Image Fusion Method Based on Algebraic Multigrid and Watershed Segmentation
A technology of watershed segmentation and multi-grid, applied in the field of image fusion, can solve the problems such as the block effect that cannot be fundamentally solved, and the block effect is limited, so as to avoid the loss of image clarity and reduce the effect of block effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
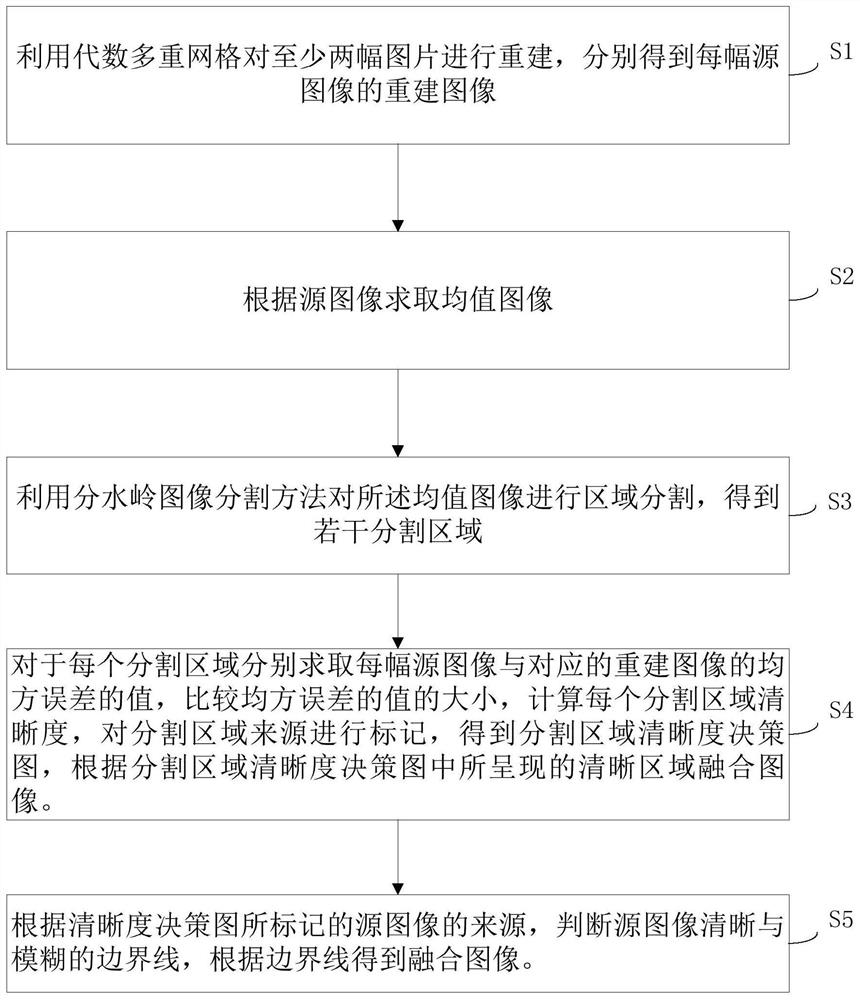
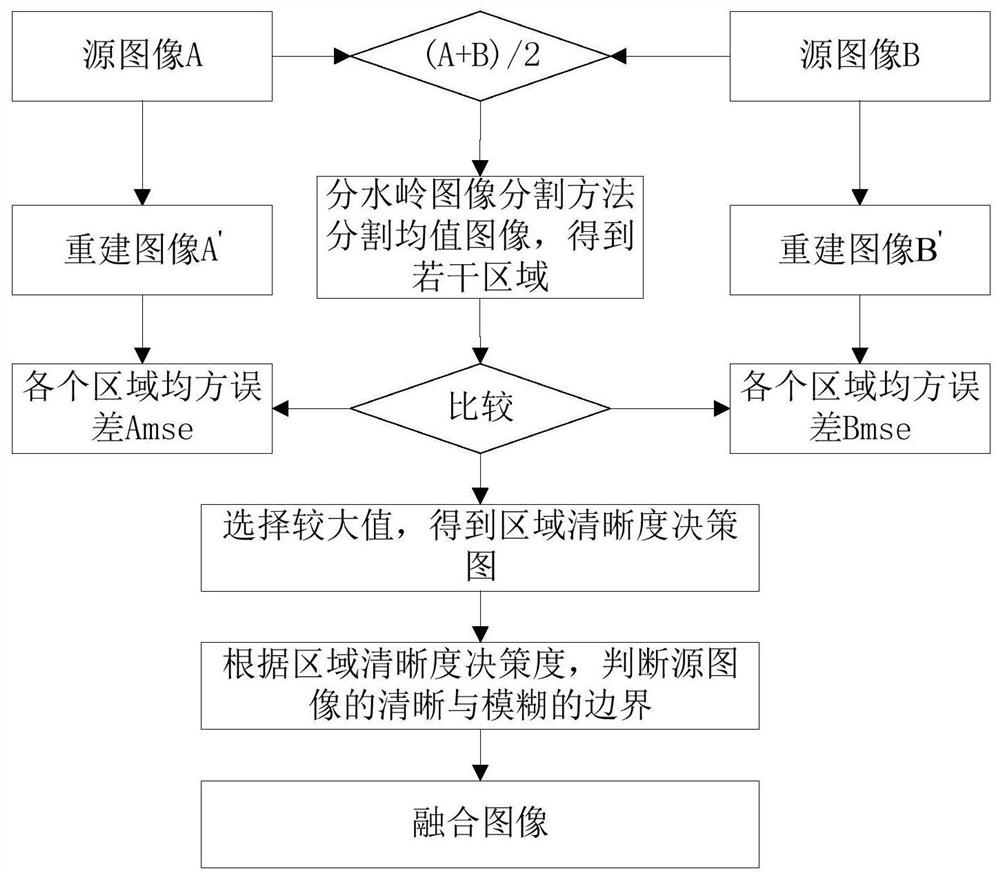
[0059] S11. Reconstruct at least two source images by using algebraic multigrid to obtain a reconstructed image of each source image respectively;
[0060] S21. Obtain an average image according to the source image, that is, average two or more source images to obtain an average image;
[0061] S31. Using a watershed image segmentation method to perform region segmentation on the mean image to obtain several segmented regions;
[0062] S41. For each segmented area, calculate the value of the mean square error of each source image and the reconstructed image of each source image, that is, calculate the source image corresponding to the boundary according to the segmented boundary of the segmented area The value of the mean square error between the area and the reconstructed image area corresponding to the boundary; compare the value of the mean square error, calculate the sharpness of each segmented area, mark the source image source of the segmented area, and obtain the defini...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Steps S22-S52 are the same as steps S2-S5, for details, refer to the description of steps S2-S5; S12 of this embodiment and S11 (or S1) of Embodiment 1 have the following improvements:
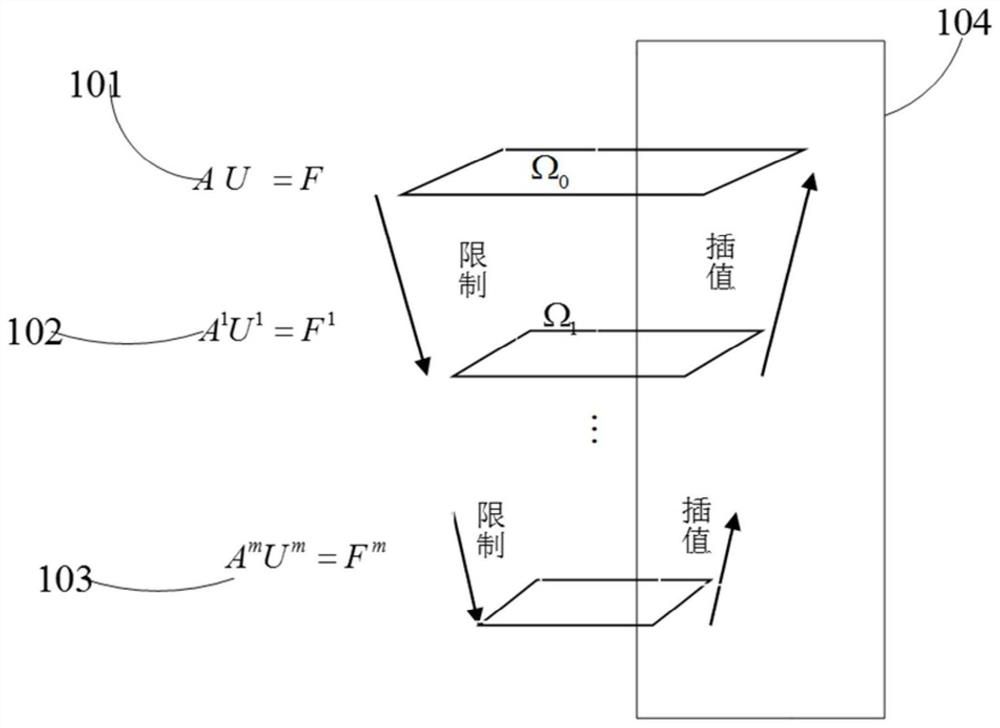
