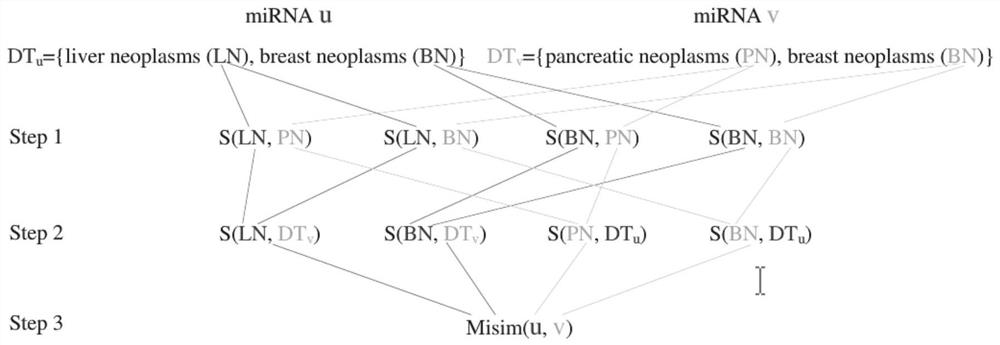
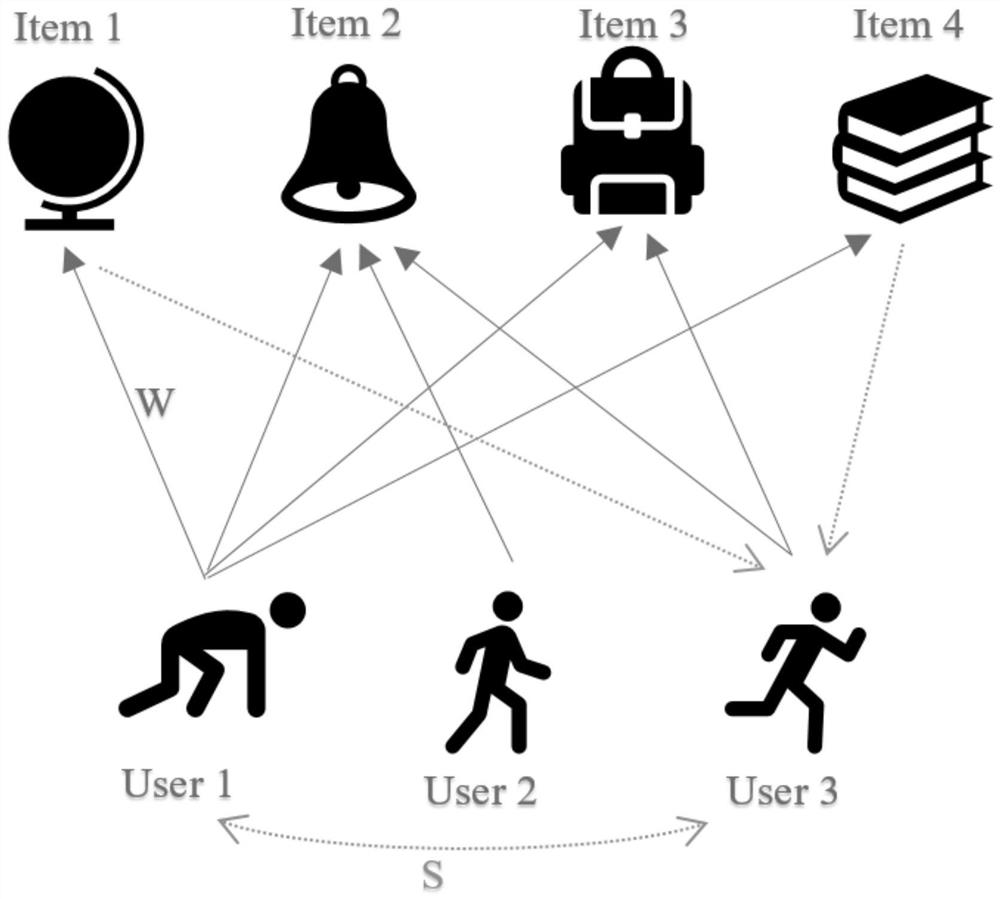
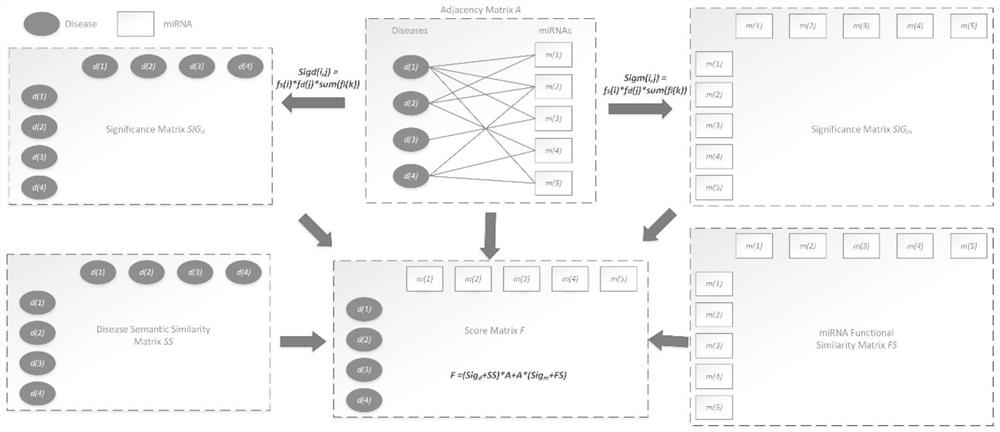
An improved method for predicting miRNA-disease associations based on collaborative filtering
A collaborative filtering and prediction method technology, applied in the field of human life medical engineering, can solve the problem that the parameter K is not easy to choose, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] (1) Database analysis:
[0102] We performed global LOOCV, local LOOCV and FFCV with HMDD database to evaluate ICFMDA. To evaluate the performance of ICFMDA, we use five state-of-the-art methods for comparison. They are HGIMDA, RLSMDA, HDMP, WBSMDA and RWRMDA. In LOOCV, each known miRNA-disease association is in turn picked as a test sample, while others are used as training samples. All untested associations were used as candidate samples. In local LOOCV, test samples are ranked among candidate samples of the disease to which they belong, while in global LOOCV, all candidate samples are ranked. The prediction is considered true if the ranking of the test sample is not lower than the given threshold. If the ranking of a candidate sample is not lower than a given threshold, the prediction is considered a false positive. After prediction of all known associations in LOOCV or FFCV, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted by calculating true positiv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com