Method for building distributed time-space multidimensional index system for mobile medical services
A mobile medical and indexing system technology, applied in the field of data indexing, can solve the problems of complexity, the efficiency and scalability of spatiotemporal indexing are not simple, and achieve the effect of improving satisfaction and meeting high concurrency requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
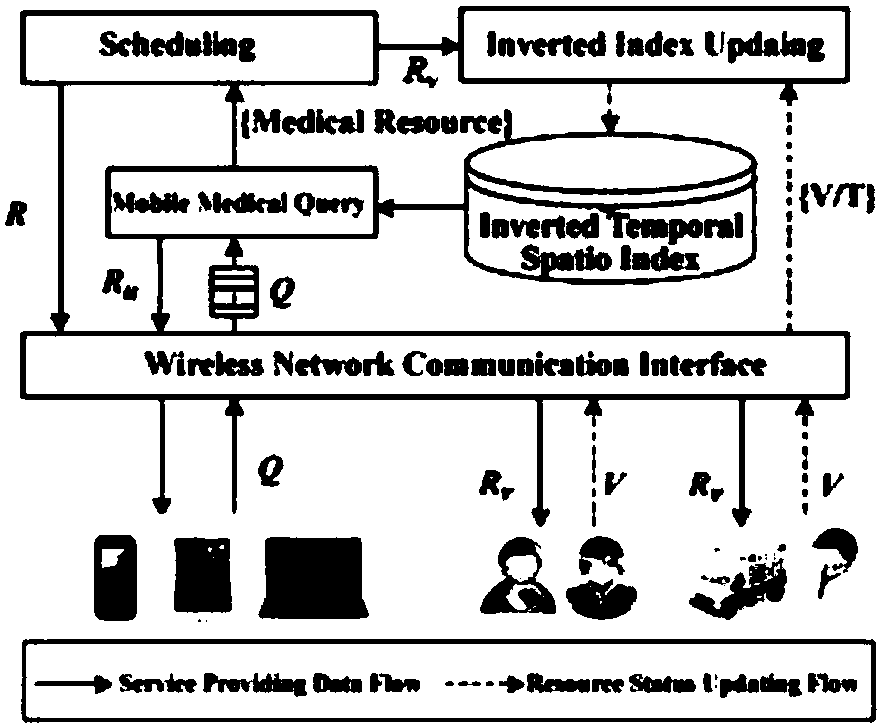
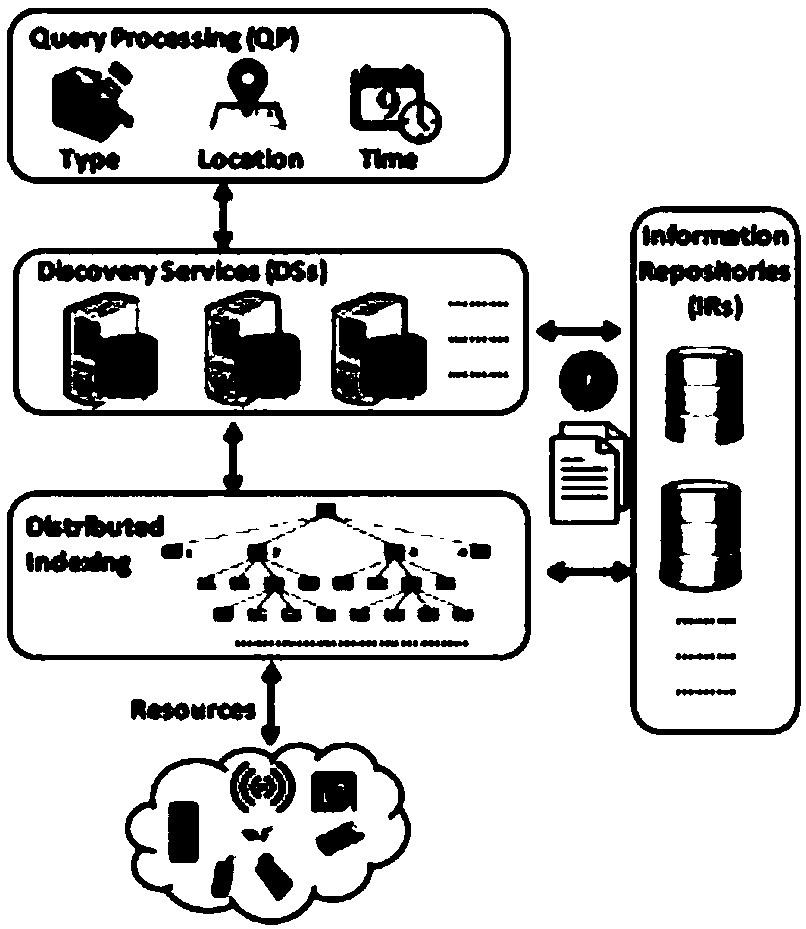
[0021] Embodiment 1: The present invention provides a distributed spatio-temporal multi-dimensional index method for mobile medical services to improve the efficiency of medical services and make full use of medical resources. The invention also improves the shortcomings of the query method in the prior art to improve accuracy and real-time performance, thereby realizing multi-dimensional indexing.