[0067] S12. Reconstruct at least two source images by using an algebraic multigrid to obtain a reconstructed image of each source image respectively; image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0068] Step 101: Initially Ω 0 , AU=F, do several iterations on this grid, and project the error to Ω 1 .
[0069] Step 102: According to A 1 u 1 =F 1 , and then do several iterations to project the error to the next level of grid.
[0070] Step 103: Continue to iteratively solve, and finally in the coarse grid Ω m , get A m u m =F m , F m =Ω m -C m ;A m is the coefficient matrix sequence, U m is the system of equations in the cyclic process of algebraic multigrid; the coarser coarse mesh Ω of algebraic multigrid m+1 =C m is the finer coarse mesh Ω m A true subset of .
[...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Steps S13-S33 are the same as steps S12-S32, please refer to the description of steps S12-S32 for details;
[0075] Step S43, using the watershed image segmentation method to segment the mean image to obtain several segmented areas including:
[0076] Use the Sobel operator to find the gradient image of the mean image;
[0077] The basic operations of morphology are expansion and erosion. The opening operation of B on A is A○B, and the closing operation is A·B, expressed as is an expansion operation, □ is an erosion operation, and the obtained gradient image is smoothed by using the expansion operation and the erosion operation;
[0078] The gradient image is segmented using the watershed segmentation method, and the two source images are divided into several different areas. Among them, the principle of the watershed image segmentation method is as follows: Image 6 shown.
[0079] The idea of the watershed algorithm comes from the topography of geodesy. The bas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com