Preparation method and application of a fluorescent chemical sensing material based on coumarin derivatives
A coumarin derivative and fluorescent sensing technology, applied in the field of chemical fluorescent sensing materials, can solve the problems of poor water solubility and unsatisfactory detection limit, achieve low detection limit, sensitive and selective recognition performance, and avoid secondary pollution Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: Preparation of fluorescent chemical sensing materials based on coumarin derivatives
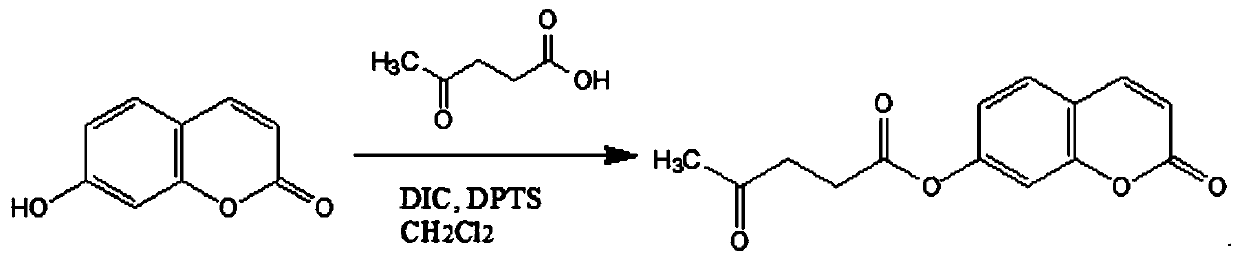
[0033] First weigh 1.276g of levulinic acid and 0.882g of N,N-diisopropylcarbodiimide (DPTS) into a beaker, then add 10mL of dichloromethane to dissolve and stir to obtain a suspended solid N,N-diisopropylcarbodiimide (DPTS) urea. Filter to obtain the filtrate. Weigh 810 mg of 7-hydroxycoumarin and 540 mg of 4-methylaminopyridine (DIC) into a three-necked flask, and add 10 mL of dichloromethane to dissolve. The filtrate was poured into a three-necked flask, washed with 10 mL of dichloromethane, and the washing solution was poured into a three-necked flask at 40°C to reflux. After heating for 4 h, it was cooled to room temperature, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure to obtain a yellow solid.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Preparation of coumarin-based fluorescent chemical sensing materials
[0035]First weigh 1.508g of levulinic acid and 1.0g of N,N-diisopropylcarbodiimide (DPTS) into a beaker, then add 30mL of dichloromethane to dissolve and stir to obtain a suspended solid N,N-diisopropylcarbodiimide (DPTS) carbourea. Filter to obtain the filtrate. Weigh 1134mg of 7-hydroxycoumarin and 756mg of 4-methylaminopyridine (DIC) into a three-necked flask, and add 30mL of dichloromethane to dissolve. The filtrate was poured into a three-necked flask, washed with 30 mL of dichloromethane, and the washing liquid was poured into a three-necked flask to reflux at 60°C. After heating for 6 h, it was cooled to room temperature, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure to obtain a yellow solid.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3: Preparation of coumarin-based fluorescent chemical sensing materials
[0037] First weigh 1.392g of levulinic acid and 1.134g of N,N-diisopropylcarbodiimide (DPTS) into a beaker, then add 20mL of dichloromethane to dissolve and stir to obtain a suspended solid N,N-diisopropyl carbodiimide (DPTS) carbourea. Filter to obtain the filtrate. Weigh 973 mg of 7-hydroxycoumarin and 648 mg of 4-methylaminopyridine (DIC) into a three-necked flask, and add 20 mL of dichloromethane to dissolve. The filtrate was poured into a three-necked flask, washed with 20 mL of dichloromethane, and the washing solution was poured into a three-necked flask at 50° C. to reflux. After heating for 5 h, it was cooled to room temperature, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure to obtain a yellow solid.
