Sequence image's automatic splicing method based on three-dimension reconstruction
An automatic stitching and sequence image technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of light-weight algorithms that are heavy and cannot handle sequence image distortion well, and achieve the elimination of homography distortion, improvement of automatic stitching quality, and elimination of mirror distortion Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
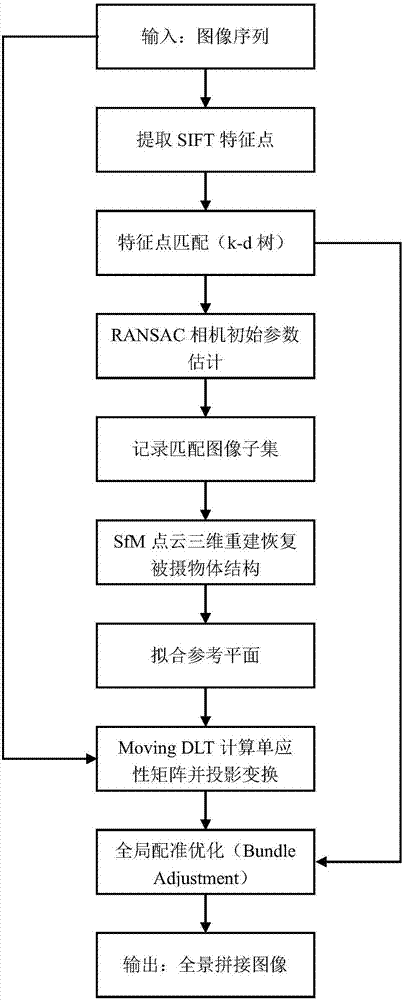
[0050] The purpose of the present invention is to propose a method for automatically mosaicing sequential images based on three-dimensional reconstruction. The method extracts SIFT feature points respectively and establishes a k-d tree for n disordered image sequences, and selects m candidate matching images for each image. , use the RANSAC algorithm to calculate the most likely photographic geometric constraints between the candidate images and form a correct matching image set, and use the SfM algorithm for 3D reconstruction to obtain the best fitting reference plane. Using the Moving DLT method to remove the homography distortion of the input image, and finally using the Bundle Adjustment method to solve the similarity transformation matrix of each image, and finally based on the Multi-band blending algorithm, the automatic stitching of panoramic images is realized.
[0051] A method for automatically mosaicing sequential images based on three-dimensional reconstruction, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com