Label anti-collision algorithm based on RFID
An anti-collision algorithm and label technology, applied in the field of radio frequency identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
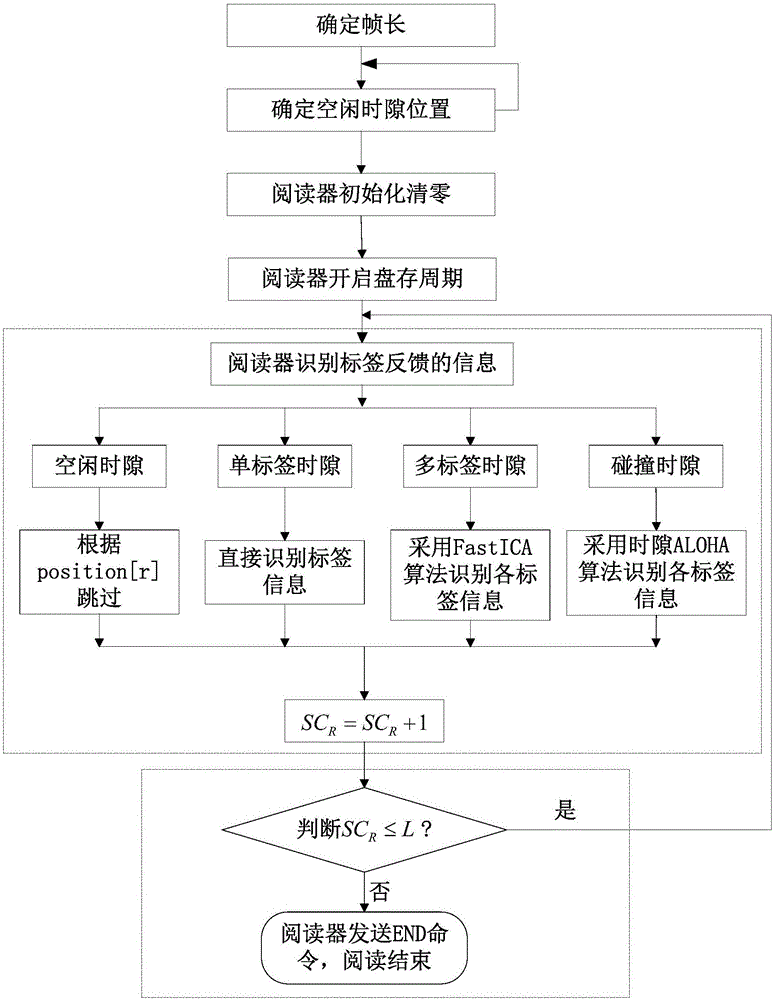
[0046] like figure 1 As shown, an RFID-based label anti-collision algorithm includes the following steps in the sequence:
[0047] (1) Determine the frame length L: Among them, n is the total number of tags within the readable range of the reader, M is the number of antennas of the reader, α=10, β=0.8, γ=0.66, α, β, γ are fitting parameters, round( ) means rounding Rounding;
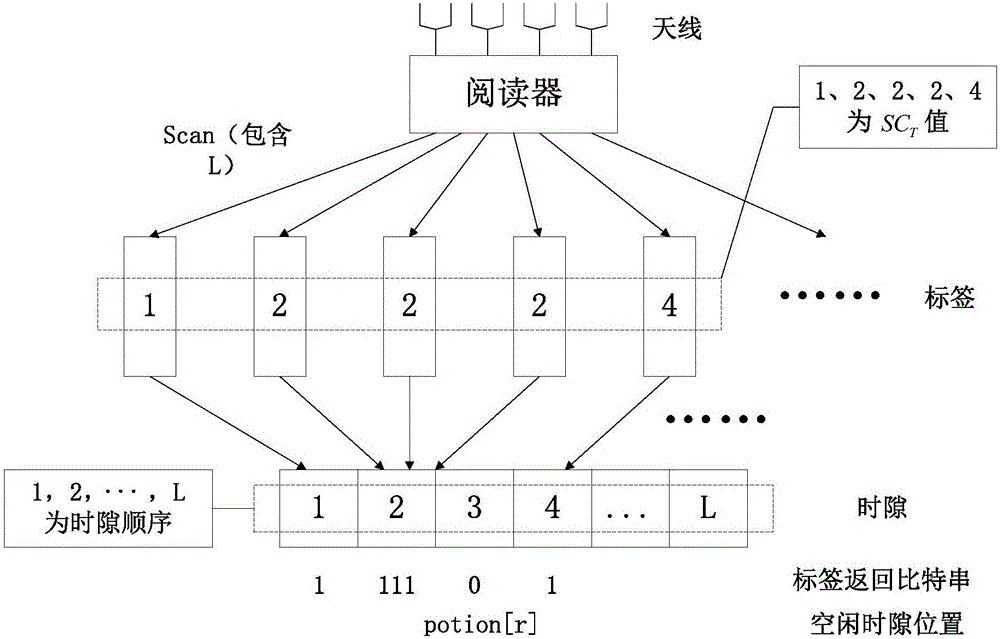
[0048] (2) Determine the position of the idle time slot: The reader sends a scan command Scan containing frame length L information to the tag group within the identifiable range, opens the time slot preview inventory, and determines the idle time according to the 1-bit information fed back by the tag to the reader. position of the gap;
[0049] (3) The reader is initialized and cleared: the value of the time slot counter of the reader is SC R Cleared, SC represents the time slot counter, and the subscript R represents that the attribute belongs to the reader;
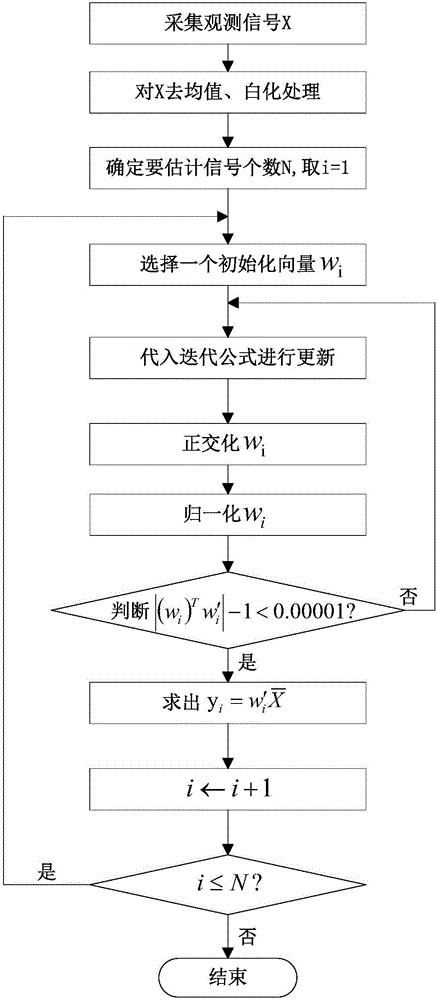
[0050] (4) The reader starts the inv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com