A head-mounted multi-depth stereoscopic image display system and display method
A stereoscopic image and display system technology, applied in the direction of instruments, etc., can solve problems such as visual fatigue
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
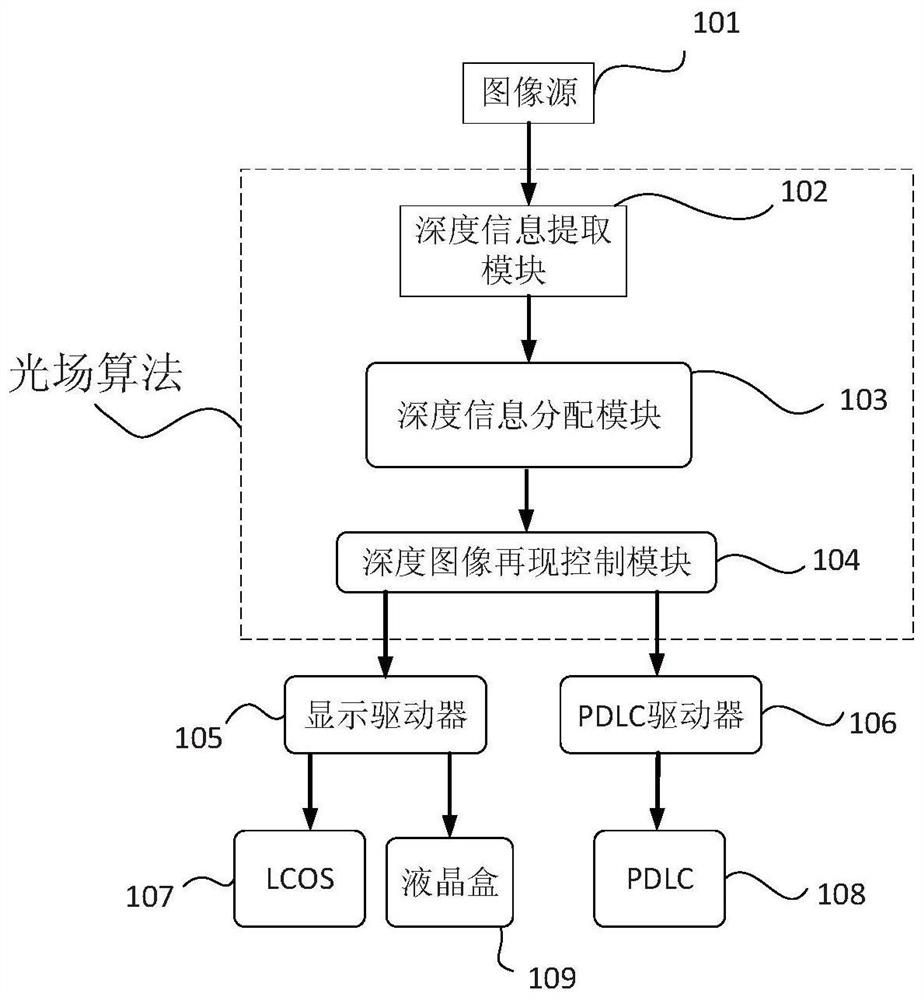
[0084] A head-mounted multi-depth stereoscopic display system, comprising:
[0085] The depth information extraction module extracts the color data and three-dimensional coordinate data of pixels in the three-dimensional image, and transmits them to the depth information distribution module;
[0086] The depth information allocation module allocates all pixels into several pixel groups with different spatial depth ranges;
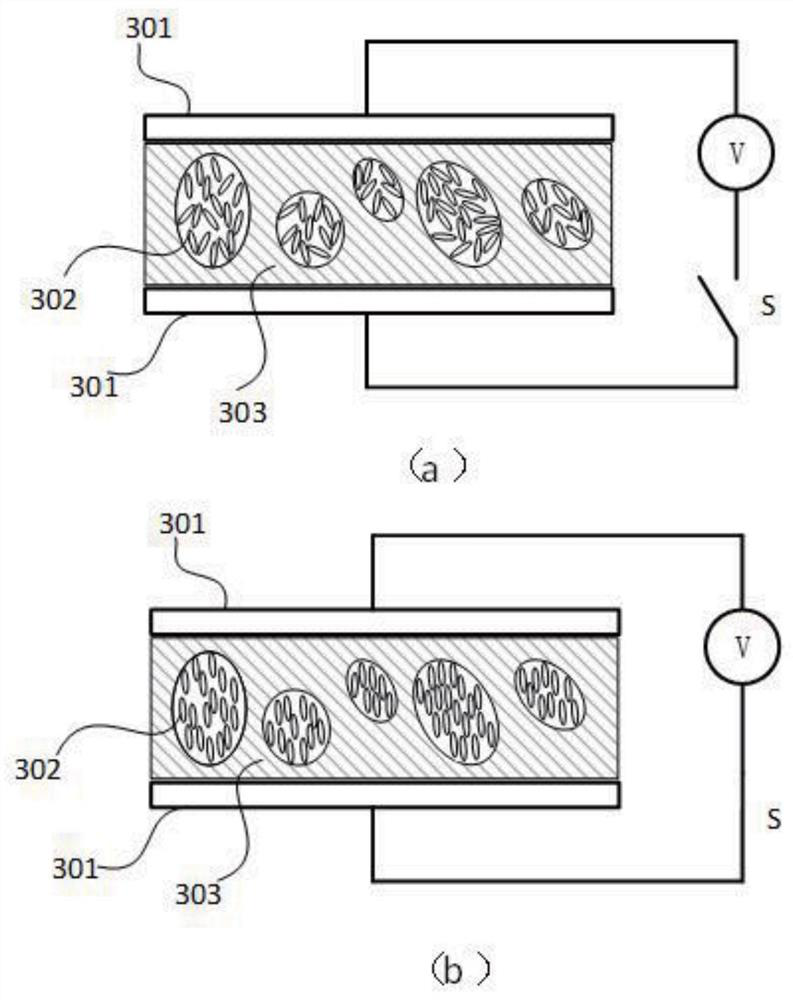
[0087] Several layers of PDLC with controllable transparent state / scattering state;
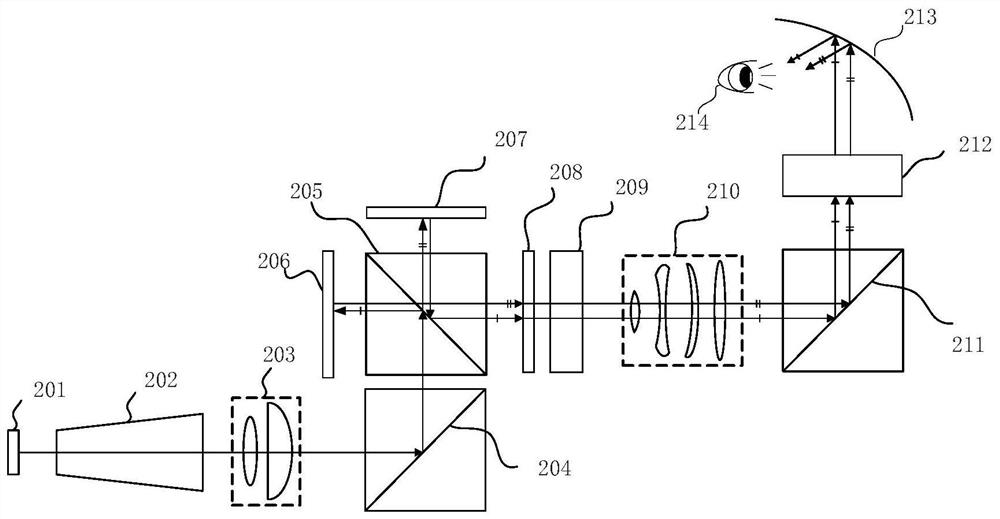
[0088] The projection unit, including a micro-display chip and a projection lens, selectively projects each pixel point group at a certain frequency to the PDLC corresponding to the depth to generate a relay stereoscopic image visible in the multi-plane optical unit;
[0089] The vision unit, including the eyepiece lenses, projects the relayed stereoscopic image in the multiplane optical unit to the human eye.
[0090] Such as figure 1 As shown, the flow of the control ...
Embodiment 2
[0138] Another embodiment of the head-mounted multi-depth stereoscopic display system such as Figure 8 As shown, compared with Embodiment 1, a gaze tracking module 110 is added.
