Unmanned ship dynamic obstacle avoidance algorithm based on speed obstacle method and dynamic window method
A dynamic window and speed obstacle technology, applied in the direction of non-electric variable control, two-dimensional position/course control, vehicle position/route/height control, etc. incompletely known issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
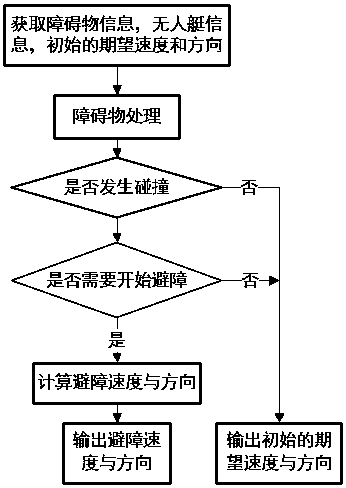
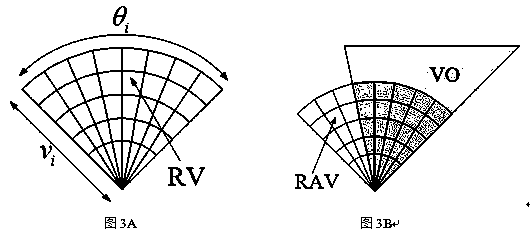
[0034] see figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , the unmanned vehicle dynamic obstacle avoidance algorithm based on the speed obstacle method and the dynamic window method, including the following steps:
[0035] Step 1: Obtain obstacle information, unmanned boat information, expected speed and direction;
[0036] Step 2: Obstacle handling;
[0037] Step 3: Determine whether the unmanned boat will collide with obstacles;
[0038] Step 4: Determine whether to start obstacle avoidance;
[0039] Step 5: Calculate the speed window and heading window;
[0040] Step 6: Calculate the attainable obstacle avoidance velocity vector;
[0041] Step 7: Select the optimal obstacle avoidance velocity vector;
[0042] Step 8: Determine whether the obstacle avoidance can be terminated;
[0043] Step 9: Output the initial desired speed and direction.
Embodiment 2
[0045] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the special features are as follows:
[0046]Obtain obstacle information, UAV information, expected speed and direction. Obtained obstacle information includes position information, size information, and motion information. The position information is represented by distance and angle in the hull coordinate system of the UAV, and the motion information is represented by speed and motion direction, and the motion direction is based on the true north direction. The obtained unmanned vehicle information includes position information, motion and attitude information. The position information is represented by (x, y) coordinates in the northeast coordinate system, and the motion information includes velocity magnitude, velocity direction, acceleration, angular velocity and angular acceleration. The attitude information is the heading angle, based on the true north direction. The desired speed and direction are giv...
Embodiment 3
[0064] The specific operation steps of the UAV dynamic obstacle avoidance algorithm based on the speed obstacle method and the dynamic window method are as follows:
[0065] Step one, such as figure 1 , Obtain obstacle information, unmanned boat information, expected speed and direction:
[0066] Obtain environmental information through the radar, vision, lidar, and sonar sensors carried by the unmanned boat itself, perform data fusion and environmental modeling to obtain the shape and position information of obstacles, and model obstacles into sizes according to the actual size of obstacles Different ellipse shapes, the shape of the obstacle is represented by the semi-major axis length and the semi-minor axis length of the ellipse, and the position information of the obstacle is represented by distance and angle in the hull coordinate system, and the distance is from the center of the unmanned vehicle to the obstacle The distance from the center, the angle is the angle of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com