Use of microrna 146-a in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of picornavirus infection and microran 146-a antagonists
A technology of small RNA and virus infection, applied in the field of microRNA
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0114] Example 1 Targets of virus-induced miR-146a
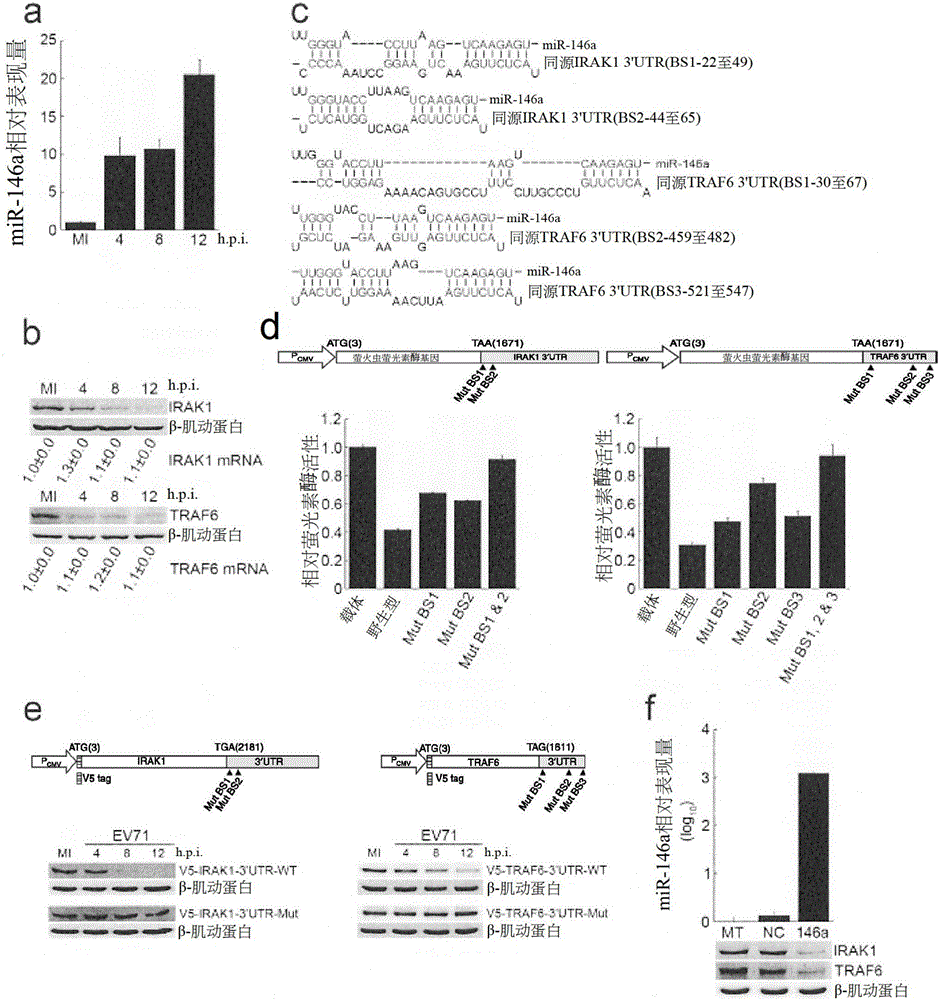
[0115] miR-146a (a microRNA induced by EV71) was selected for further investigation in this study due to its regulatory activity in TLR signaling and IFN production ( figure 1 a). In order to determine whether IRAK1 and TRAF6 are affected by EV71 infection, the expressions of IRAK1 and TRAF6 at different post-infection time points were first detected. Expression of both proteins, but not mRNA, was inhibited (figure 1 b). Taken together, these results show that miR-146a can be induced by EV71 infection and targets IRAK1 and TRAF6. However, the precise miR-146a binding sites of IRAK1 and TRAF6 have not been fully demonstrated, and the inhibitory activity of individual binding sites has not actually been assessed. Therefore, we further used PicTar (http: / / pictar.org / ) and RNA22 (http: / / cbcsrv.watson.ibm.com / rna22.html) to predict potential miR-146a binding sites within the 3′UTR of IRAK1 and TRAF6 point( figure 1 c). Subs...
