A process for preparing ethylene cracking material by hydrogenation of dry gas
A technology for ethylene cracking and hydrogen production, which is used in the processing of gas mixtures, the petroleum industry, and the treatment of hydrocarbon oil. , to avoid the effect of concentrated release
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
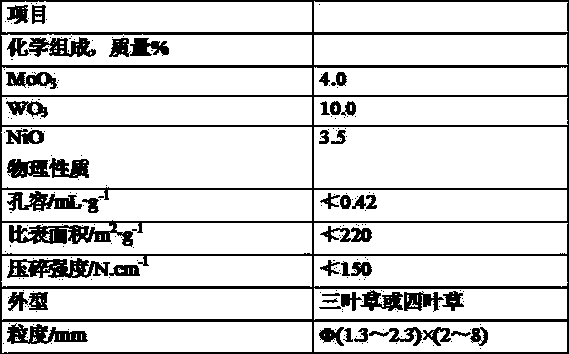
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
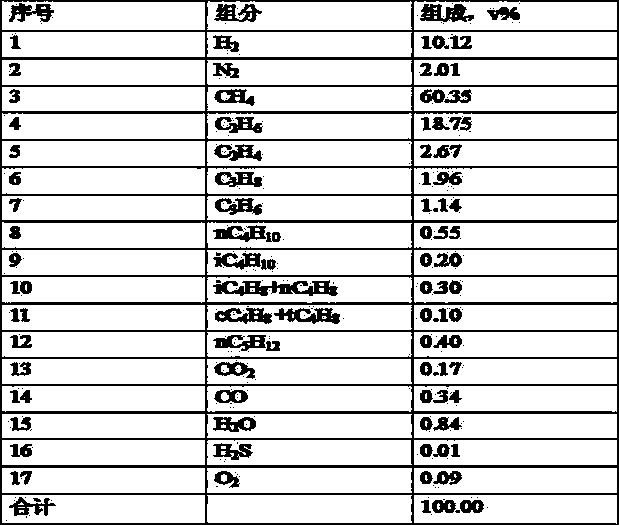
[0047] A fixed-bed reactor was used for the reaction, and the materials were fed from above. The catalysts listed in Table 3 were used. The raw material gas for hydrogenation was coking dry gas, and the composition was shown in Table 2. In addition to the coking dry gas, the reaction feed also includes refined naphtha, which is fed in parallel with the coking dry gas. The main properties of refined naphtha are shown in Table 5. The reaction conditions and results are shown in Table 6.
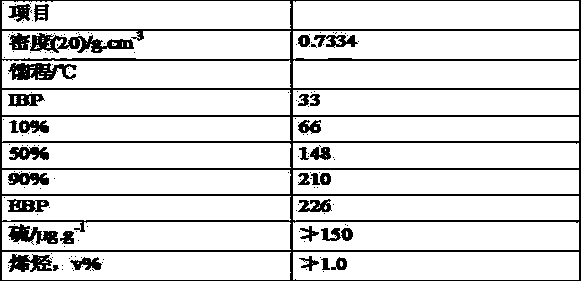
[0048] Table 5 Main properties of refined naphtha
[0049]
[0050] Table 6 Operating conditions and results of hydrogenation reactor
[0051]
[0052] 1-5*, is the temperature of different bed heights along the dry gas feeding direction.
[0053] From the reaction results in Table 6, it can be seen that after the introduction of refined naphtha, the reaction "temperature envelope" was greatly reduced, and the reaction temperature rise was reduced from the original 110°C to 66.7°C; but...
Embodiment 2
[0055] A fixed-bed reactor was used for the reaction, and the materials were fed from above. The catalysts listed in Table 3 were used. The raw material gas for hydrogenation was coking dry gas, and the composition was shown in Table 2. In addition to the coking dry gas, the reaction feed is also fed into the catalytic diesel, which is fed in parallel with the coking dry gas. The main properties of catalytic diesel are shown in Table 7. The reaction conditions and results are shown in Table 8.
[0056] Table 7 Main properties of catalytic diesel
[0057]
[0058] Table 8 Hydrogenation reactor operating conditions and results
[0059]
[0060] 1-5*, is the temperature of different bed heights along the dry gas feeding direction.
[0061] From the reaction results in Table 8, it can be seen that after the introduction of catalytic diesel oil, the "temperature envelope" of the reaction can also be greatly reduced, and the reaction temperature rise is reduced from the ori...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The reaction adopts a fixed-bed reactor with upper feed, and uses the catalysts listed in Table 3. The feed gas for hydrogenation is thermally cracked dry gas, and its composition is shown in Table 2. In addition to the thermal cracking dry gas, the reaction feed also feeds a piece of catalytic diesel oil, which is fed in parallel with the thermal cracking dry gas. The main properties of catalytic diesel are shown in Table 7. The reaction conditions and results are shown in Table 9.
[0064] Table 9 Operating conditions and results of hydrogenation reactor
[0065]
[0066] *: Since the total amount of olefins in the feed gas is 8.83v%, while the hydrogen content is only 7.781v%, so when hydrogenation reaction is carried out, hydrogen should be supplemented according to about 5% of the dry gas feed amount.
[0067] From the reaction results in Table 9, it can be seen that after the introduction of catalytic diesel oil, the reaction "temperature envelope" can also ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com