[0139] Such as Figure 8 , 9 As shown in , it more clearly expresses the image processing process after the eye-tracking module is used. After the image source is generated, the RGB and three-dimensional coordinate data of each pixel of the image source are obtained by the depth information extraction module, and at the same time, the gaze information obtained at this moment is packaged together and sent to the depth information distribution module.
[0140]The allocation module allocates the image source pixel and its surrounding pixels at the depth of the line of sight to the PDLC layer corresponding to the depth for display. When the gazing depth of the line of sight is exactly the same as the depth set by the PDLC, these pixels are allocated to the PDLC layer for display; when the gazing dept...
Embodiment 3
[0146] Another embodiment of the head-mounted multi-depth stereoscopic display system is an extension of Embodiment 2. Compared with Embodiment 2, it reduces the number of components used to selectively implement the transparent state / scattering state switching mode, Therefore, the limitation on the refresh rate of the projection unit is further reduced.
[0147] The control method of embodiment 3 is basically the same as the control method of embodiment 2, the main difference lies in the image processing process after the gaze tracking module is integrated. Therefore, the following focuses on the differences between Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 2 in the subsequent image processing process.
[0148] Such as Figure 9 , as shown in 11, in embodiment 2, we have already described that the human eye can only see the image within the 5° field of view, and the image outside the 5° field of view, the human eye sees the picture is blurred , it exists as the background of the image wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com