example 2
[0116] Example 2 AP1 up-regulates the expression of miR-146a
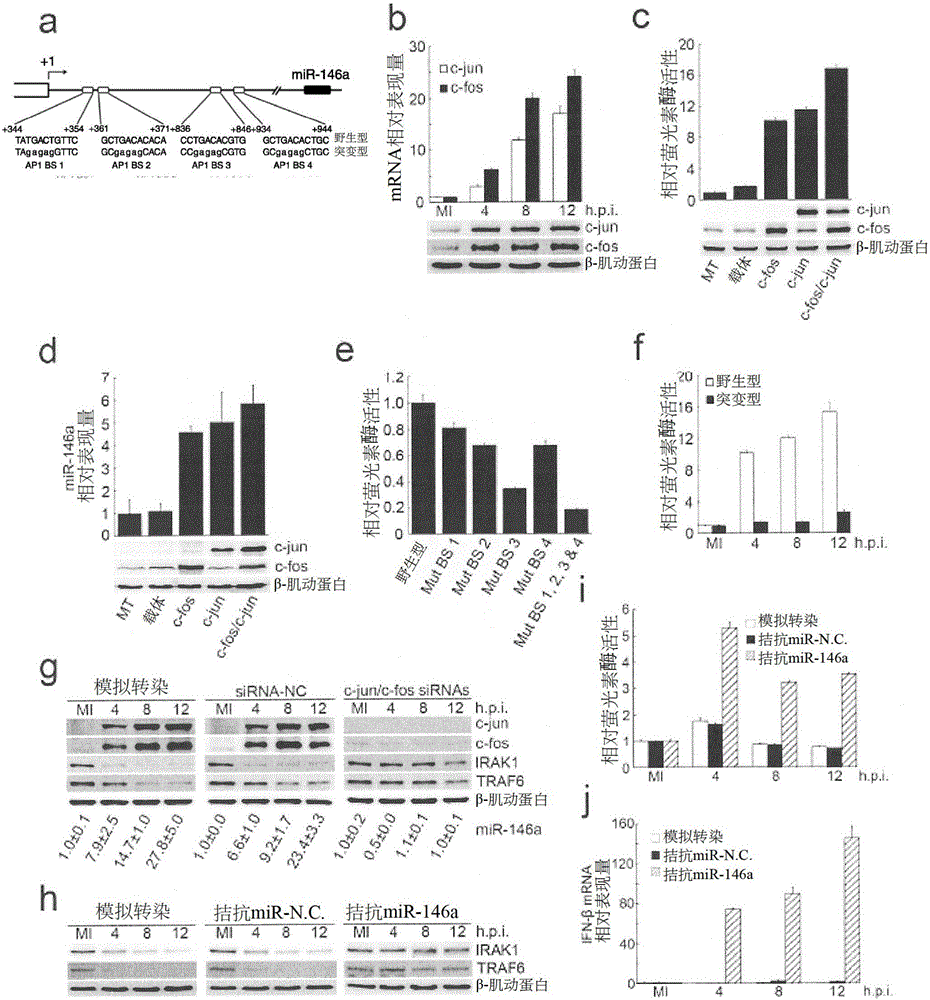
[0117] To determine which transcription factor is responsible for regulating virus-induced miR-146a, EV71-altered transcription factors analyzed by microarray were intersected with potential transcription factor binding sites within the miR-146a promoter region. AP1(c-jun / c-fos) was the only candidate identified in the crossover. Four potential AP1 binding sites were predicted within the miR-146a promoter region ( figure 2 a). The expression of AP1(c-jun / c-fos) was measured by real-time RT-PCR and western blotting, and the results showed that c-jun and c-fos were significantly increased in EV71 infection ( figure 2 b). The miR-146a promoter region was constructed in a luciferase reporter gene vector and analyzed in the presence of exogenously expressed c-jun and c-fos. The forced expression of c-jun, c-fos or both transcription factors can enhance the transcriptional activity of miR-146a promoter as well as t...
