A dynamic control method and system for space non-cooperative target navigation capture
A technology of non-cooperative goals and control methods, applied in general control systems, control/regulation systems, adaptive control, etc. Meet the real-time requirements of the control algorithm and other issues, and achieve the effects of easy programming and software implementation, real-time calculation, and easy calculation code output
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
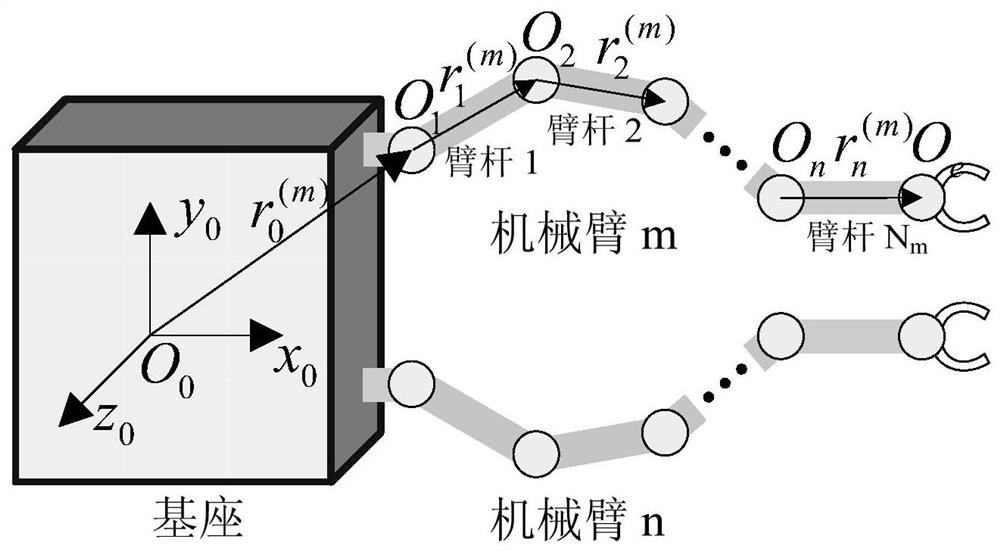
[0093] The implementation process of the whole invention is as follows: figure 1 shown. The specific implementation is described in detail as follows:
[0094] (1) Establish the kinetic energy expression of each body. The calculation equation provided by the present invention is an open mathematical description, which is convenient to realize the calculation code output, and is based on a semi-model, semi-hardware control system and semi-physical simulation.
[0095] The kinetic energy expression of the base is set as
[0096]
[0097] Among them, v 0 and ω 0 is the velocity and angular velocity of the base relative to the inertial system, m 0 is the mass of the base, P 0 is the static moment of the base, given by the mass properties of the base, I 0 is the moment of inertia matrix of the base, given by the quality characteristics of the base, and 1 is a 3*3 unit matrix.
[0098] Similarly, the kinetic energy expression of the k-th arm of the m-th robotic arm is set ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com