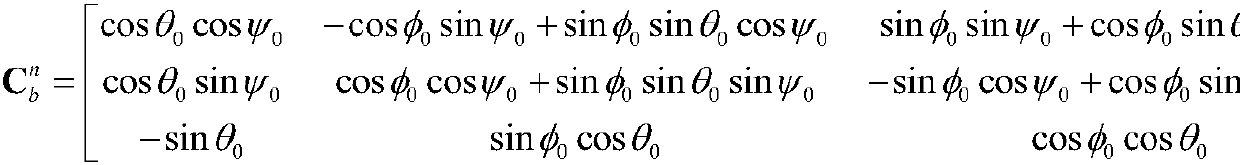Inertial pedestrian positioning method based on self adaptive zero-velocity interval adjustment
A zero-speed interval, positioning method technology, applied in the field of inertial pedestrian positioning based on adaptive zero-speed interval adjustment, can solve the problem of not proposing a method of adaptively adjusting the length of the zero-speed detection window, and not mentioning the zero-speed detection window length system. Solve problems such as the influence of pose information accuracy and applicability, and the decrease of pedestrian positioning system positioning accuracy, so as to meet real-time requirements, reduce insufficient error compensation, and enhance applicability.
Active Publication Date: 2018-08-03
HARBIN ENG UNIV
View PDF5 Cites 25 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Harbin Engineering University wrote "MIMU / GPS / Magnetometer Individual System Integrated Navigation Technology Research" written by Liu Fengli in 2013. This article proposed a zero-speed correction technology based on the hidden Markov model, which uses the output data of the gyroscope. Zero-speed detection, to a certain extent, improves the applicability of the zero-speed correction algorithm when moving fast, but at the same time causes the positioning accuracy of the pedestrian positioning system to decrease when moving slowly
The above literatures are all about adaptively adjusting the zero-speed detection threshold under different motion speeds of pedestrians, improving the zero-speed detection accuracy by adjusting the threshold, or improving the zero-speed detection algorithm for a specific gait, so as to improve the zero-speed detection accuracy. In summary, none of the literature mentions the influence of the length of the zero-speed detection window on the accuracy and applicability of the system's calculated pose information under any gait, nor does it propose a method for adaptively adjusting the length of the zero-speed detection window
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment
[0128] The beneficial effects of the present invention are verified in the following manner:
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Login to View More
Abstract
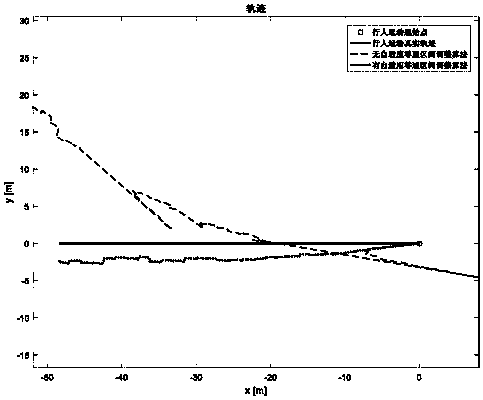
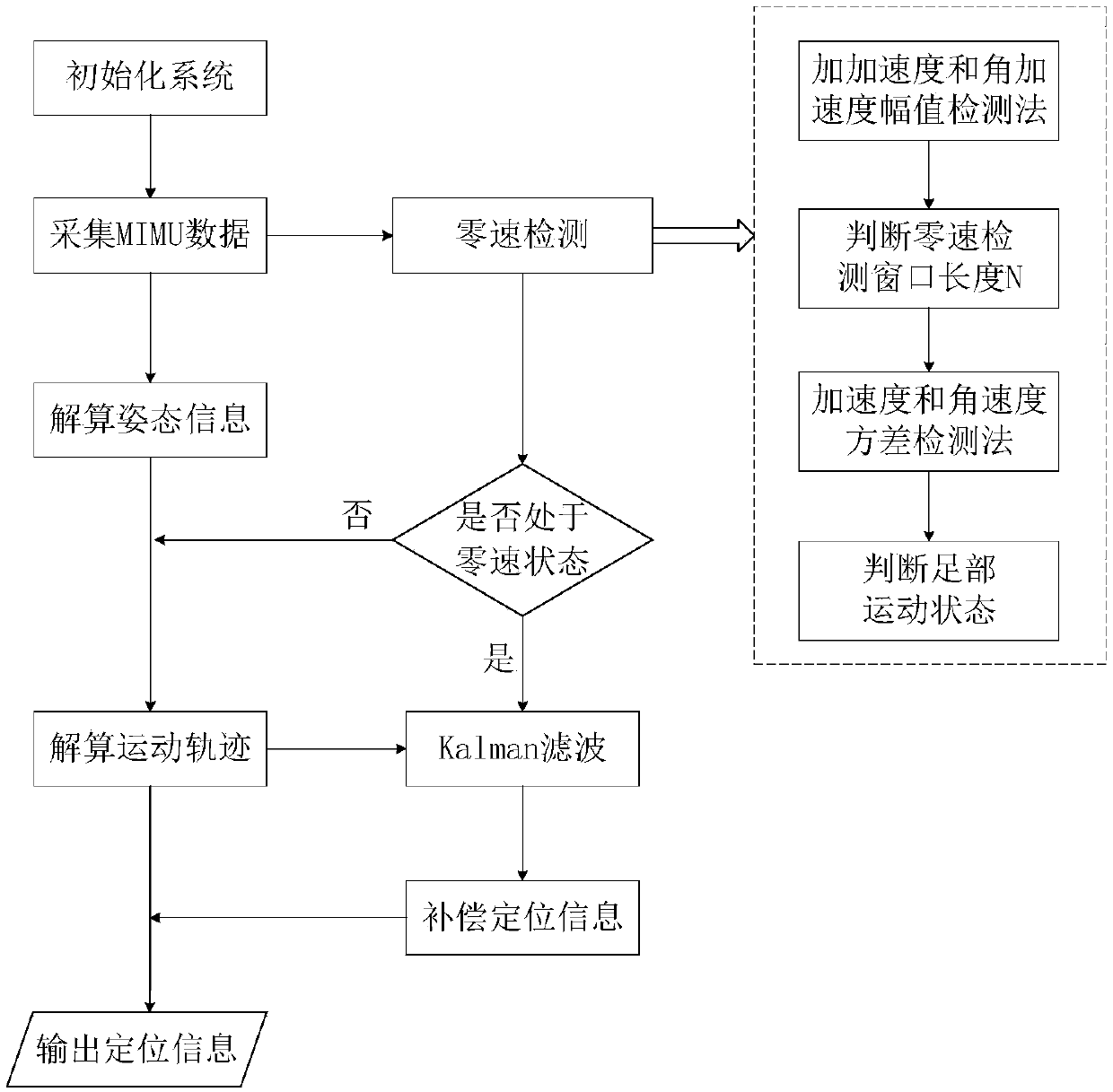
