Power failure risk computing method for electric power system containing double-fed wind power plant
A risk calculation, power system technology, applied in wind power generation, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve the problem of no inertia contribution, problems, roughness and other problems of the system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
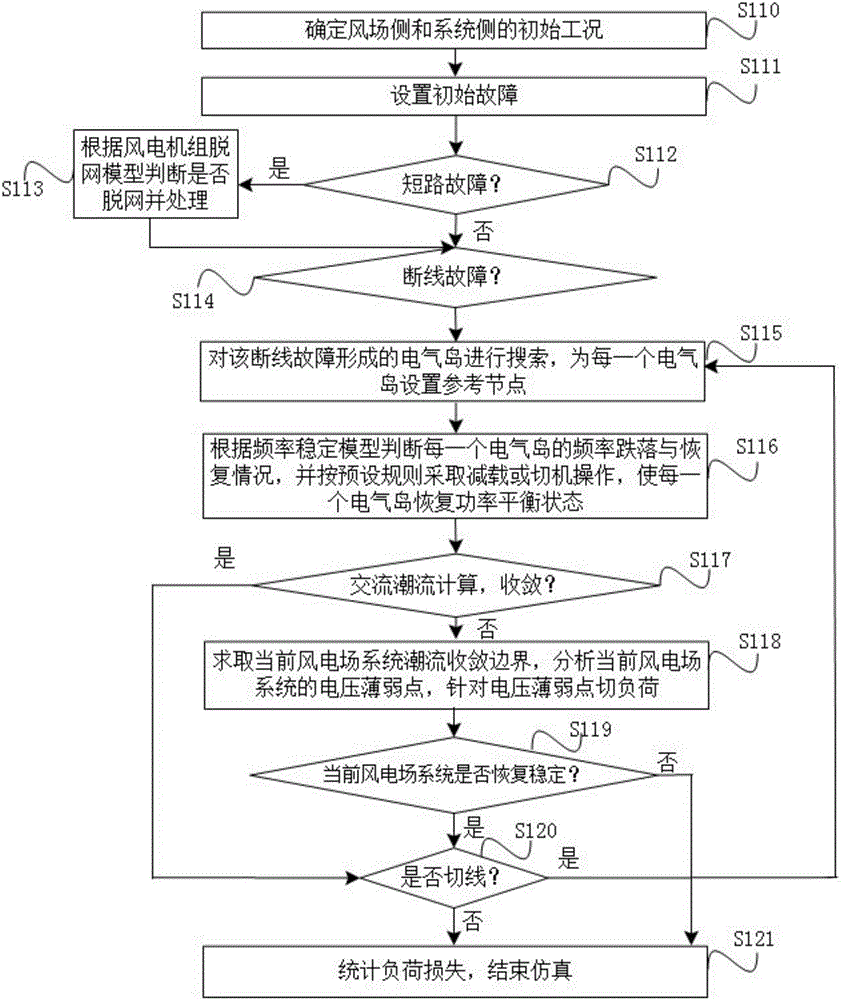
[0097] see figure 1 As shown, the method for calculating the blackout risk of a power system including a doubly-fed wind farm provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0098] Step S110, determining the initial working conditions of the wind farm side and the system side.
[0099] Before the simulation process, it is necessary to pre-build some models on which the simulation process is based, mainly including frequency stability model, voltage stability model, wind turbine off-grid model and initial fault model, etc.
[0100] Determining the initial working conditions on the system side includes calculating the predicted active output of wind turbines and the output of synchronous generators, etc.
[0101] Step S111, setting an initial fault.
[0102] Set the initial fault, that is, according to the initial fault model, sample the initial fault situation of the current simulation. The initial fault is the disturbance set for the system at the beginning of t...
