A method for improving the survival rate of artificially bred juvenile giant clam multiplication and release
A technology of proliferation, release and artificial breeding, which is applied in the fields of application, climate change adaptation, fish farming, etc. It can solve the problems of difficulty in reaching the bottom sowing specifications and the survival rate of the larvae of clam clam.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] A kind of technology that improves the survival rate of artificially bred giant clam juveniles in the South my country Sea multiplication and release comprises the following steps:
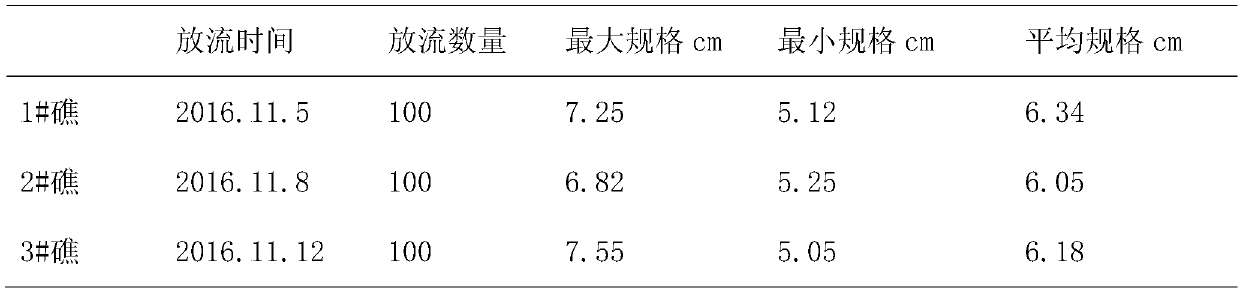
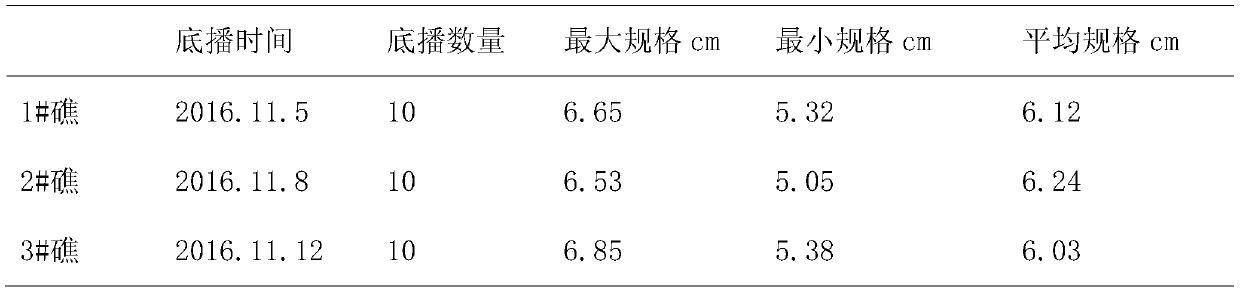
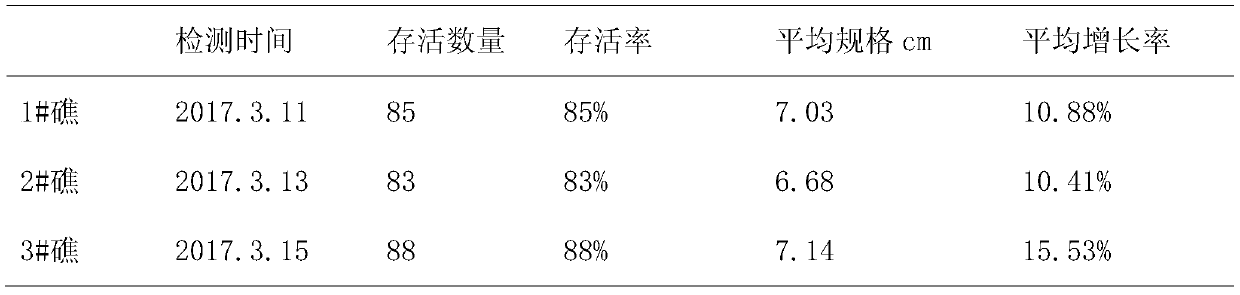
[0020] 1. Selection and treatment of artificially bred juvenile giant clam shells: In this multiplication and release experiment, juvenile giant clam shellfish came from our breeding base in Sanya, and juvenile giant clam shellfish were selected with a size of 5cm-8cm, with an average of 6.2cm. Use coral reef fragments, coral sand and other calcium carbonate materials to cover good giant clam juveniles to protect the foot silk holes. Within a week before going to sea, giant clams secrete foot silk to adhere to coral sand and small coral reef fragments.
[0021] 2. Transport of giant clams: Change the opaque living water tanks of ordinary fishing boats into transparent plexiglass hatch covers, because the main nutritional mode of giant clams depends on the zooxanthellae on the mantle, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com