The invention discloses an inertial pedestrian positioning method based on self adaptive zero-velocity interval adjustment, and belongs to the pedestrian positioning technical field relying on an inertial navigation system. An inertial device is fixed on a foot part of a pedestrian, positioning information of the pedestrian is calculated in real time according to the measured acceleration speed and angular velocity, at the same time, a self adaptive sliding window detection method is designed by combination of an acceleration speed and angle acceleration speed amplitude detection algorithm, the zero-velocity detection window length is self-adaptively adjusted in the system calculating process, and the zero-velocity detection accuracy is improved. The zero-velocity correction algorithm is used for compensating the pedestrian posture information in a zero-velocity interval, and the compensated posture information is taken as final positioning information and is outputted. The applicability of the inertial pedestrian positioning system at arbitrary motion speed is enhanced, the problem of insufficient error compensation caused by the change of pedestrian movement speed is reduced, positioning accuracy can be improved without any external auxiliary information, the calculation quantity is small, and the method is simple and easy to operate.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the technical field of pedestrian positioning based on an inertial navigation system, and in particular relates to an inertial pedestrian positioning method based on adaptive zero-speed interval adjustment. Background technique [0002] At present, the most common pedestrian positioning system is the Global Positioning System (Global Positioning System, GPS). However, in environments such as high-rise streets and relatively closed indoor environments, pedestrians cannot normally receive GPS signals, and thus cannot be located. The inertial navigation system (INS, hereinafter referred to as inertial navigation system) is an autonomous navigation system that does not rely on external information and does not radiate energy outward, and is suitable for complex and changeable pedestrian movement environments. It is precisely because of the rapid development of micro-inertial sensors, which have the advantages of small size, light w...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): G01C21/18G01C21/20
CPCG01C21/18G01C21/20
Inventor 王秋滢郭铮崔旭飞张明惠刘凯悦钟万青匡春旭程铭尹娟
Owner HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com