Embodiment 2
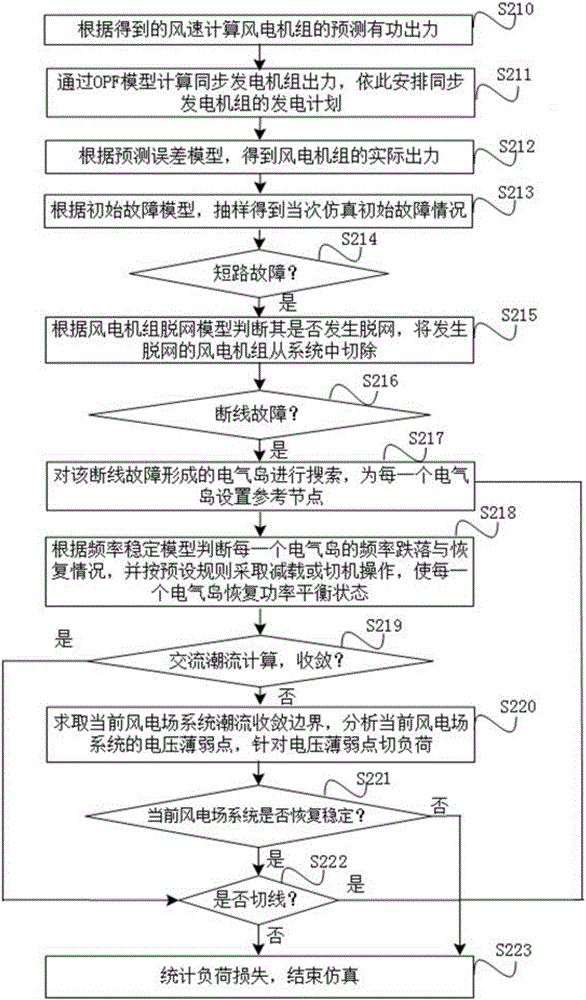
[0117] The embodiment provided in the second embodiment is a preferred solution of the present invention. see figure 2 shown, including steps:
[0118] Step 210, construct a wind speed model according to the natural wind speed and its probability distribution at different wind turbines, obtain the wind speed at each wind turbine by sampling according to the wind speed model, and calculate the predicted active output of the wind turbine according to the obtained wind speed.
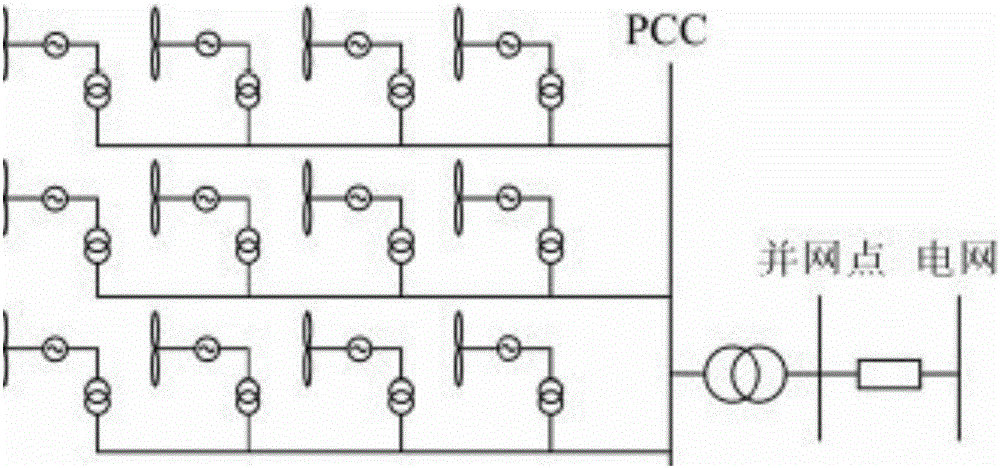
[0119] The structure layout adopted by the wind farm in this embodiment is as follows: image 3 As shown, multiple wind turbines are connected into a "trunk line", and multiple "trunk lines" are connected to the PCC point in parallel. A wind farm step-up substation is installed at the PCC point, and the step-up substation is then connected to the grid connection point. The electric energy is sent to the grid through the transmission line after the step-up station. Wherein, the distance between the win...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com