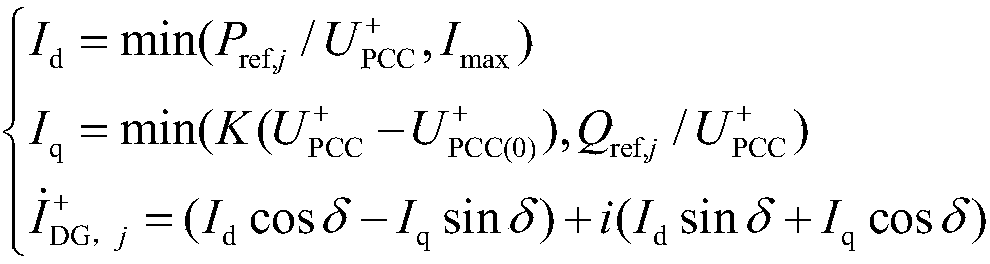A Fault Location Method for Distributed Power Distribution Network Containing Multiple T-Connection Inverters
An inverter-type distributed and distributed power supply technology, which is applied in the fault location and detection of faults according to conductor types, etc., can solve the problem that the voltage of the grid connection point cannot be easily obtained, the fault current distribution is difficult to solve, and the fault location method of the distribution network is no longer available. Application, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
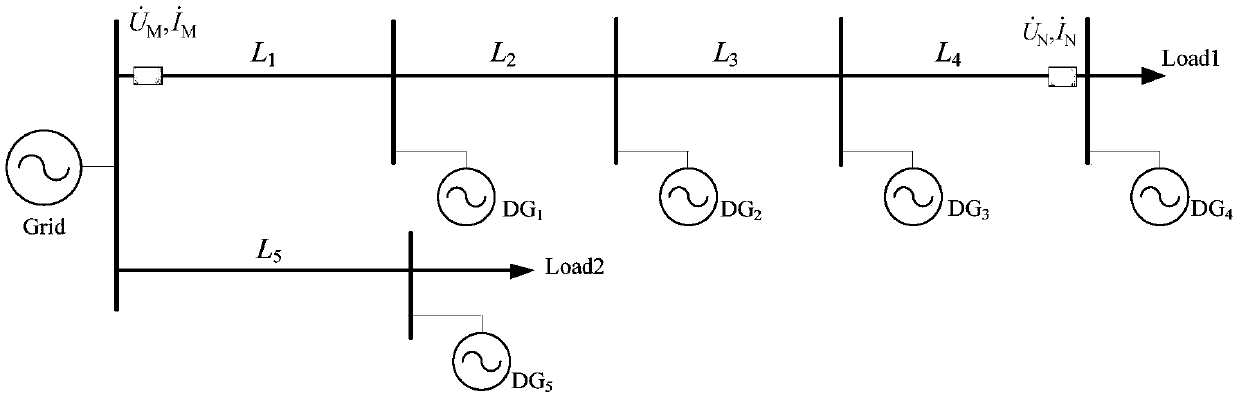
[0060] This embodiment takes figure 1 Take the 10kV neutral point ungrounded simple distribution network as an example, the system reference capacity is 500MVA, the reference voltage is 10.5kV, and the system impedance value is x s = 0.126Ω. The lines are all overhead lines, and their line parameters are x 1 = 0.347Ω / km, r 1 = 0.27Ω / km. Feeder 1 has 4 inverter-type distributed power sources connected, and the feeder is divided into 4 sections, the length of each section is 0.8km, 1km, 2km, 3km; feeder 2 has only one inverter-type distributed power supply connected , whose length is 4 km. The capacities of IIDG1~IIDG5 are 2MW, 2MW, 1MW, 1.5MW and 1.2MW respectively, and the output of each IIDG during normal operation is 1.8MW, 1.5MW, 1MW, 1.5MW and 1.2MW respectively. Load 1 is 7MW, load 2 is 4MW, and the power factor is 0.9.
