Method for quickly identifying honey varieties and adulterated honey
A technology for honey and varieties, which is applied in the field of spectral detection for identifying adulterated honey, and achieves the effects of wide application value, simple and fast operation process, and easy operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
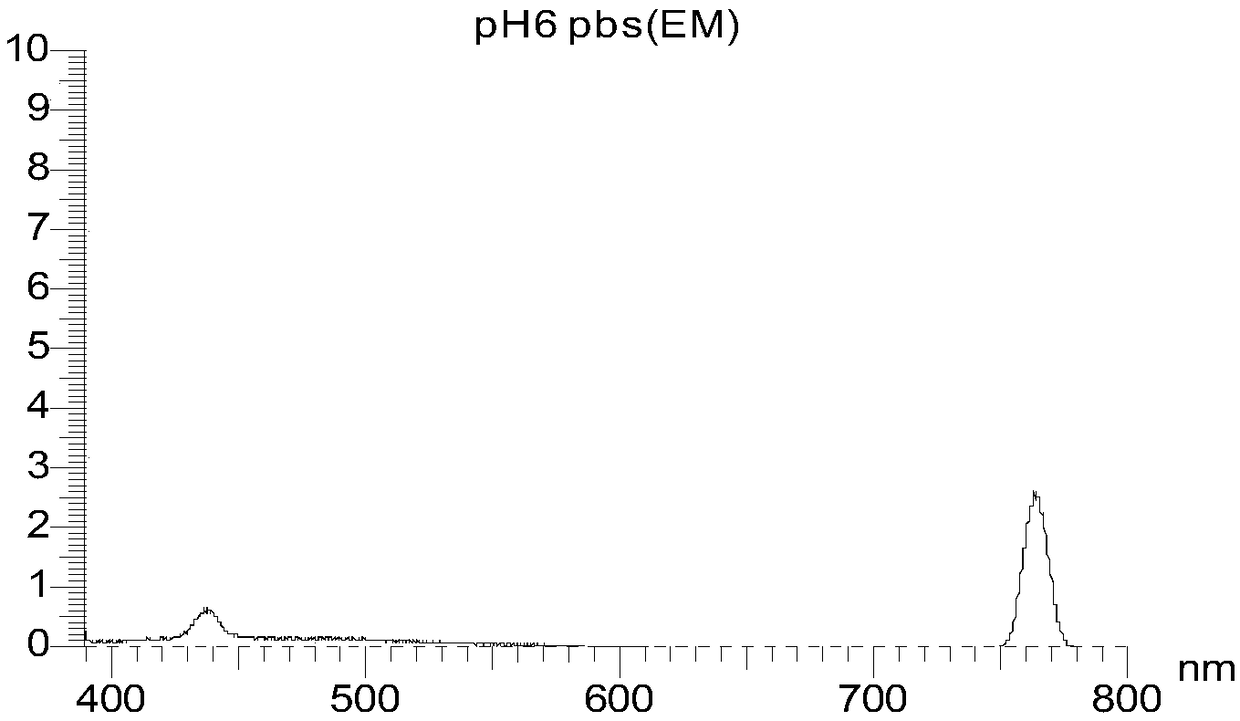
[0068] 1. Adopt common high fructose syrup samples of experimental samples, including 5 corn syrup samples (see the test results in Figure 9 ), 5 samples of rice syrup ( Figure 12 ), 3 samples of invert syrup-beet high fructose syrup ( Figure 10 ), 3 sucrose syrup ( image 3 ), tapioca high fructose syrup 5 ( Figure 11 ).
