Dynamic estimation method for P-wave and S-wave velocities in carbon dioxide flooding process
A technology of oil displacement process, carbon dioxide, applied in the field of exploration geophysics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] According to the actual situation of the work area, a suitable model is selected, and the applicability of the model is verified by using the traditional method to estimate the compression and shear waves before displacement. The Xu-White model comprehensively considers the influence of matrix properties, shale content, porosity size and pore shape in rocks, and the properties of fluid contained in pores on velocity, and the physical meaning of this model is clear.
[0032] like figure 1 as shown, figure 1 It is a flow chart of the dynamic estimation method of compressional and shear wave velocity in the carbon dioxide flooding process of the present invention.
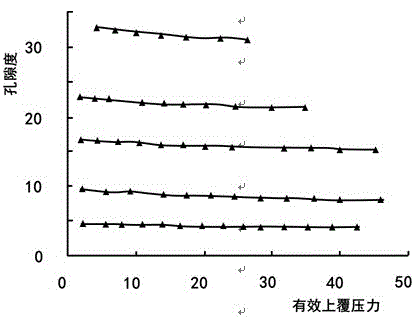
[0033] Step 101 , affected by the injection of carbon dioxide, not only the fluid inside the reservoir will change, but also the porosity and pore shape of the reservoir will change accordingly, resulting in a change in rock elastic modulus. The total porosity of the rock after carbon dioxide displacement can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com