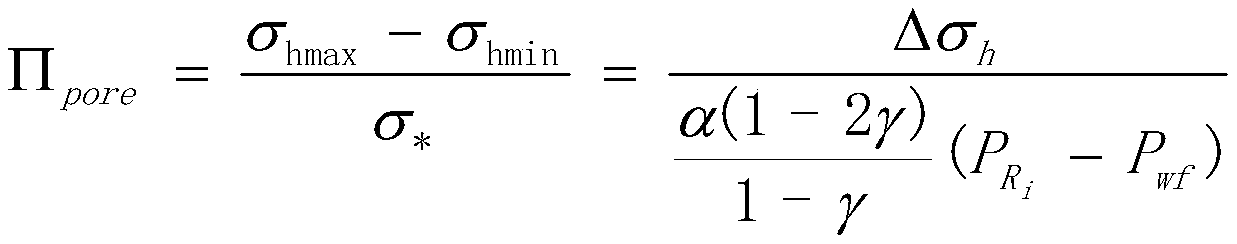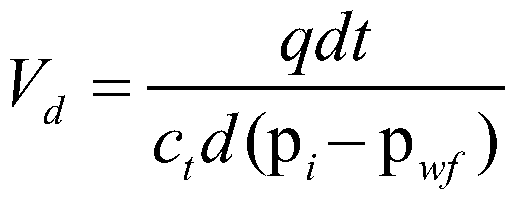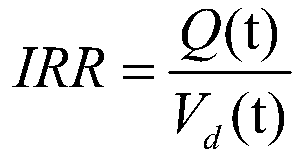A method for selecting wells and layers for repeated fracturing of gas wells
A technology for repeated fracturing and gas wells, which is applied in wellbore/well components, earthwork drilling, data processing applications, etc. It can solve problems such as unreliable experience, numerous calculation parameters, and inaccurate calculations, and achieve strong portability, Effects with high accuracy and simple calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] This embodiment provides a method for selecting wells and layers for repeated fracturing of gas wells, comprising the following steps:
[0037] Step 1) Calculate the poroelastic stress-steering coefficient Π according to the rock mechanics parameters Poisson's ratio, in-situ stress, gas zone formation pressure, and bottomhole flow pressure poro , Π poro Gas wells <2 are the primary target gas wells for refracturing;
[0038] Step 2) Calculate the gas leakage volume V according to the gas reservoir pressure coefficient, bottom hole flow pressure, single well daily gas production, and production time of the primary target gas well selected for refracturing d ;
[0039] Step 3) Calculate the instantaneous recovery rate IRR according to the cumulative gas production and gas leakage volume of the primary target gas well selected for refracturing, when V d >3.3, select the gas well with IRRd 0.21 as secondary target gas wells for refracturing;
[0040] Step 4) Calculate t...
Embodiment 2
[0046] On the basis of Embodiment 1, this embodiment provides a method for selecting wells and layers for repeated fracturing of gas wells. The process is as follows:
[0047] Step 1) Calculate the poroelastic stress steering coefficient Π according to the rock mechanics parameters Poisson's ratio, in-situ stress, formation pressure of the gas zone, and bottomhole flow pressure poro ,Calculated as follows:
[0048]
[0049] Where: σ hmax —Maximum in-situ horizontal stress, MPa; σ hmin —Minimum in-situ horizontal stress, MPa; σ * —stress difference caused by pore pressure gradient, mm; γ—Poisson’s ratio; —gas reservoir pressure, MPa; P wf —Bottomhole pressure, MPa.
[0050] select Π poro The gas wells with <2 are the primary target gas wells for refracturing.
[0051] Step 2) Calculate the gas leakage volume V according to the gas reservoir pressure coefficient, bottom hole flow pressure, single well daily gas production, and production time of the primary target gas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com