Method for preventing spontaneous combustion of coal in upper and lower levels of goafs in contiguous coal seam groups
A coal seam group and short-distance technology, applied in dust prevention, mining equipment, earthwork drilling and mining, etc., can solve problems such as large amount of engineering, poor effect, and reduction of oxygen depth in goafs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
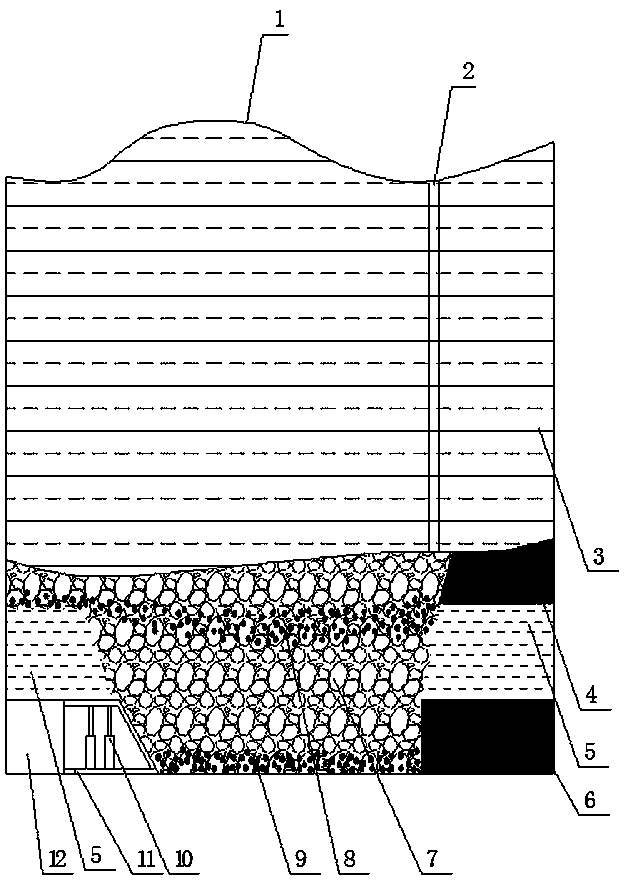
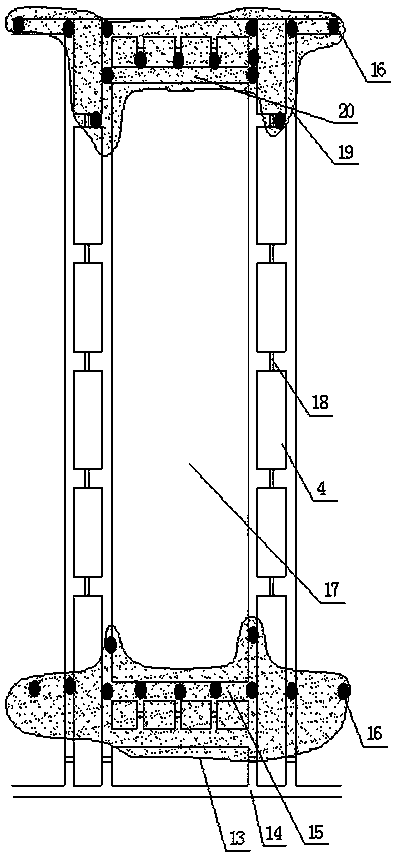
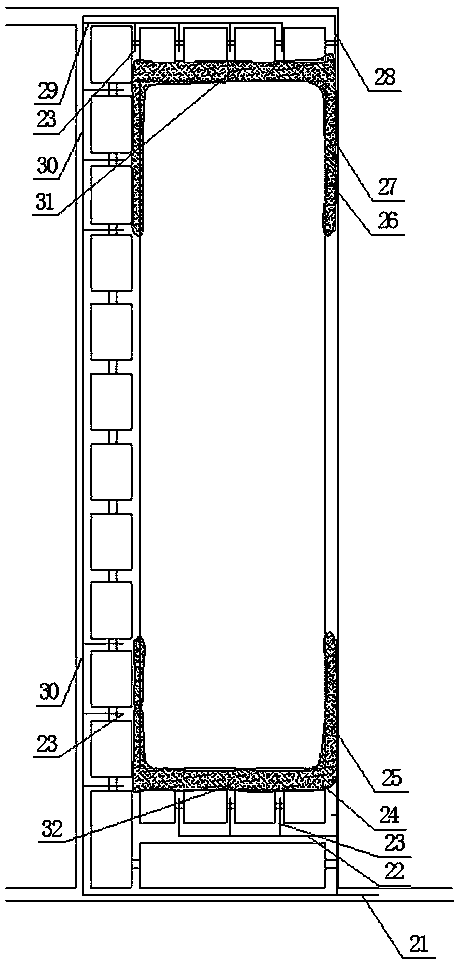
[0016] Take a mine in the west of my country as an example to prevent spontaneous combustion of coal in the goaf of the upper and lower coal seams by using the joint grouting of the upper and lower shafts when mining near-distance coal seams. The coal seam being mined in this mine is the No. 9 coal seam (9106 working face), the upper layer is the 4107 goaf, and the average distance between the No. 4 coal seam and the No. 9 coal seam is about 45m. The burial depth of the No. 4 coal seam is 68-125m, the average thickness of the coal seam is 6.5m, and the thickness of the remaining top coal reaches 2.2m, which is left in the goaf in a broken state. The mining of No. 4 coal began in 1998 and ended in 2005. There are 8 fully-mechanized mining faces in the mining area, all of which are arranged along the inclination of the coal seam. Both No. 4 coal and No. 9 coal belong to spontaneous combustion coal seams, and the spontaneous combustion period is 3 months.
[0017] No. 4 coal sea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com