Method for calculating second-order Markov chain by using chemical reaction network
A chemical reaction network, Markov chain technology, applied in chemical process analysis/design, calculation, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problem that no one has considered high-order Markov chain design and steady-state distribution calculation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The technical solution of the present invention will be further introduced below in combination with specific implementation methods and accompanying drawings.
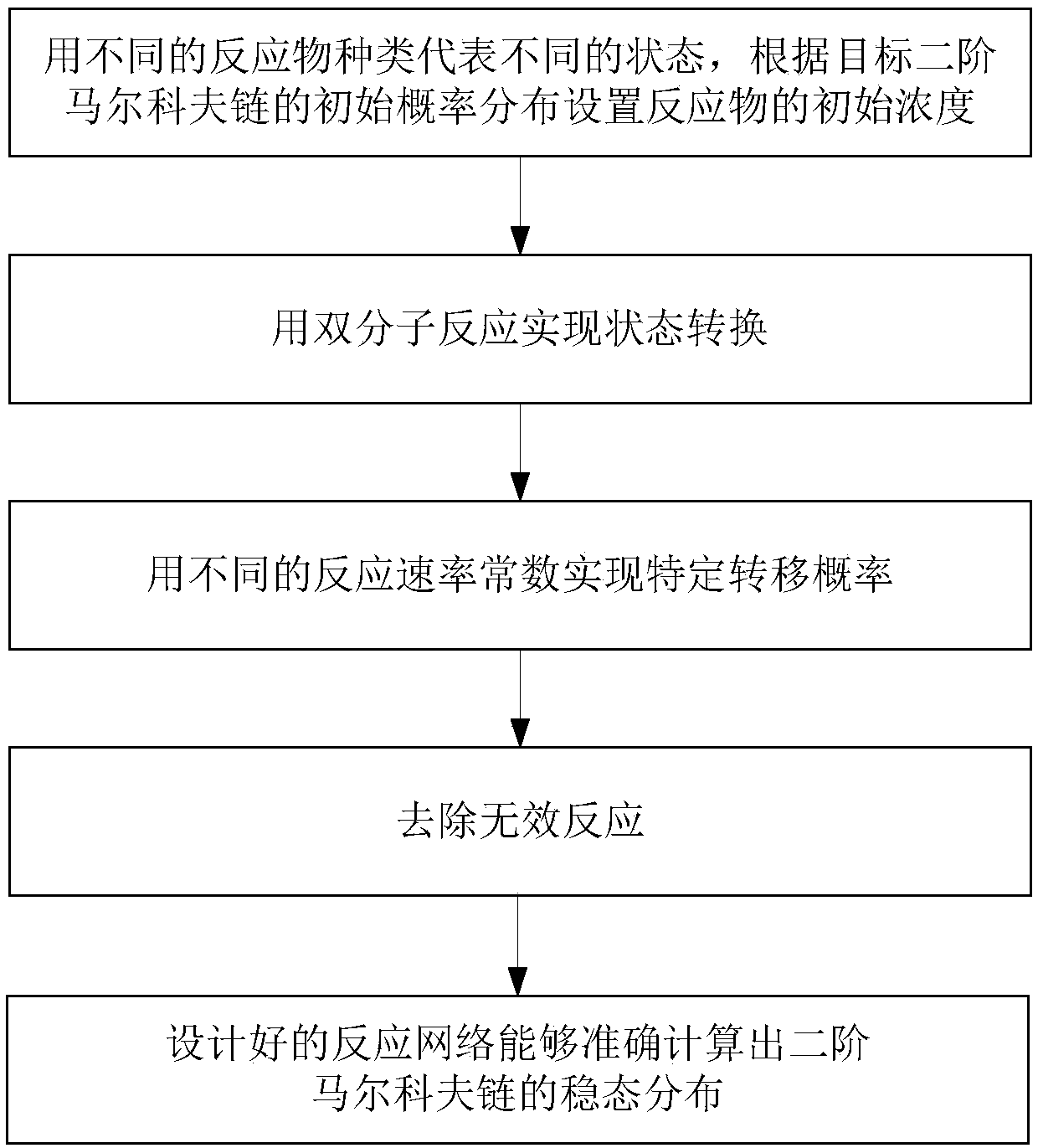
[0021] This specific embodiment discloses a method for calculating a second-order Markov chain with a chemical reaction network, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