[0022] In order to achieve the above purpose, the technical solution adopted by the present invention is as follows: Firstly, the research and overview of the present situation of the distributed indexing method are carried out. Then, a new distributed efficient indexing method is proposed, which allows spatio-temporal high-dimensional indexing of mHealth resources in a distributed environment. Third, carry out big data experiments, which strongly prove the effectiveness and scalability of the indexing method, and also prove that the method can effectively support time and space q...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2: Study the factors affecting the performance of the algorithm through experiments. Mainly, in-depth experiments are conducted to evaluate the state-of-the-art spatial algorithms for IDI and to study IDI in detail. We first introduce the details of the experimental setup, including datasets, default parameters, and system environment, then evaluate the performance and analyze the experimental results.
[0038] (1) Setup and configuration: Build a server cluster with 32 servers. Each server is composed of dual-core AMD2.0GHz CPU, 73GB SCSI hard disk and 8GB memory, and Ubuntu10.10 server operating system and hadoop1.2 are installed. Each slave node cluster runs a TaskTracker and DataNode maintenance process runs. The DFS block default size is 64MB. Apply both solutions on the same cluster of nodes. In the experiment, the Real Data Set (RDS), Dalian's medical vehicle GPS dataset, including 110 systems of medical ambulances and traffic conditions in the cit...
Embodiment 3
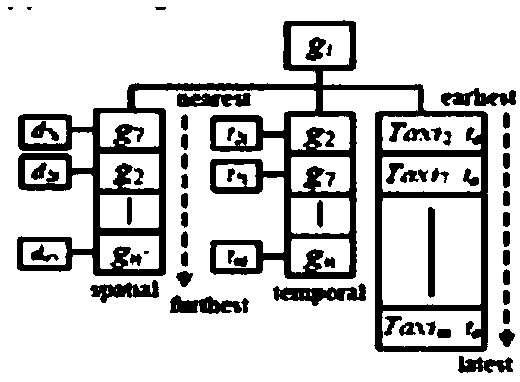
[0042] Embodiment 3: The efficiency of index creation is significantly improved: firstly, the efficiency of constructing MRITS, MRIV, MRTree and MRV indexes is evaluated by changing the number of cluster nodes from 2 to 32. refer to Figure 6 , which illustrates the impact of node data changes on the index construction time of RSD and SDS datasets. These three index structures increase almost linearly as the cluster nodes grow. However, the construction time of MRITS is the shortest compared to the number of nodes of MRIV, MRtree and MRV. Especially when the number of nodes is 8 and 16, MRITS is 50% faster than MRIV, 6 times faster than MRTree, and 4 times faster than MRV. This is because on the basis of the existing medical area, the time-space index of the inverted medical area is directly divided, no pre-calculation is required, and only the grid indexing process is required. The index structure based on R-tree and Voronoi requires a complex construction process. Due to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com