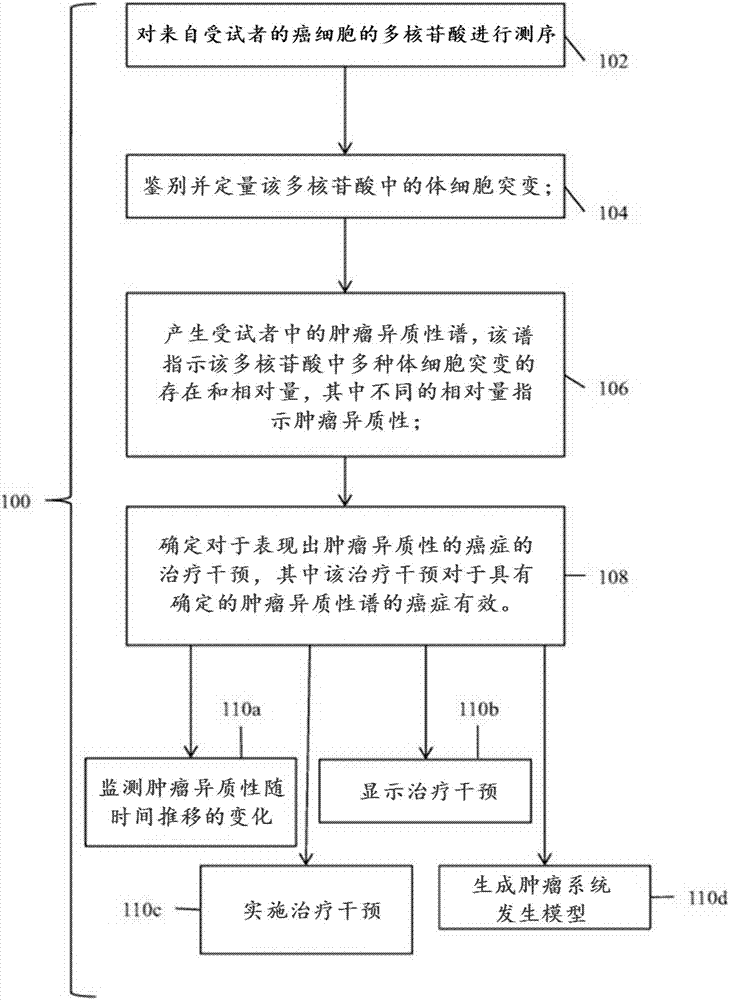
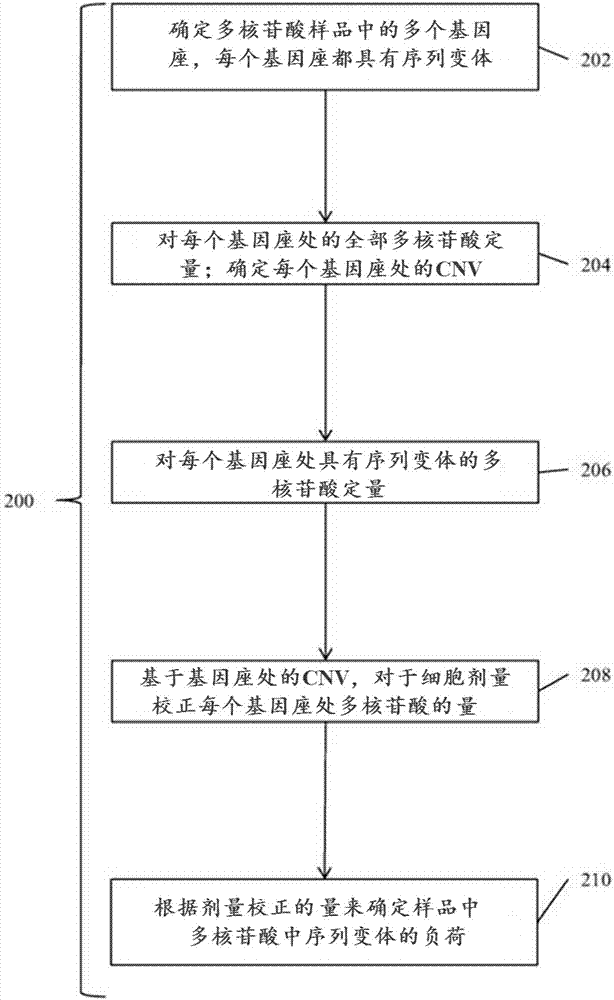
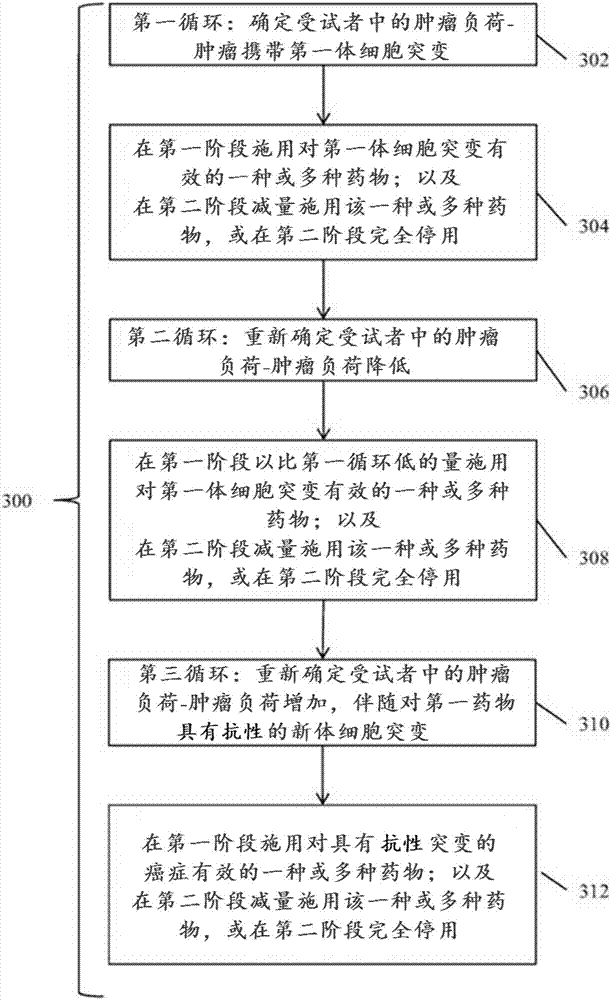
Detection and treatment of disease exhibiting disease cell heterogeneity and systems and methods for communicating test results
A diseased cell and heterogeneity technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological determination/testing, sequence analysis, etc., can solve problems such as reducing the quality of care for cancer patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0239] Example 1. Copy number variation detection method
[0240] blood collection
[0241] A 10-30 mL blood sample was collected at room temperature. Samples were centrifuged to remove cells. Plasma was collected after centrifugation.
[0242] cfDNA extraction
[0243] Samples were digested with proteinase K. Precipitate DNA with isopropanol. DNA was captured on a DNA purification column (eg, QIAamp DNABlood Mini Kit) and eluted in 100 μl of the solution. DNA below 500bp was selected by Ampure SPRI magnetic bead capture (PEG / salt). The resulting product was suspended in 30 μl HO 2O middle. The size distribution was examined (major peak = 166 nucleotides; minor peak = 330 nucleotides) and quantified. 5 ng of extracted DNA contained approximately 1700 haploid genome equivalents ("HGE"). The general relationship between the amount of DNA and HGE is as follows: 3 pg DNA = 1 HGE; 3 ng DNA = 1K HGE; 3 μg DNA = 1 M HGE; 10 pg DNA = 3HE; 10 ng DNA = 3K HGE;
[0244] ...
Embodiment 2
[0256] Example 2. Method of Correcting Base Calls by Determining the Total Number of Undiscovered Molecules in a Sample
