CO-training method based on unlabeled-sample consistency determination
A collaborative training, unlabeled technology, applied in the field of multi-view learning, can solve the problems of multi-angle remote sensing increasing the difficulty of joint analysis of ground objects in the same area, and low classification accuracy of multi-angle remote sensing images, so as to improve the classification effect and improve the classification. The effect of accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
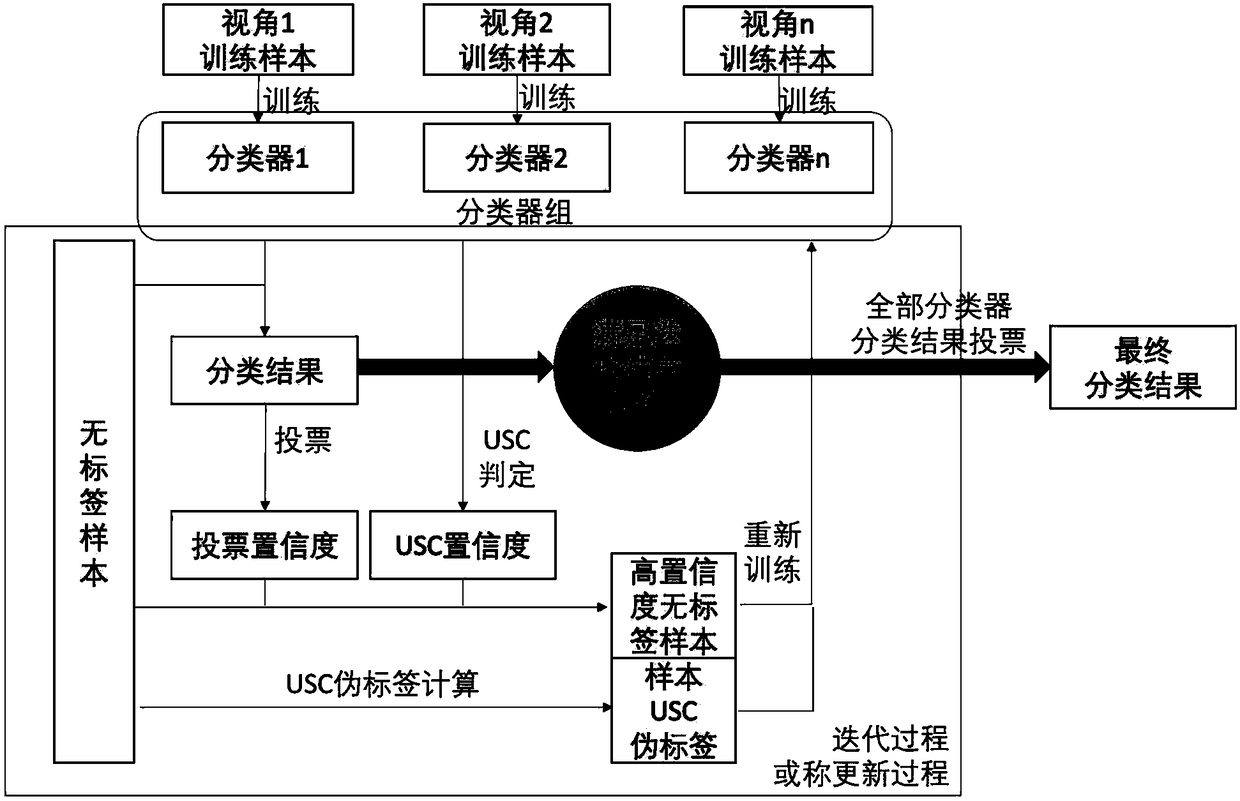
[0025] Specific implementation mode 1: The specific process of a collaborative training method based on unlabeled sample consistency judgment in this implementation mode is as follows:
[0026] Consistency judgment is: compare the difference in classification performance of classifiers adding unlabeled samples, and determine the confidence of unlabeled samples by comparing the consistency of unlabeled samples before and after adding unlabeled samples to the classifier; based on a simple idea, if a A sample and a label are added to the training sample of the classifier. If the classification effect of the classifier is exactly the same, it can be considered that the sample corresponds to the label completely. In other words, the classifier adds a new training sample and label. , the closer the classification performance is, the higher the confidence between the sample and the corresponding label will be; however, this idea is of limited value for ordinary single-view samples, al...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0038] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that: the classifier in step 1 is a supervised or semi-supervised classifier.
[0039] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in step 2, the confidence and pseudo-label of the unlabeled sample in the captured image are determined, and according to the confidence and pseudo-label of the unlabeled sample in the captured image, The label selects the trusted samples of the unlabeled samples in the captured image; the specific process is:
[0041] Step two one:
[0042] Take the first perspective as the main perspective, and the rest of the perspectives as non-main perspectives,
[0043] Perform USC judgment in the non-main view to obtain the USC sequence of the non-main view. The number of USC sequences of the non-main view is N-1. The USC sequences of the non-main view are superimposed, and the unlabeled samples of the main view are obtained according to the superimposed sequence. USC confidence (the lower the value of the superimposed sequence, the higher the USC confidence); (USC judgment is performed in the non...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com