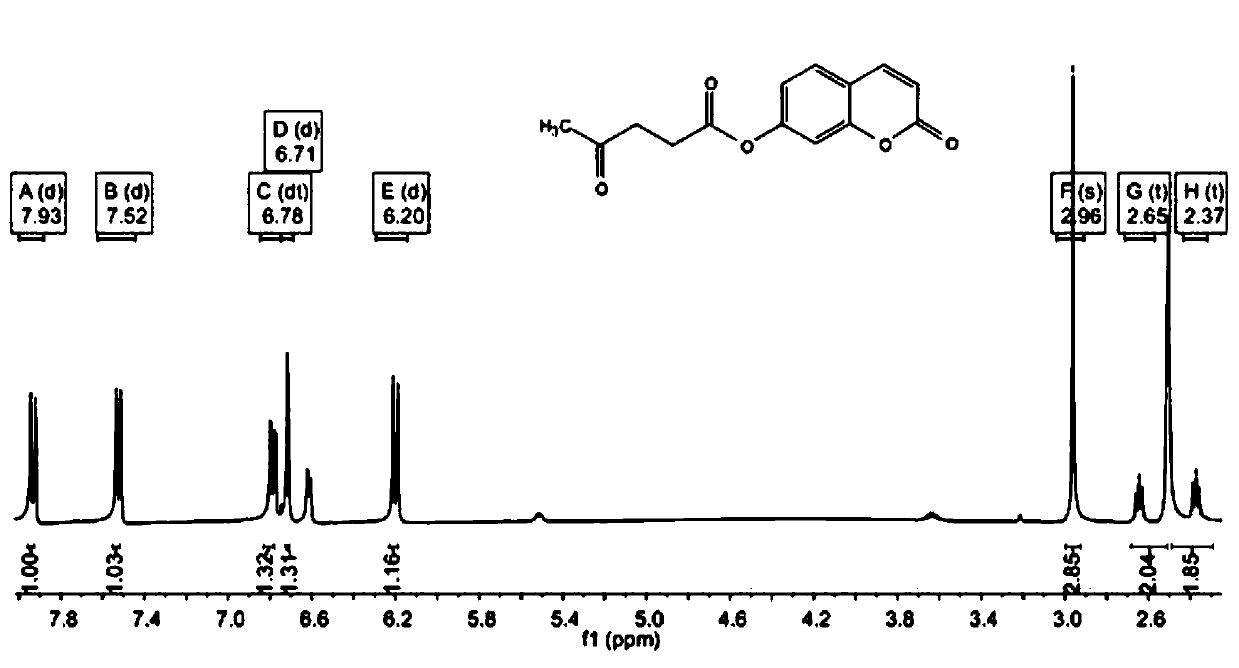
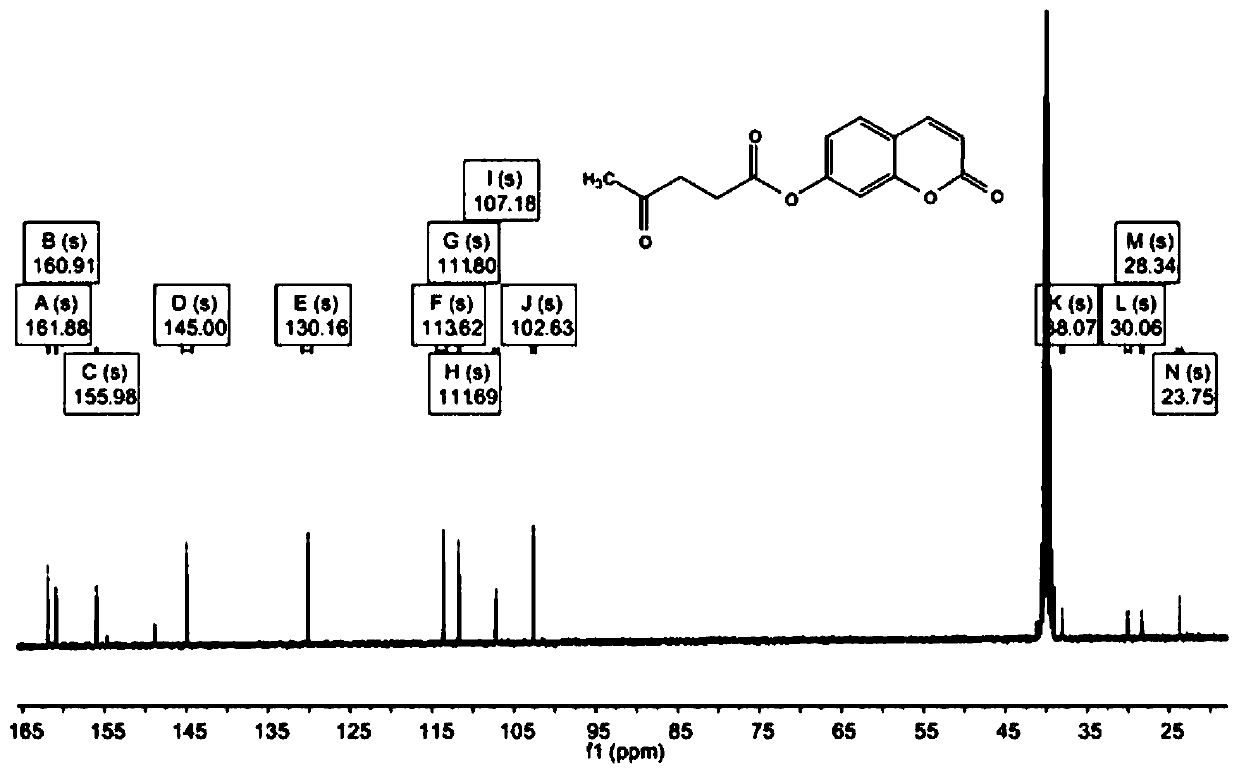
[0038] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of the synthesis process of fluorescent sensing materials based on coumarin derivatives.
[0039...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com