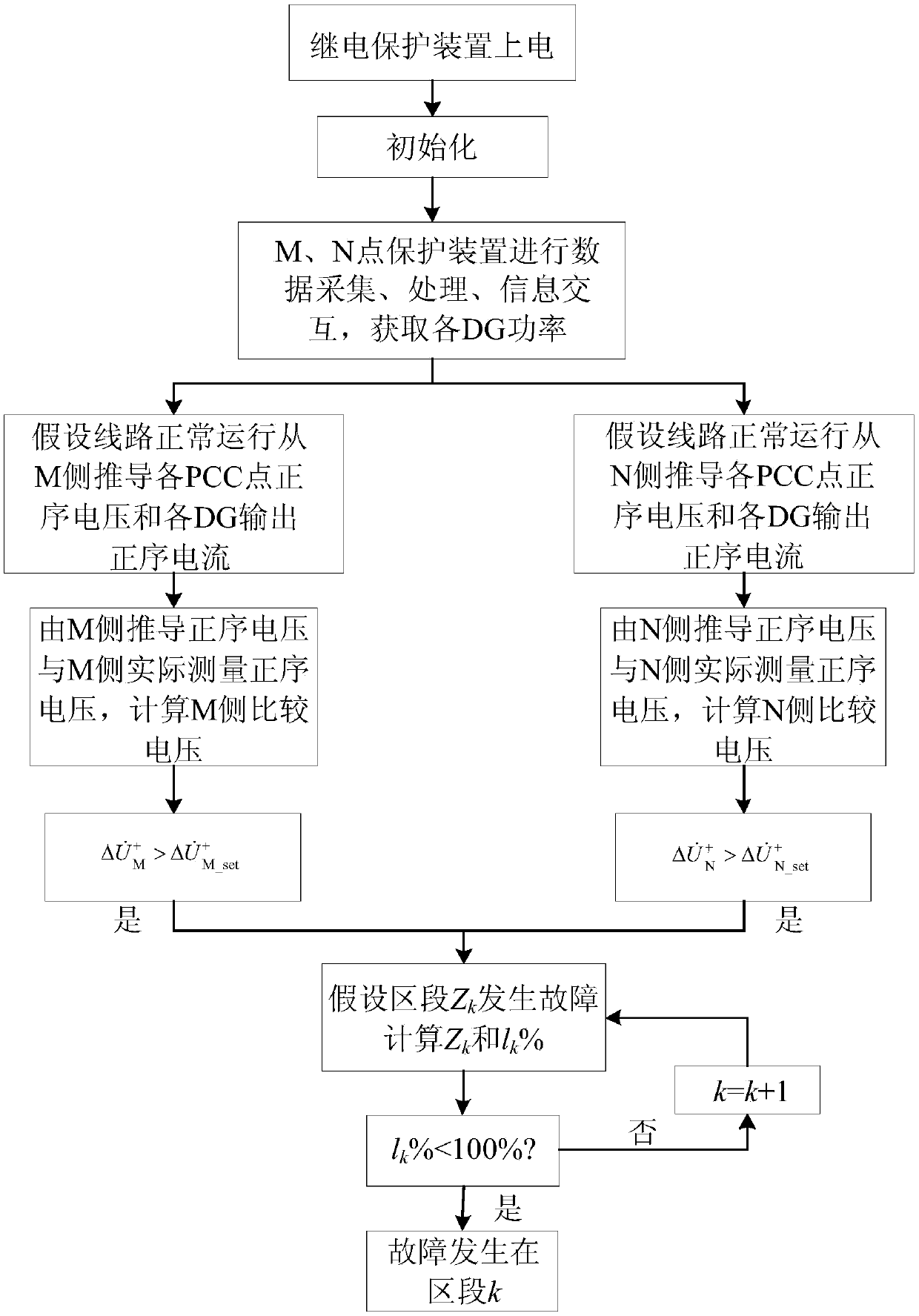
[0061] Using PSCAD / EMTDC simulation software to simulate and analyze the system, in the feeder internal fault criterion, k rel is 1.2, and ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com