Complementary integrated empirical mode decomposition method for adaptive determination of decomposition parameters
An empirical mode decomposition and self-adaptive technology, applied in the field of complementary integrated empirical mode decomposition, can solve nonlinear and non-stationary signals that cannot be adaptively acquired by adding noise, insufficient to cause local extreme point changes in the original signal, nonlinear , non-stationary signal blindness and other problems, to achieve the effect of reducing the number of integration averages, reducing the amount of calculation, and improving the accuracy of decomposition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
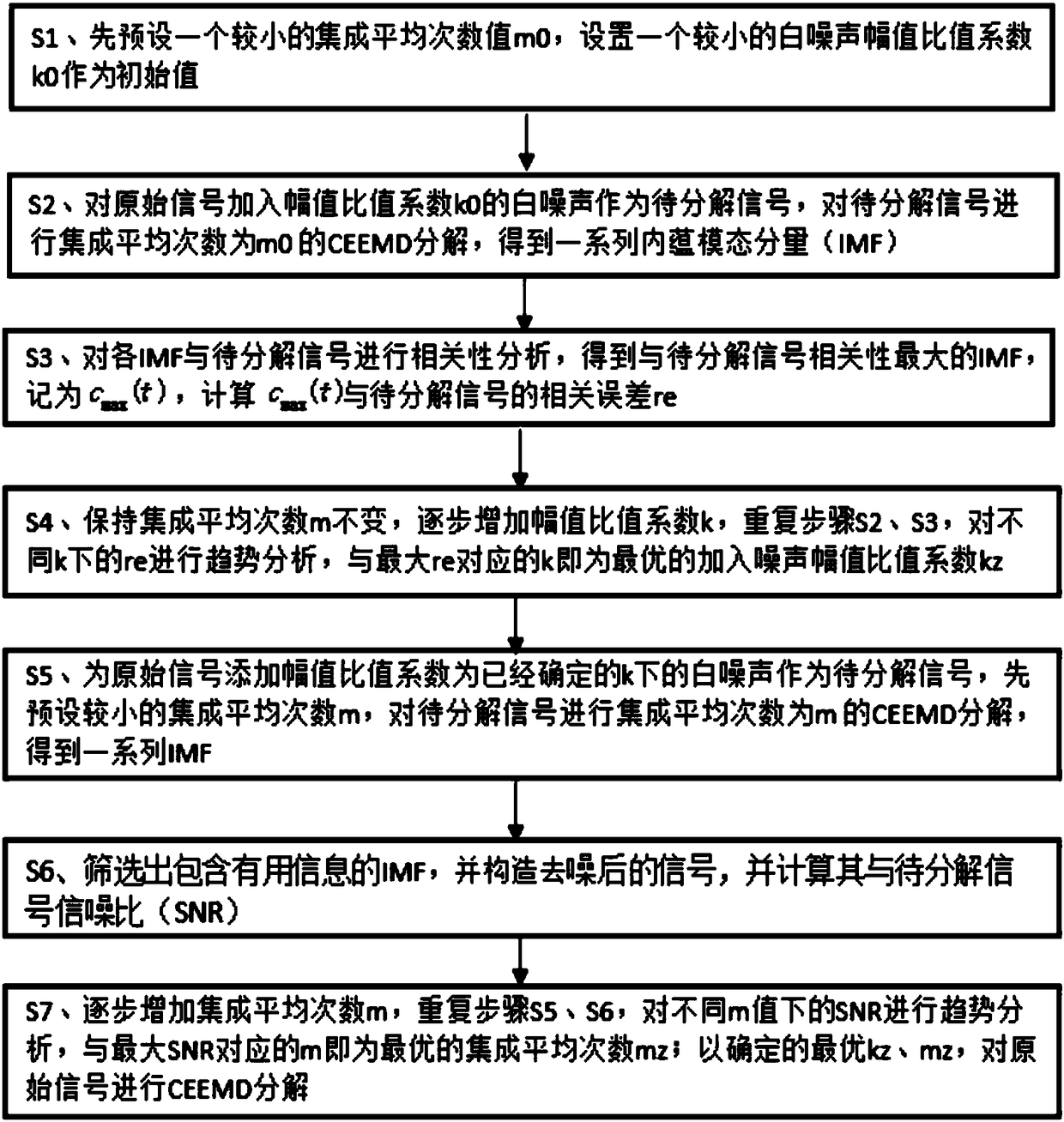
[0026] In order to make the technical solutions and advantages of the present invention more clear, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention are clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention:
[0027] Assuming that the original signal to be analyzed is composed of a periodic exponential decay pulse signal with a repetition period of 0.01s, a band-limited Gaussian white noise and a sinusoidal signal, figure 2 is the time-domain waveform of the original signal to be analyzed, image 3 is the time-domain waveform of the three signal components contained in the original signal to be analyzed.
[0028] In order to more clearly illustrate the embodiment of the present invention or the technical solution in the prior art, the following will apply the following to the embodiment figure 1 The analysis of a complementary integrated empirical mode decomposition method with adaptive determin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com