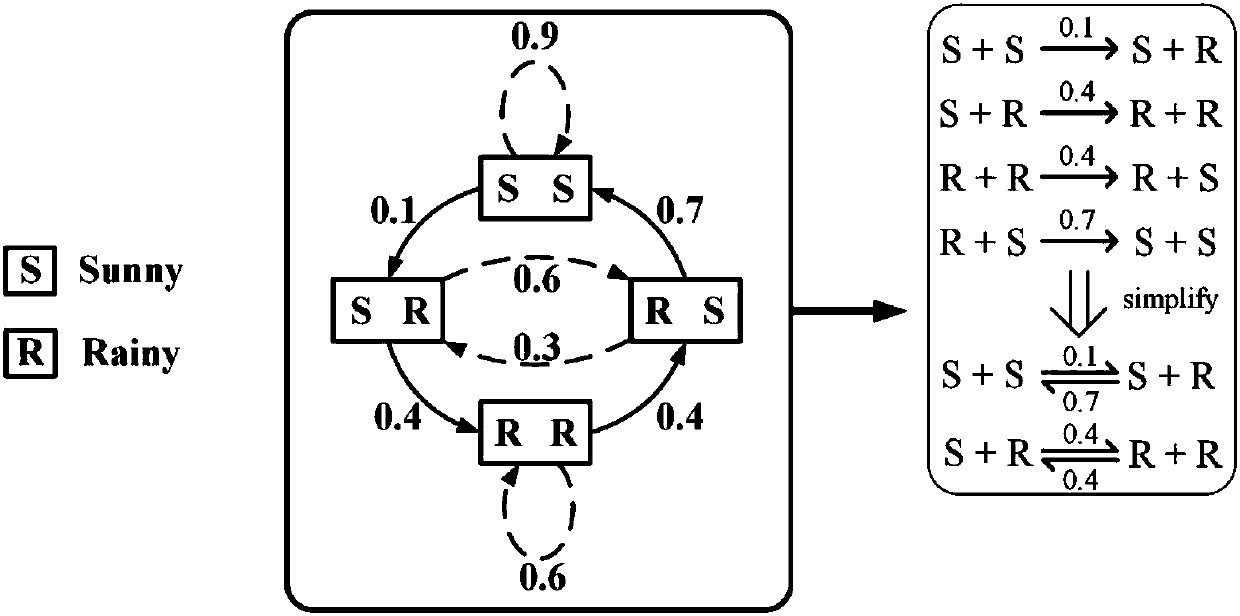
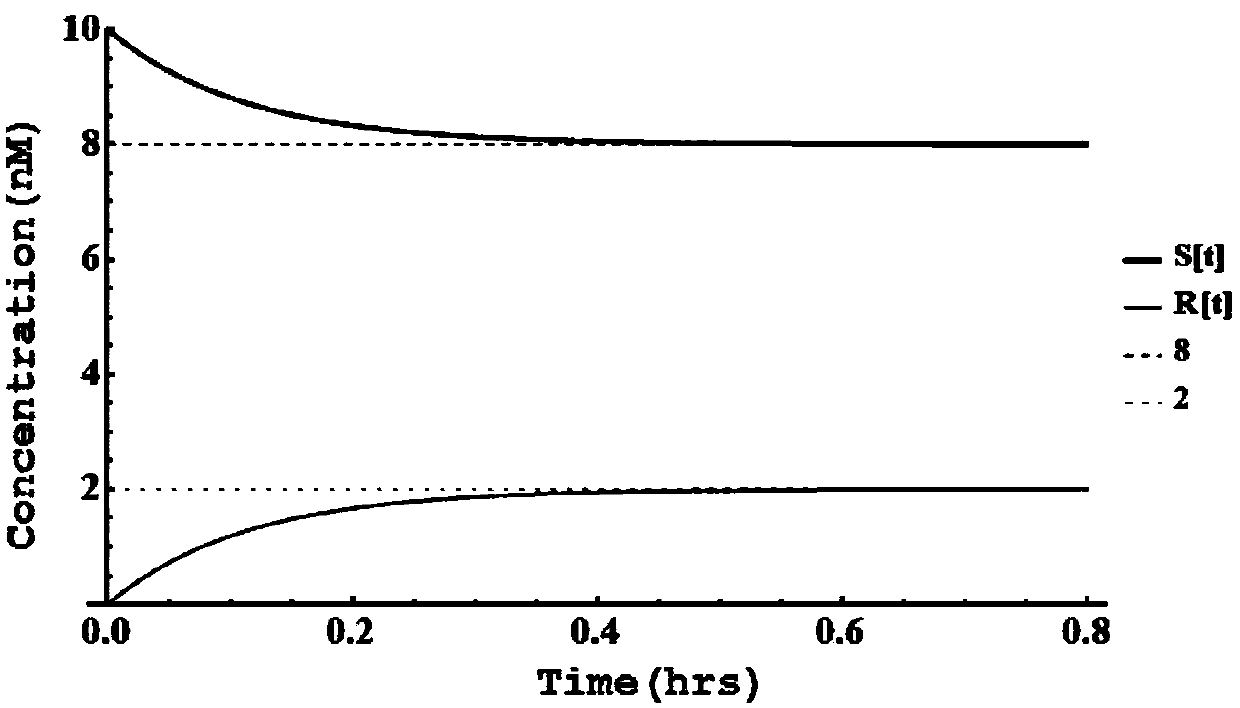
[0022] S1: Design a chemical reaction network, use different reactant types to represent different states in the target second-order Markov chain, that is, the required reactant types are the same as the number of states in the target chain and correspond one-to-one. Set the initial concentration of the corresponding reactant according to the initial probability distribution of each state of the target second-order Markov chain, that is, the initial concentration is the same or proportional to the corresponding probability value.
[0023] S2: Use a bimolecular reaction to achieve each state transition of the target second-order...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com