A Modular Method for Obtaining the Failure Probability of the Top Items in the Fault Tree of Nuclear Power Plant
A failure probability and fault tree technology, applied in electrical testing/monitoring, instrumentation, control/regulation systems, etc., can solve problems such as inability to store computer memory, large number of disjoint cut sets, and huge BDD structure, etc., to reduce Effects of memory consumption, accurate results, and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The present invention is described in more detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing example:
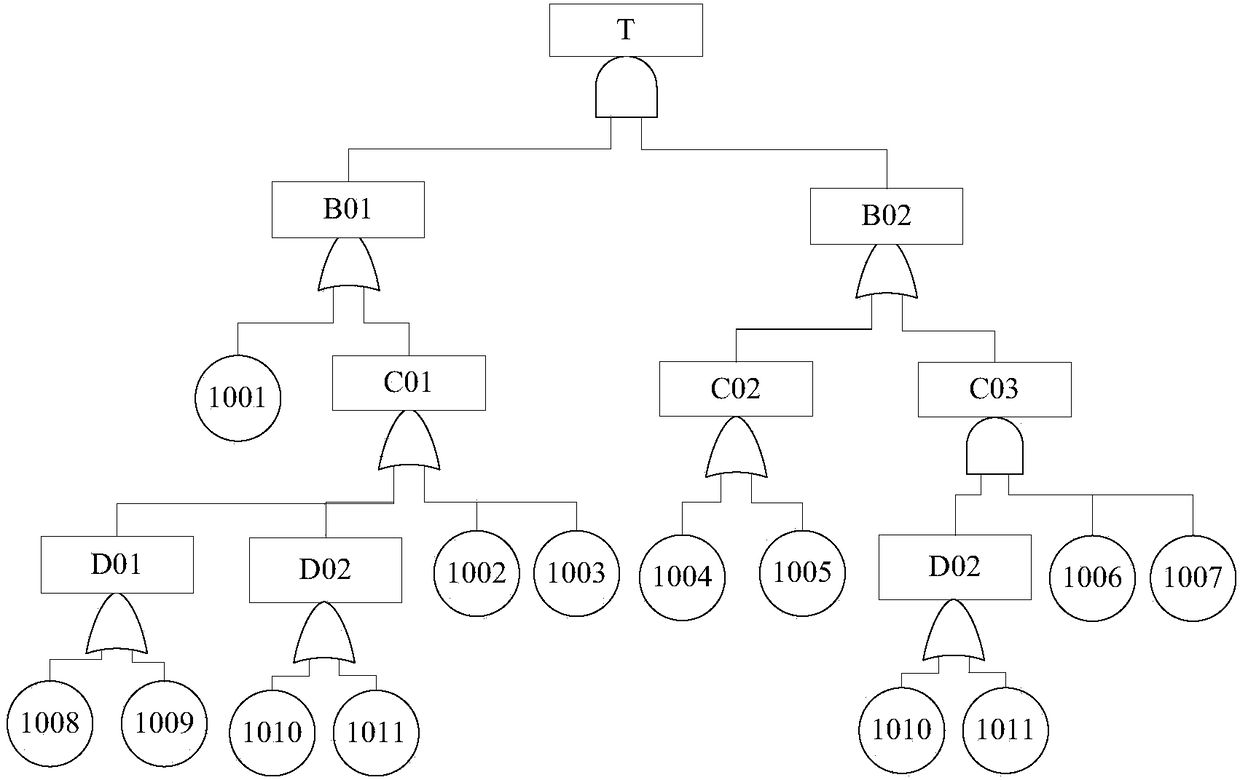
[0036] The technical solution of the present invention is: a method for modularly solving the fault tree model, figure 1 It is a flowchart of the present invention, in conjunction with accompanying drawings, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0037] (1) Establish a fault tree according to the requirements.
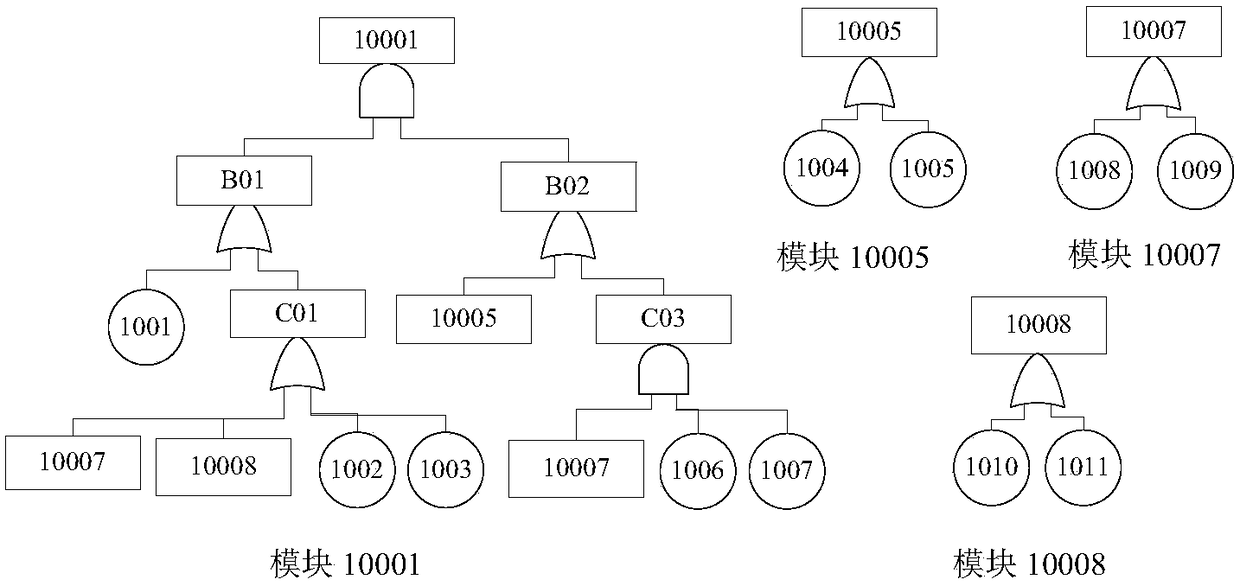
[0038] (2) Modularize the fault tree. The definition of a fault tree module is: a subtree with at least two events, and its bottom event does not appear in other places in the fault tree. Fault tree modularization requires two traversals of the fault tree.
[0039] (3) Transform the modularized fault tree into a BDD structure. Before converting the fault tree into a BDD structure, the order of the bottom events must be determined first, and then the BDD structure of the corresponding fault tree can be obtained according to the If-Then-Else (ITE)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com