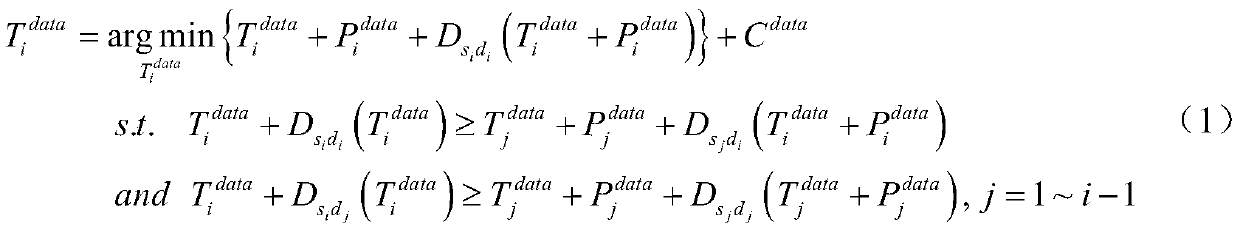Multi-node Parallel Communication Method for Competitive Channel Underwater Acoustic Networks Containing Moving Nodes
A technology of moving nodes and underwater acoustic networks, which is applied in wireless communication, transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of prolonging the average time of multi-node communication, and cannot be well adapted to underwater applications including moving nodes and effective data transmission time. Problems such as small proportion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
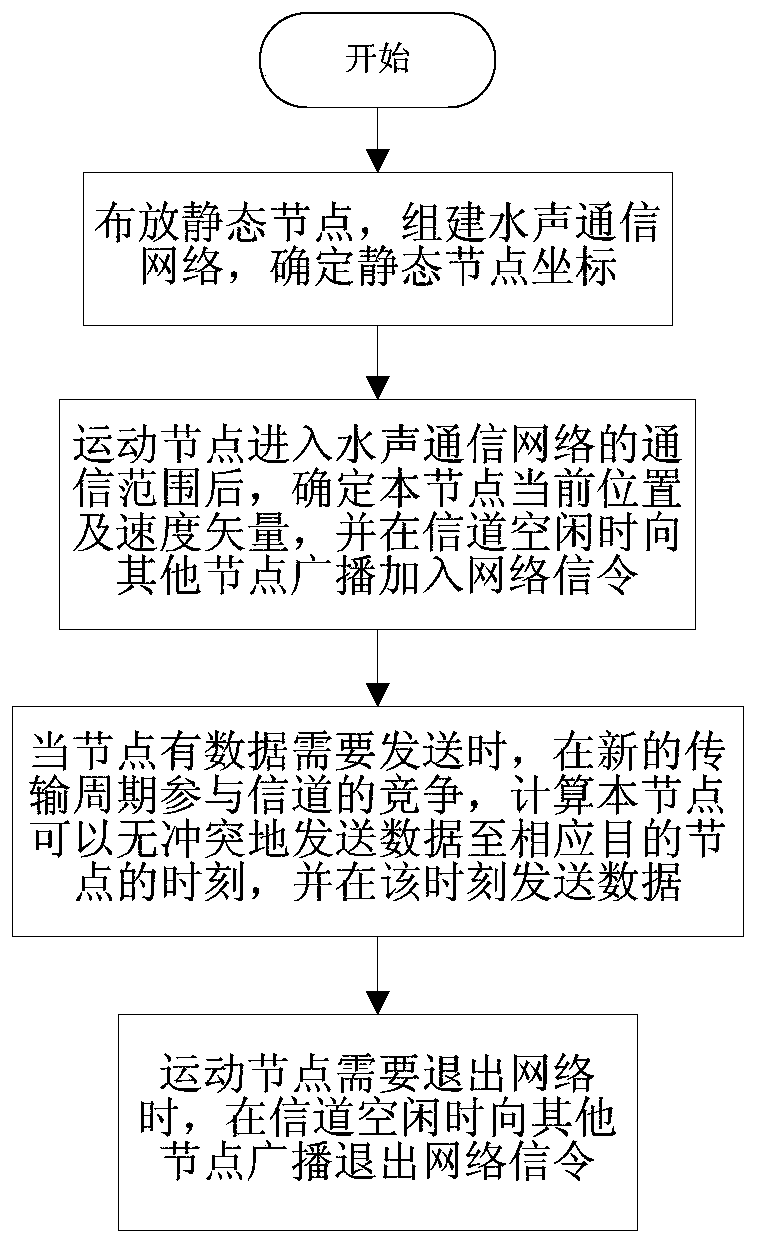
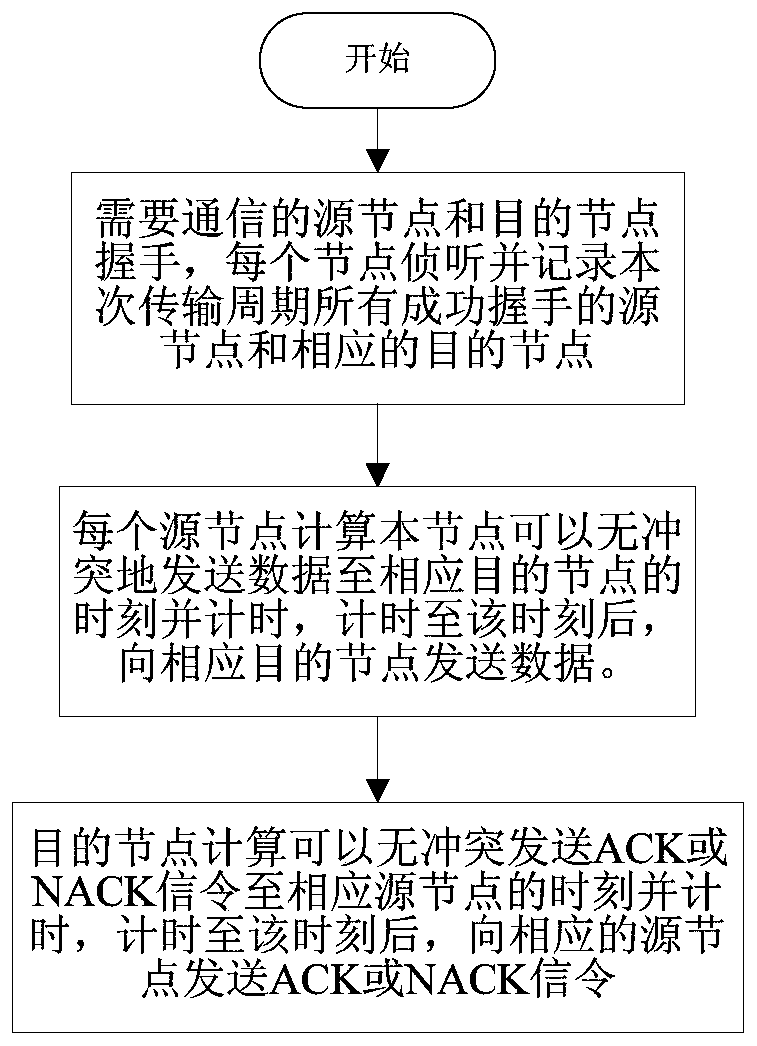
[0053] The specific implementation steps of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples, but the embodiments of the present invention are not limited thereto. If there are processes that are not specifically described in detail below, those skilled in the art can refer to the prior art. of.
[0054] The embodiment of the present invention is an underwater acoustic communication network with 6 nodes, including 3 stationary nodes A, B, and C and 3 moving nodes D, E, and F, and the communication mode between each node is omnidirectional, semi-dual The bandwidth used for communication is 6KHz, and the speed of sound underwater is 1500m / s. All nodes in the network can monitor the signals of other nodes, and each node has a synchronous clock signal. When there are N (1≤N≤3) nodes in the network that need to send data, if the existing handshake-based underwater acoustic network media access control protocol is used,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com