Autonomous positioning and node map constructing method for underwater robot
An underwater robot and autonomous positioning technology, applied in the direction of height or depth control, can solve the problems of inability to obtain angle relationship, inability to determine random node position, infeasibility, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
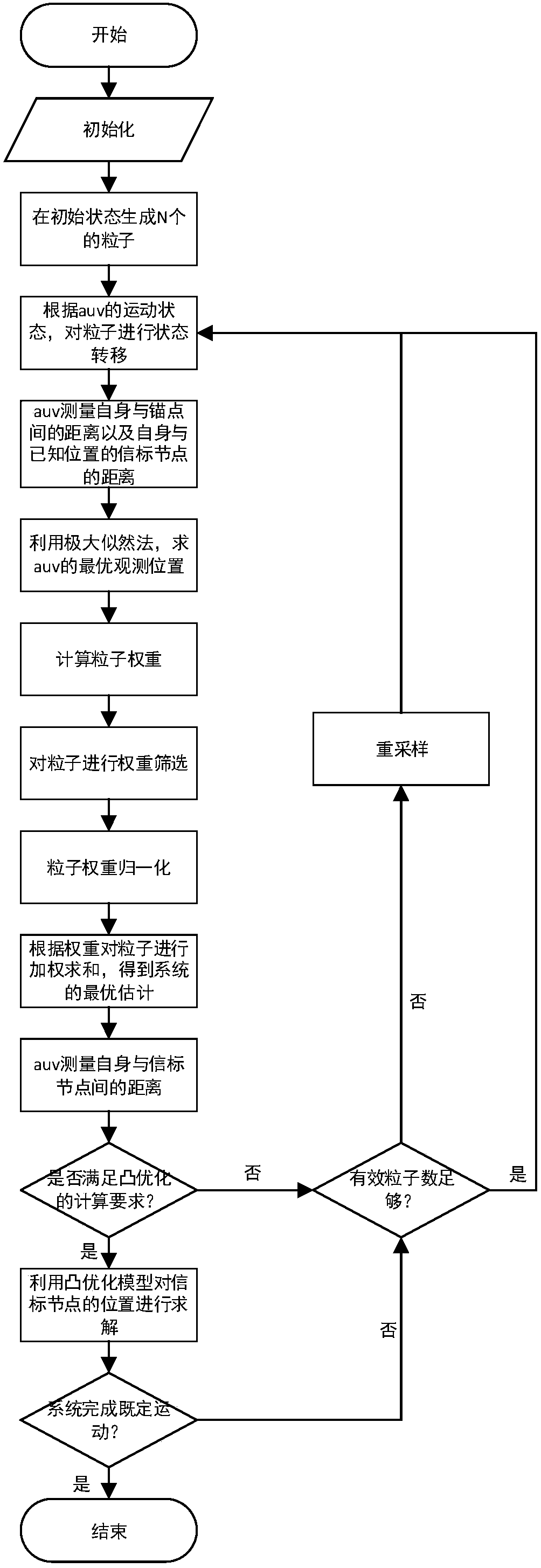
[0069] In the following, an example of randomly distributing a node network composed of several unknown nodes in the sea area, using AUV to construct a node map and at the same time autonomously positioning the AUV to illustrate the method of the present invention.
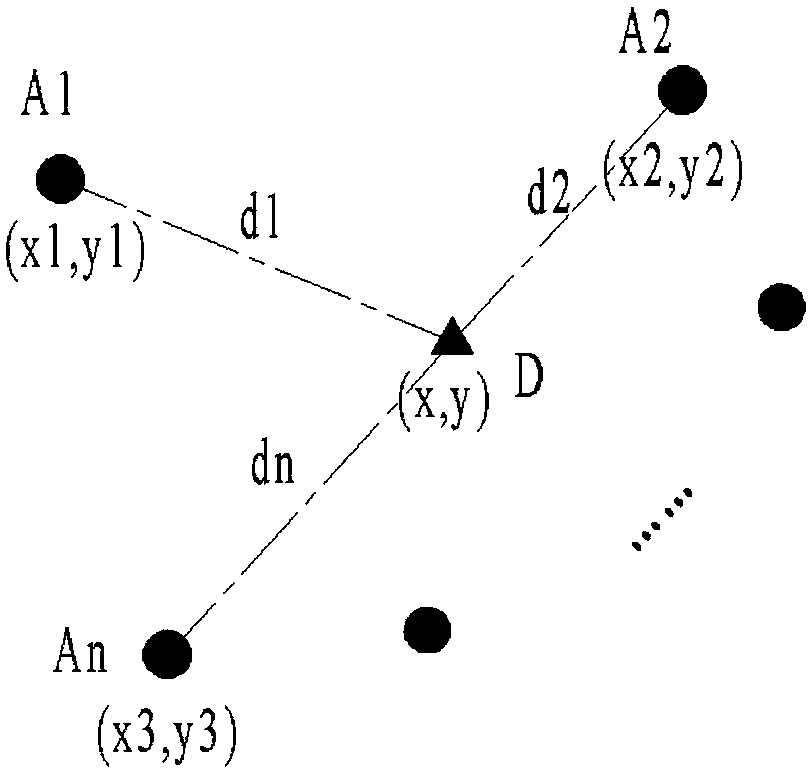
[0070] (1) In the initial position of the AUV, 4 nodes with known positions are arranged artificially, and the 4 nodes are arranged in a square (see figure 2 ). The AUV uses these 4 nodes to solve the observation position of the AUV in the initial stage by using the maximum likelihood method. 200 particles are generated at the initial stage, and the positions of all particles are the same as the observation positions in the initial stage of the AUV.
[0071] Since formulas (1-1) ~ (1-7) give general calculation forms, the specific calculation forms are related to the probability distribution of their design and AUV movement. The following examples illustrate the specific meanings of variables, functions and probabili...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com