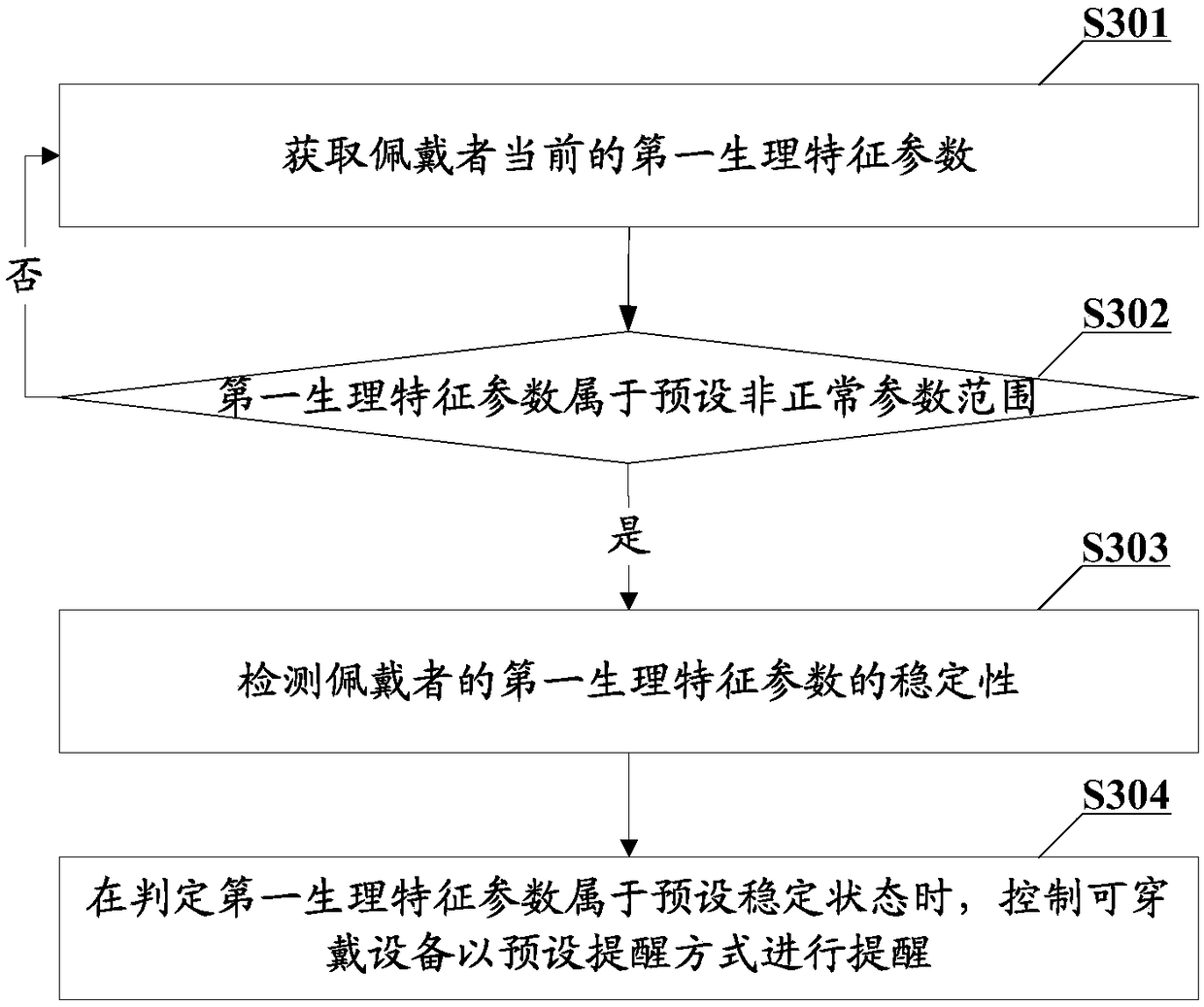
[0074] In order to solve the problem that the existing wearable device only displays the stored physiological characteristic parameters to remind the user when it receives the viewing instruction issued by the user, it will not display the acquired physiological characteristic parameters when it does not receive the viewing instruction issued by the user. The characteristic parameters are displayed, causing users to be unable to understand their own physical conditions and low user satisfaction. This embodiment provides a wearable device control method, which is applied to wearable devices. It should be noted that in this embodiment, Wearable devices may be implemented in various forms. For example, wearable devices include but are not limited to wearable devices such as smart watches and smart bracelets.
[0075] Such as image 3 as shown, image 3 The basic flow chart of the wearable device control method provided in this embodiment, the wearable device control method incl...
no. 2 example
[0116] In order to better understand the present invention, this embodiment is described in conjunction with a more specific example, assuming that the wearable device is a smart watch, please refer to Figure 7 as shown, Figure 7 It is a detailed flowchart of the wearable device control method provided in the second embodiment of the present invention, the wearable device control method includes:
[0117] S701. Determine whether the smart watch is in a wearing state.
[0118] If yes, go to S702, if not, end.
[0119]In this embodiment, it is possible to determine whether the smart watch is in the wearing state by judging whether there is an obstruction within the preset distance by the proximity sensor on the smart watch. If yes, go to S702, and if not, end.
[0120] It should be understood that in other embodiments, it is also possible to judge whether the smart watch is in the wearing state in other ways. In this embodiment, the distance is only used to describe the way ...
no. 3 example
[0147] This embodiment provides a wearable device, which can be implemented in various forms. For example, wearable devices include but are not limited to wearable devices such as smart watches and smart bracelets.
[0148] See Figure 9 As shown, the wearable device provided in this embodiment includes a processor 901 , a memory 902 and a communication bus 903 .
[0149] Wherein, the communication bus 903 in this embodiment is used to realize connection and communication between the processor 901 and the memory 902;
[0150] The processor 901 is used to execute one or more programs stored in the memory 902, so as to realize the following steps:
[0151] Obtain the current first physiological characteristic parameter of the wearer, determine whether the first physiological characteristic parameter belongs to the preset abnormal parameter range, and if so, detect the stability of the wearer’s first physiological characteristic parameter, and determine whether the first physio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com