DCE and LSS-based infrared image and visible image registration method
An infrared image and image registration technology, applied in image enhancement, image analysis, image data processing and other directions, can solve the problems of blurred target boundary, large amount of calculation, and difficult to accurately segment, achieve dynamic control of evolution degree and reduce the number of iterations , the effect of reducing complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific preferred embodiments, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited thereby.
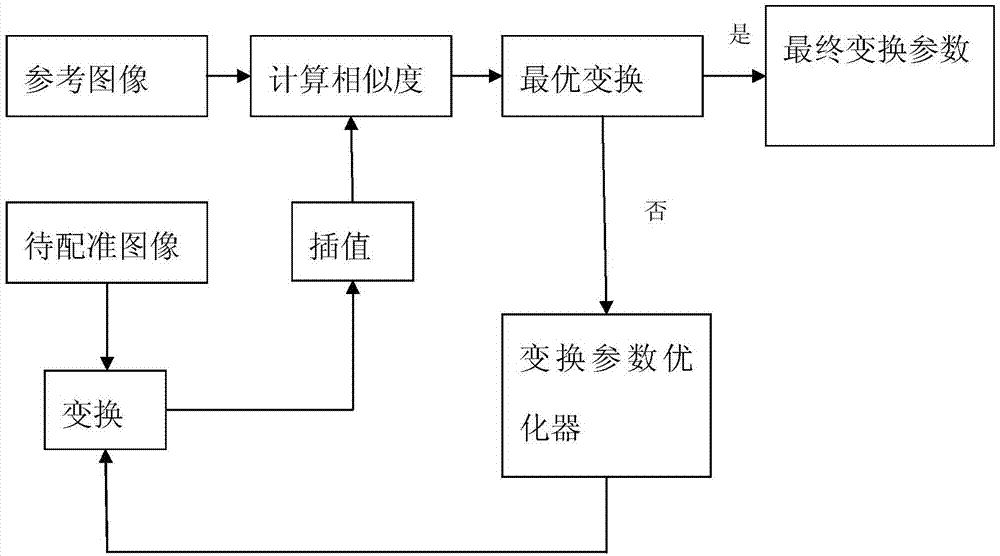
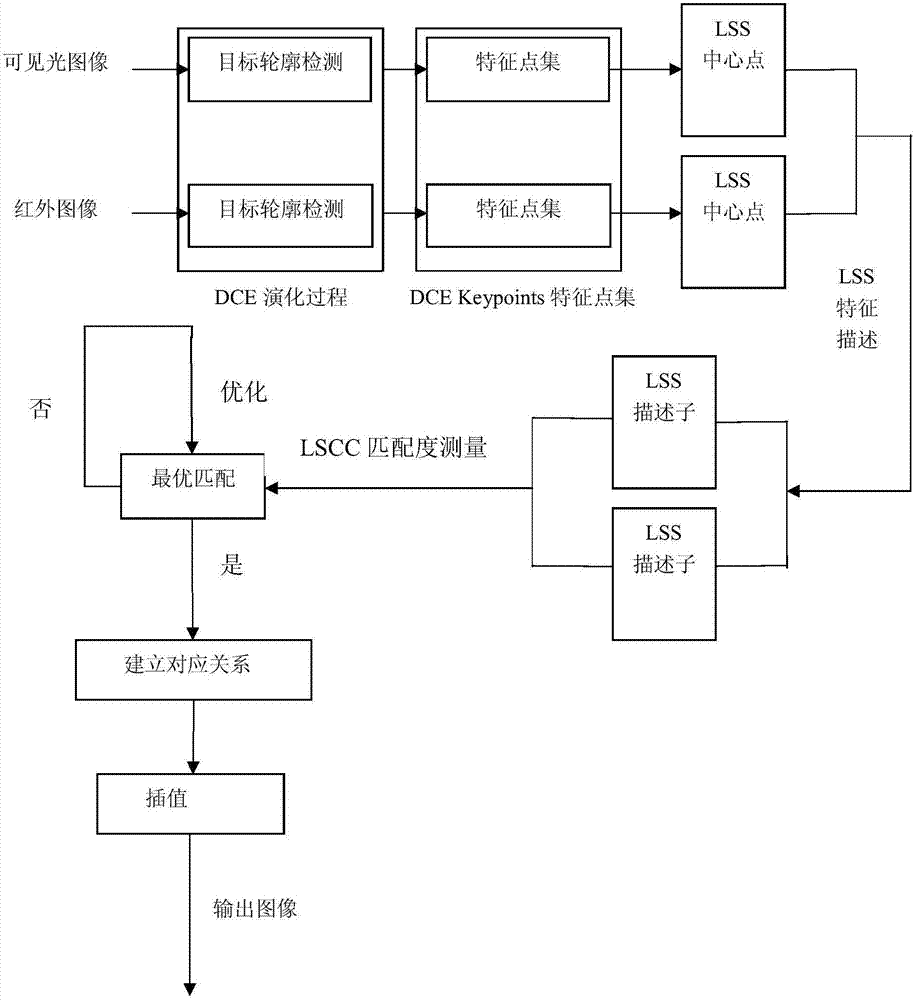
[0054] Such as figure 2 As shown, this embodiment is based on DCE and LSS infrared image and visible light image registration method, the steps include:
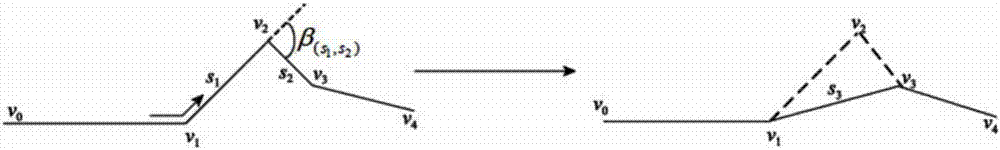
[0055] S1. DCE feature point extraction: use DCE to detect the target contours of the infrared image and the visible light image to be registered respectively, and extract each DCE feature point corresponding to the vertex in the target contour, and obtain the corresponding infrared image and visible light image respectively to be registered. DCE feature point set;
[0056] S2. LSS feature description: use the LSS method to describe each DCE feature point in each DCE feature point set;
[0057] S3. Similarity measurement: According to the description result of step S2, calculate the matching degree between ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com