example 3
[0119] Example 3 miR-146a is important for EV71 pathogenesis in vivo
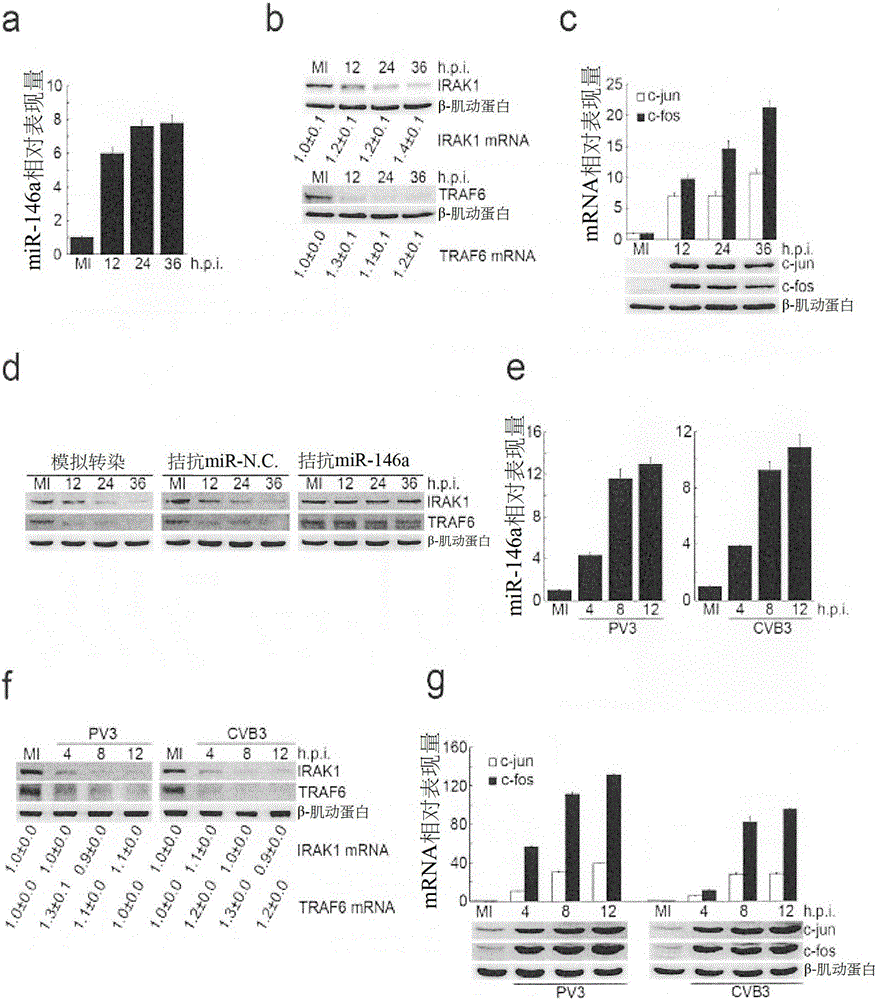
[0120] Since the Mus miR-146a sequence is consistent with the homologous miR-146a sequence, it is speculated that Mus miR-146a may bind to Mus IRAK1 and TRAF6 3′UTR and inhibit their expression. There are three potential binding sites in the Mus IRAK1 3′UTR, and two in the Mus TRAF6 3′UTR ( Figure 4 a). To characterize the role of miR-146a in EV71 infection in vivo, first, because human EV71 has low infectivity or non-infectivity in mice, mouse-adapted EV71 (hereafter referred to as mEV71) was generated and used to establish EV71 infection mice. mouse model 1 . Different mEV71 plaque forming units (PFU) were used to titrate the most preferred mEV71 dose to be used in the following in vivo mEV71 infection assays. Via natural oral route, 1×10 via mEV71 8 and 2×10 8 The 10-day survival rates of PFU-infected mice were 60% and 20%, respectively, and were selected for further experiments. miR-146a express...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com