[0257] After the fragments are amplified and the sequences of the amplified fragments are read and compared, the fragments are base called. Variation in the number of amplified fragments and undiscovered amplified fragments may introduce errors in base calling. These variations were corrected for by counting the number of amplified fragments not found.
[0258] When performing base calling on locus A (arbitrary locus), it is first assumed that there are N amplified fragments. Sequence reads may come from two types of fragments: double-stranded fragments and single-stranded fragments. The following is a theoretical example of calculating the total number of molecules not found in a sample.
[0259] N is the total number of molecules in the sample.
[0260] Assume that the number of duplexes detected is 1000.
[0261] Assume that the number of detected...
Embodiment 3
[0283] Example 3. Identification of genetic variants among cancer-associated somatic variants in patients
[0284] The assay is used to analyze a panel of genes to identify genetic variants in cancer-associated somatic variants with high sensitivity.
[0285] Cell-free DNA is extracted from the patient's plasma and amplified by PCR. Genetic variants are analyzed by massively parallel sequencing of amplified target genes. For a panel of genes, all exons were sequenced, as such sequencing coverage has been shown to have clinical utility (Table 3). For another set of genes, sequencing coverage included those exons with previously reported somatic mutations (Table 4). The smallest detectable mutant allele (limit of detection) depends on the patient's sample cell-free DNA concentration, which varies from less than 10 to more than 1,000 genome equivalents per mL of peripheral blood. In samples with lower amounts of cell-free DNA and / or low levels of gene copy amplification, amp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com