A calibration device for real-time tracking of the position of free bone fragments
A real-time tracking and calibration device technology, applied in the calibration field, can solve problems such as design, precise positioning and installation of free bone fragments, patient trauma, etc., and achieve the effects of improving surgical efficiency, low picking difficulty, and improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. This embodiment is carried out on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation and specific operation process are given, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments.
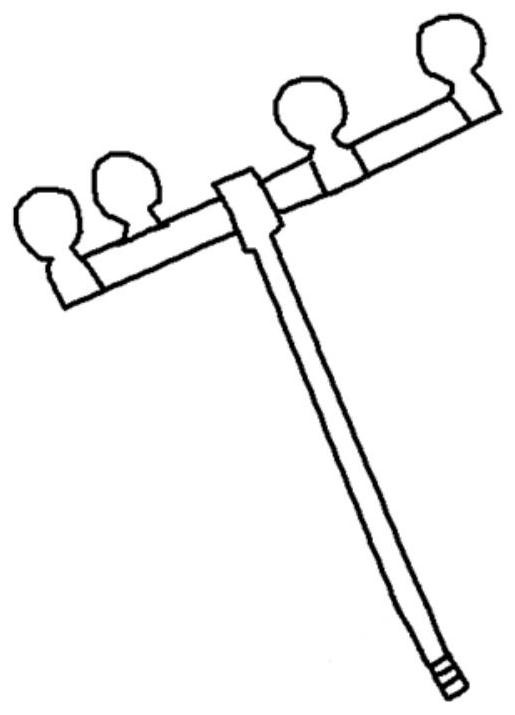
[0035] A calibration device for real-time tracking of the position of free bone fragments, such as figure 1 shown, including:
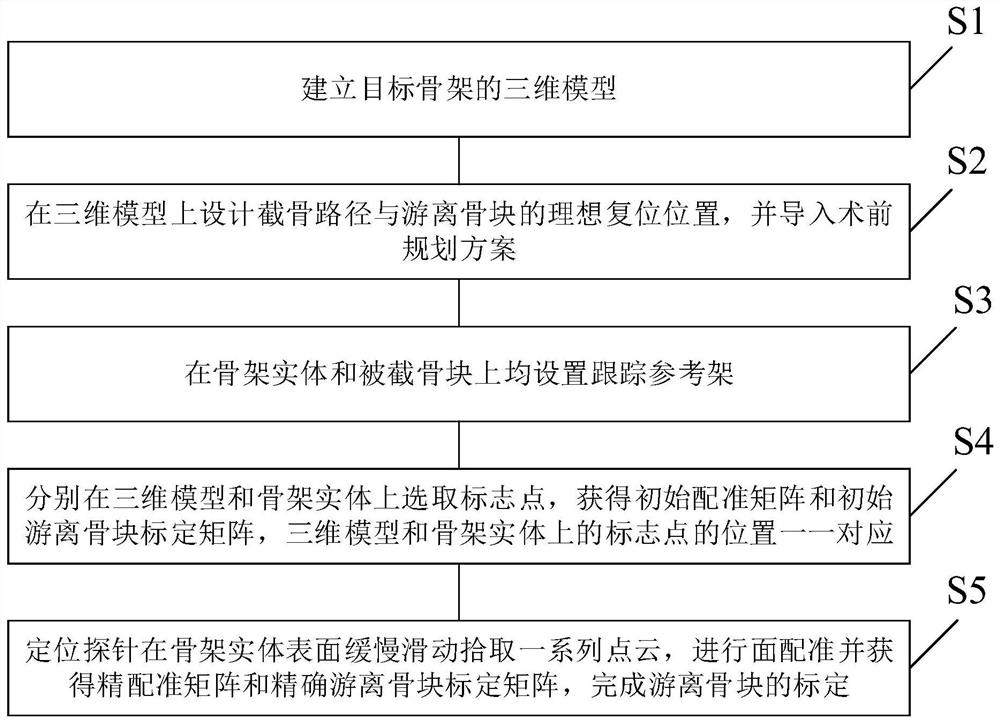
[0036] Step S1: Establish a 3D model of the target skeleton: perform image segmentation and 3D reconstruction based on CT data to obtain a 3D model of the target;
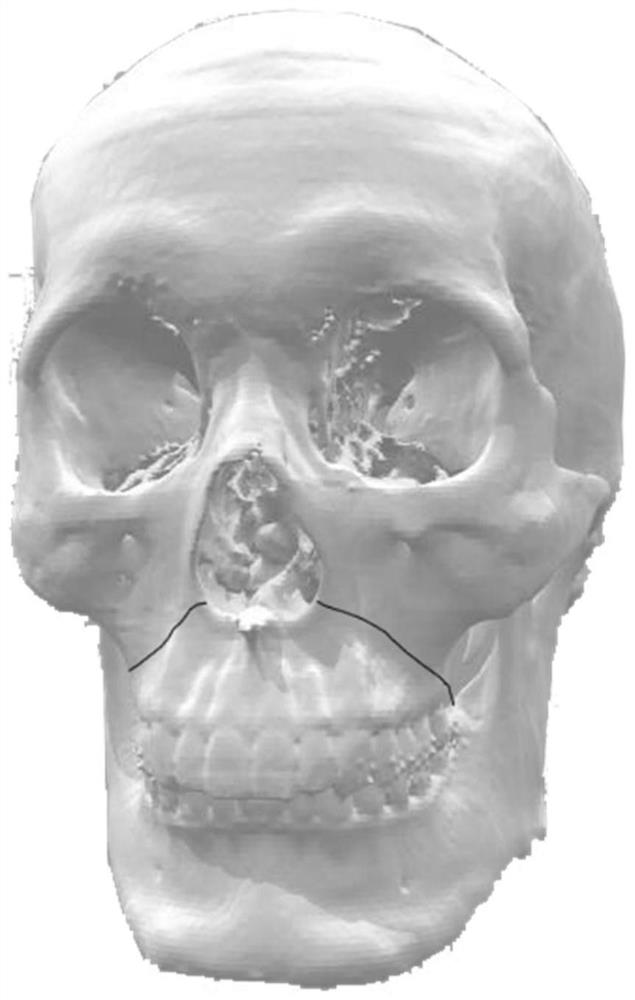
[0037] Step S2: if figure 2 As shown, the osteotomy path is designed on the 3D model, the free bone model is obtained through virtual cutting technology, and the cut bone is reset to the ideal position according to the 2D and 3D views, and the preoperative planning scheme is imported into the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com