Modal MRF (Markov Random Field) based underwater forward-looking sonar image segmentation method
A forward-looking sonar, image segmentation technology, applied in image analysis, image enhancement, image data processing and other directions, can solve problems such as over-smoothing, loss of contour information, limited patch noise processing by MRF model, and achieve fast convergence, good The effect of the split effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0046] Such as Figure 9 As shown, a forward-looking sonar image segmentation method based on modal Markov random field includes the following steps:
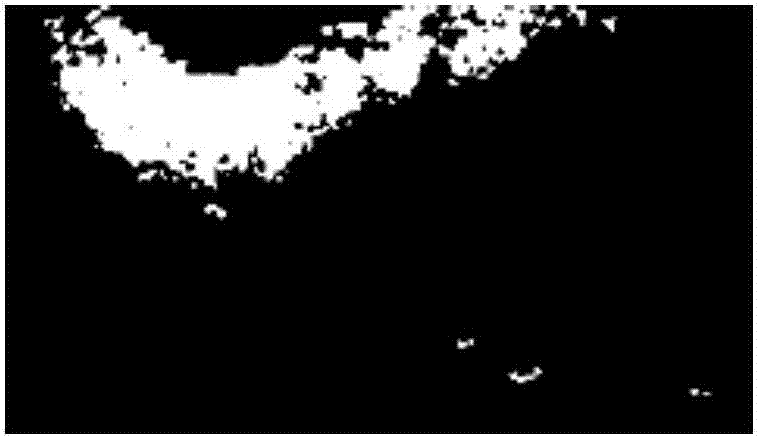
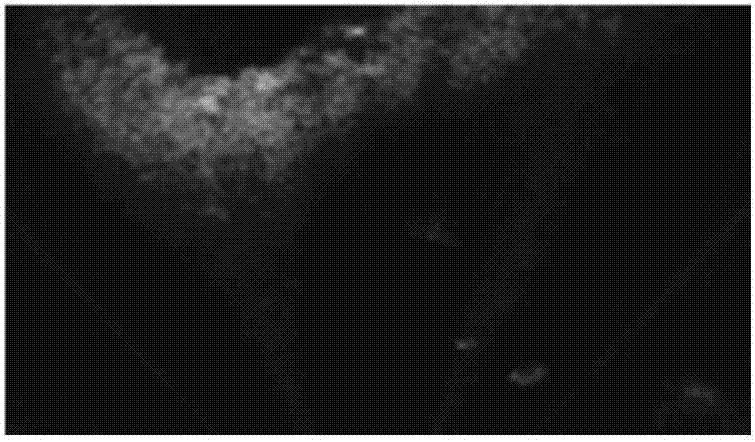
[0047] Algorithm input: Forward-looking sonar image X={x i} i=1,...,H×W (Such as figure 1 shown), where x i Indicates the gray value of the i-th pixel, H and W are the height and width of the image, respectively.
[0048] Algorithm output: category matrix L={l i} i=1,...,H×W ; l i Indicates the category of the i-th pixel.
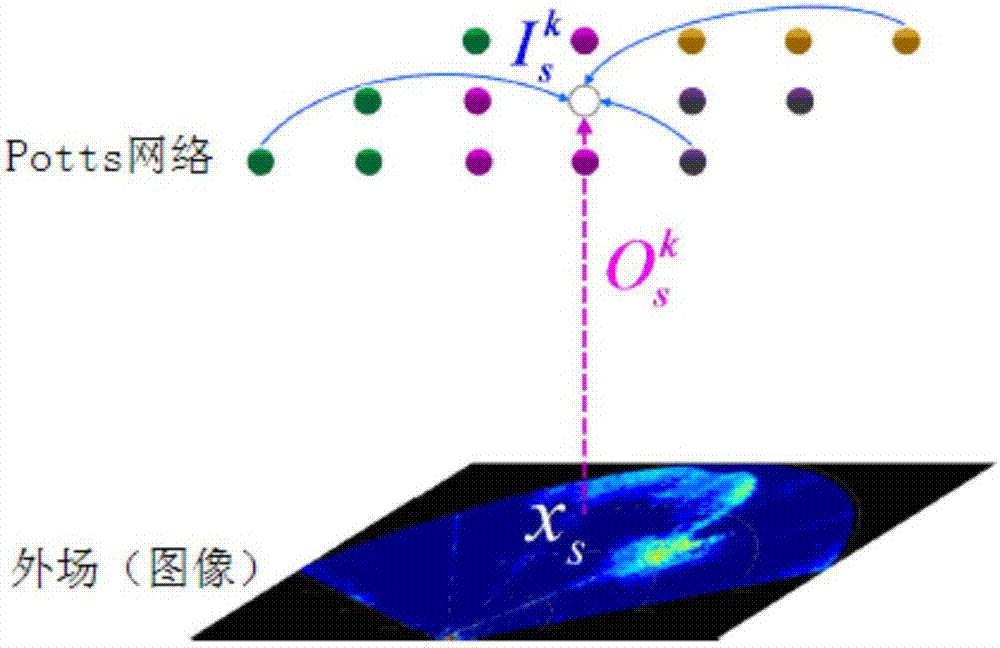
[0049] Step 1: Set the state number Q of the Potts unit, and use the variable q to represent any state, that is, q=1,...,Q. For forward looking sonar images, Q is generally set to 2 or 3.
[0050] Step 2: Potts network initialization. The fuzzy C-Means (FCM) algorithm is used to cluster the sonar images, and the number of clusters is the state number of the Potts unit. The resu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com