Power grid node importance calculation method based on network embedding and support vector
A technology of support vector regression and node importance, which is applied in the field of power system, can solve problems such as difficult calculation of node importance, full consideration of actual electrical quantity information of the power grid, failure to take into account the information of nodes themselves, etc.
Active Publication Date: 2018-11-13
ZHEJIANG UNIV
View PDF3 Cites 5 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0004] The calculation method based on the index is convenient to calculate, but because the scale and structure of the power grid vary widely, it is difficult to make a unified definition of the node importance for the huge "set" of the power network, so the method based on the index inevitably has some emphasis and subjectivity
For example, the Internet sorting algorithm pays more attention to the connection r
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
 Login to View More
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
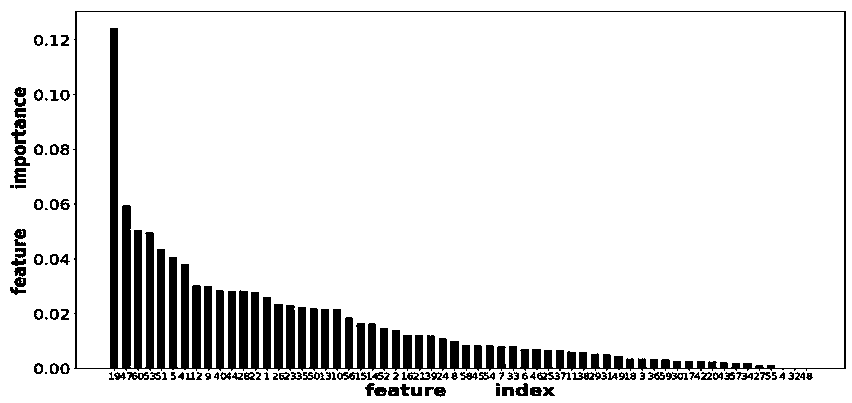
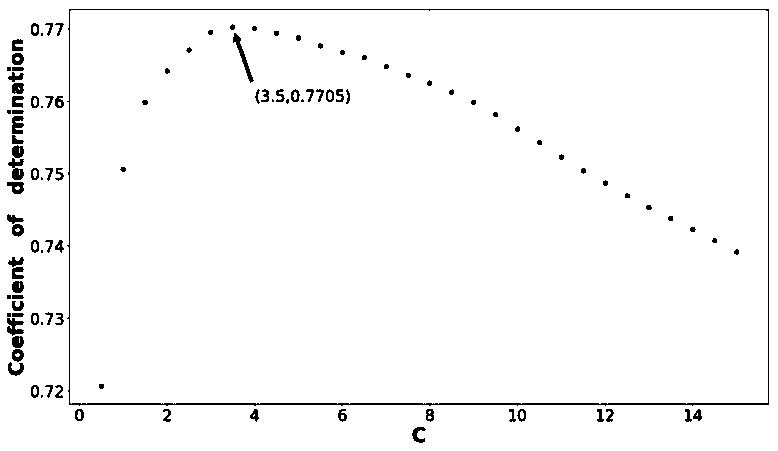
The invention proposes a power grid node importance calculation method based on network embedding and support vector, wherein firstly, the grid simulation software is used for simulating failure consequences of each node in various operating modes of a to-be-evaluated power grid; an electrical quantity feature is extracted from the simulation data, and the TADW algorithm is used for extracting thecomplete feature of the node; a node failure consequence label is determined based on the studied power grid preference; and then, the sample data are used for training a SVR model. In the training process, the cross-validation method is used for selecting the SVR model hyperparameters; the tree model-based method is used for feature selection. The power grid node importance calculation method based on network embedding and support vector in the invention can effectively evaluate the node importance according to the information learned from the training samples, and can more effectively adaptto the particularity of different power grids compared with the traditional index-based evaluation method.
Description
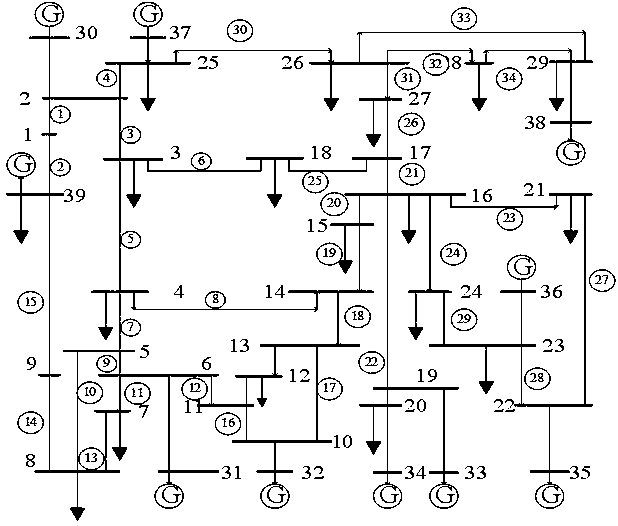
Technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the field of power systems, and specifically is a method for calculating the importance of grid nodes. Background technique [0002] In recent years, some major blackouts worldwide have highlighted the importance of protecting key nodes in the power system. Studies have shown that most power grids meet the “small-world characteristics” and have robustness in the face of random attacks and vulnerability to deliberate attacks. In a specific operation mode, only a few key nodes in the power grid will fail. Very serious consequences. Therefore, how to identify such nodes and conduct key defenses under severe weather and other scenarios is not only a requirement for power grid security, but also a need for differentiated management of power grids in accordance with economic principles. [0003] When the parameters of power grid entities such as generators, transformers and lines are known, the fault transient simulation of grid nodes can...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): G06Q10/06G06Q50/06
CPCG06Q10/0639G06Q50/06
Inventor 王慧芳张晨宇
Owner ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com