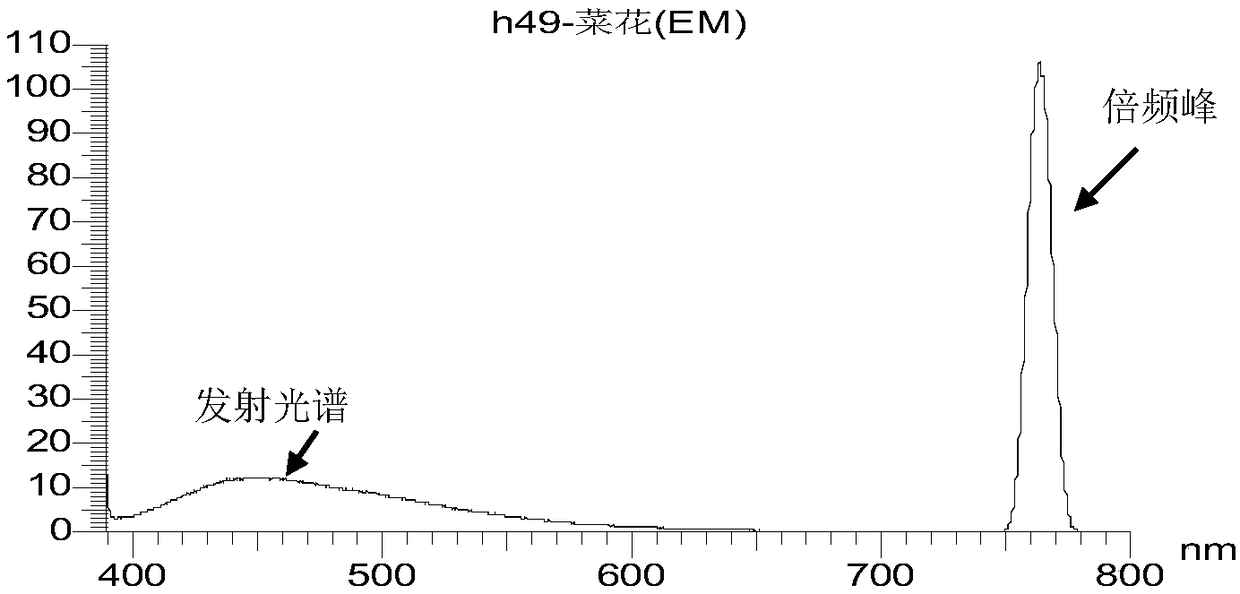
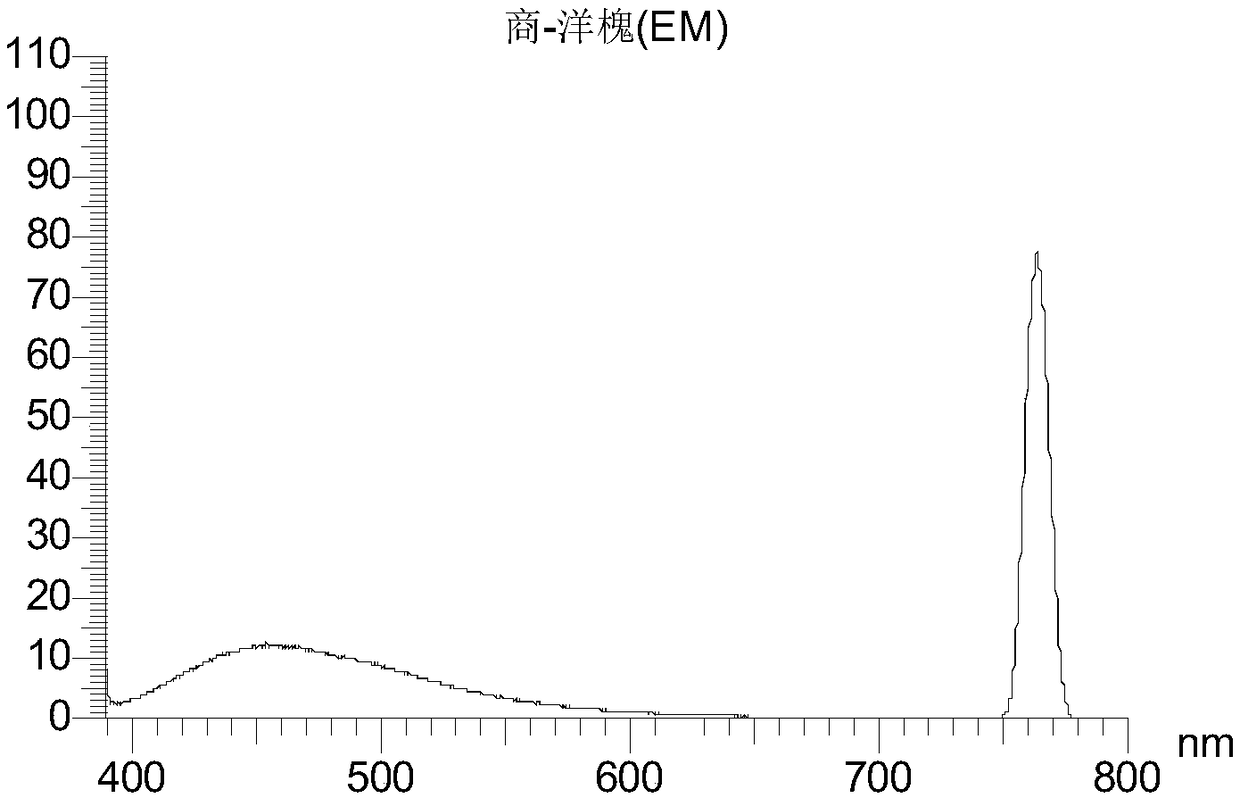
[0069] 2. Real honey samples for experiments: 10 pieces of rapeseed honey ( figure 2 ), 13 acacia honey ( image 3 ), jujube flower honey 10 pieces ( Figure 4 ), 8 linden honey ( Figure 5 ), Vitex 4 ( Figure 6 ), 5 goji berries ( Figure 7 ), 12 multifloral mixed honeys ( Figure 8 ).
[0070] 3. For adulterated samples, real honey is mixed with different syrups to form 10%, 20%, 30%, and 50% adulterated honey. There were 5 C4 plant syrup positive samples (identified by the national standard isotope method, among which 4 samples had a syrup content greater than 30%, and 1 sample was between 7% and 10%).
[0071] 4. Variety identification...
Embodiment 2
[0078] To verify the detection limit of the method, the sensitivity of the method was determined by adding different proportions of syrup to different honeys. Taking linden honey as an example, when 30% syrup is added, it can be accurately identified by the intensity of the emission spectrum and the octave peak. See Figure 15 , the excitation wavelength 380nm fluorescence emission spectrum of the linden honey mixed with 30% molasses (with reference to the horizontal line, when visible linden honey adds 30% molasses, its 380-650nm characteristic peak and the corresponding double frequency peak intensity are all obvious reduce).
[0079] Verification: Take 10 positive samples (confirmed as syrup adulteration samples by isotope method), and use this method to detect, 9 of them have the characteristics of syrup, and 9 of them are determined to be positive samples. The undetected positive sample was detected by isotope mass spectrometry and its adulterated amount of syrup was 13...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Embodiment 3 Manuka Variety Identification Analysis
[0081] Manuka honey is a high-value honey variety that has been identified in a number of ways. This method was also used to analyze 6 Manuka honeys from different sources. It was found that Manuka honey is different from ordinary honey varieties. When excited at 380nm, its emission wavelength ranges from 400nm to 650nm, which is higher than that of ordinary honey from 380nm to 650nm. The range of 650nm is obviously different, and its double frequency peak is far lower than the ordinary intensity. When mixed with different syrups, its emission wavelength range moves forward regularly. Mixed with 30% syrup or other ordinary honey such as rapeseed and acacia. When it is used, its emission wavelength range is 385nm-650nm, which is also obviously different from that of ordinary honey 380-650nm. Therefore, the method can effectively screen Manuka honey mixed with 30% syrup or other honey adulteration. see details Figur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com