Chain network external fault location extension method
A technology of chain network and out-of-area faults, which is applied in the direction of fault location, measuring electricity, and measuring devices, can solve the problems of difficulty in fault location and high operating costs of the double-terminal traveling wave method, and achieve the goal of overcoming the difficulty of fault location and measuring The results are accurate and reliable, and the effect of reducing construction costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
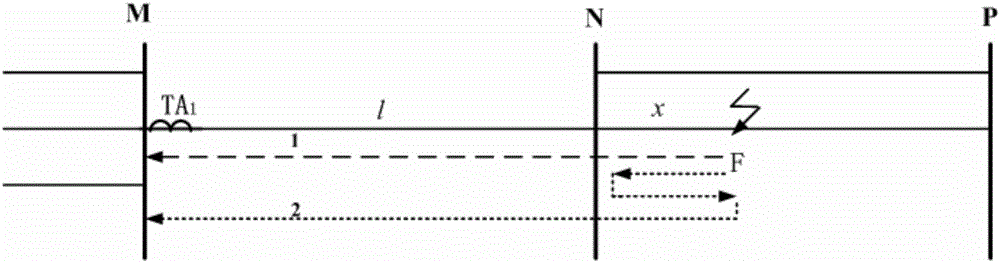
[0033] Such as figure 1 Shown is a chain network composed of three substations M, N, P, and the lengths of each line are: the length of the healthy line MN is l=10km, and the length of the faulty line NP=90km. Assume that a phase-A ground fault occurs 55km away from the N-terminal of the bus on line NP, the initial fault angle is 120°, the transition resistance is 10Ω, and the sampling rate is 1MHz.
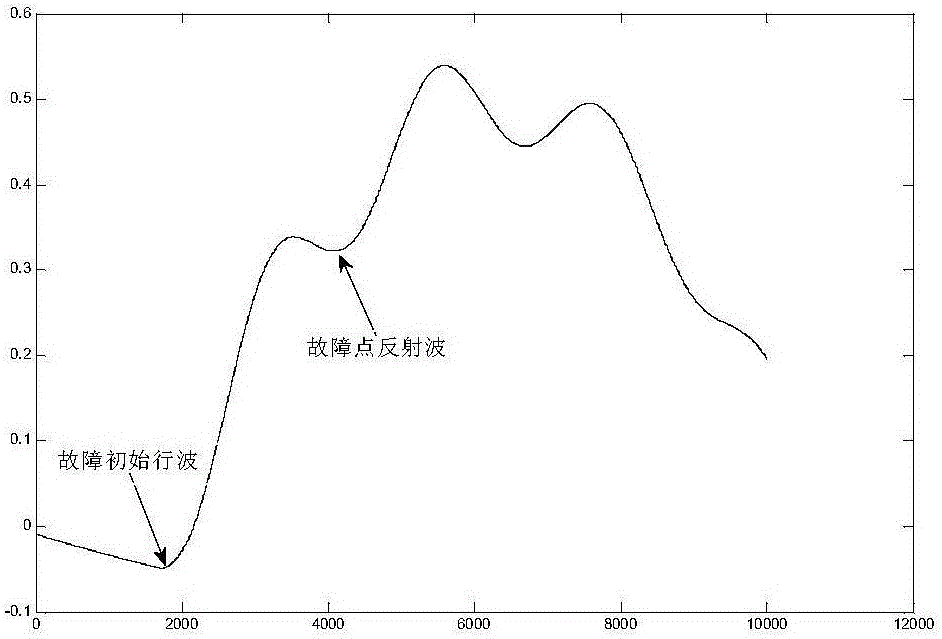
[0034] according to figure 2 The time corresponding to the current traveling wave diagram to find out the fault wave head is t 1 = 0.213867s,t 2 =0.216270s; find the fault wave head time difference Δt=t 2 -t 1 =0.002403s, v is taken as the empirical wave velocity, and its size is 2.98×10 8 m / s; finally use the formula (3) to calculate the fault distance l f =l-v·Δt / 2=54.2km, meeting the requirements within the error range.
Embodiment 2
[0036] Such as figure 1Shown is a chain network composed of three substations M, N, P, and the lengths of each line are: the length of the healthy line MN is l=10km, and the length of the faulty line NP=90km. Assume that a phase A ground fault occurs at a distance of 20km from the N terminal of the busbar on the line NP, the initial fault angle is 90°, the transition resistance is 10Ω, and the sampling rate is 1MHz.
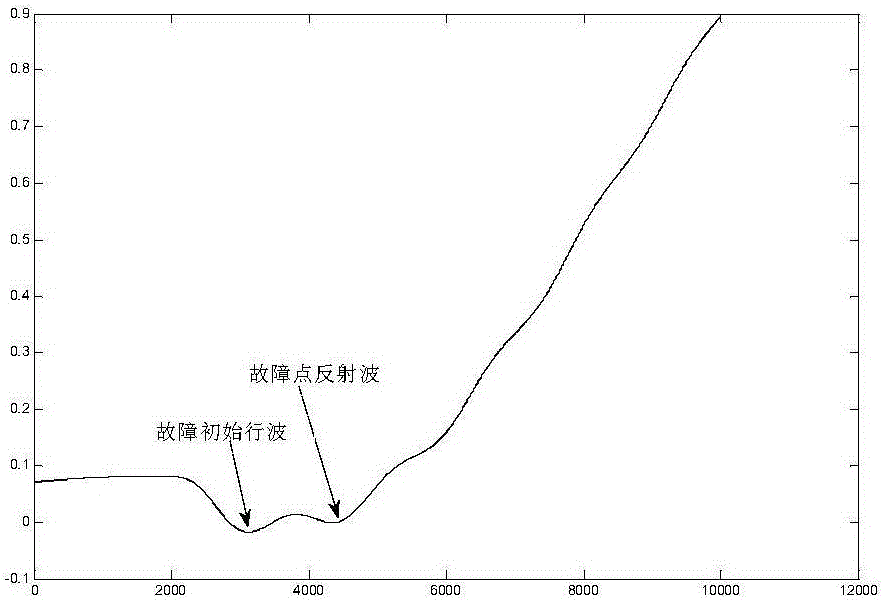
[0037] According to the current traveling wave diagram shown in Figure 3, find out the time corresponding to the fault wave head as t 1 = 0.208068s,t 2 =0.209440s; find the fault wave head time difference Δt=t 1 -t 2 =0.000668s, v is taken as the empirical wave velocity, and its size is 2.98×10 8 m / s; finally use the formula (2) to calculate the fault distance l f =v·Δt / 2=20.44km, meeting the requirements within the error range.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com