Method for breeding cordyceps sinensis host larvae in turns
A larval and mixed feeding technology, applied in animal husbandry and other directions, can solve the problem of not mentioned rotation feeding, and achieve the effect of speeding up the growth cycle of larvae, enriching feeding options, and reducing feed costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
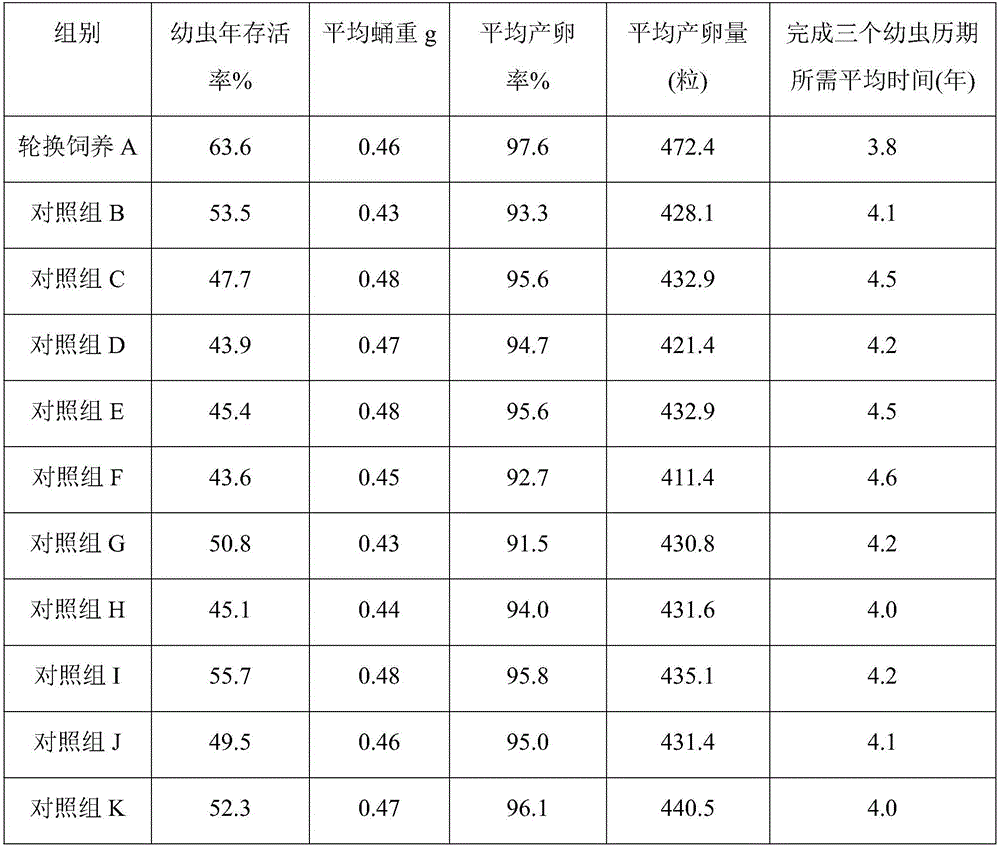
Embodiment 2
[0039] Reference Example 2. Screening of Salvia Miltiorrhiza
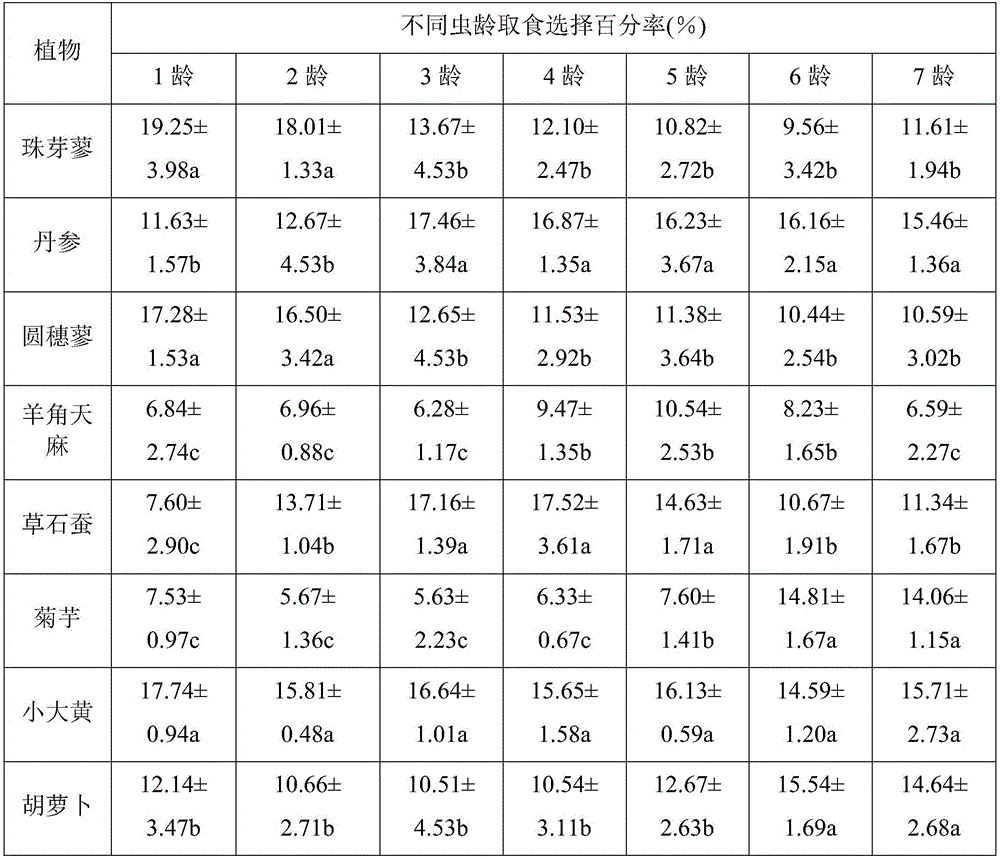
[0040] Screening process: More than 100 kinds of Chinese herbal medicines or ingredients were tested, and the following 8 kinds of ingredients that can meet large-scale production were selected from the feeding effect, shelf life, and larval growth parameters. The comparative feeding effects of Danshen Polygonum villosa, small rhubarb, Polygonum rotundum, Gastrodia chinensis, Jerusalem artichoke, caddis, and carrots are shown in the table below.
[0041] feed
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiment 1 The selection of feed by bat moth larvae in different age stages
[0043] Place a filter paper for moisturizing in a transparent plastic Petri dish with a diameter of 12cm, and cut the rhizomes of optional ingredients into 1cm 3Cube-shaped size, and placed on the filter paper in a circle evenly along the periphery of the petri dish. There are 2 pieces of each plant rhizome in each device. For example, in this scheme, the larvae choose to feed on 8 kinds of plant rhizomes. The order is ABCDEFGHABCDEFGH. At the beginning of the experiment, the 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 instar larvae of the tested bat moth after 24 hours of starvation treatment were placed in the center of 7 pieces of wet filter paper, and the lids of the petri dishes were respectively covered, and then placed Measure selectivity under the conditions of temperature 12°C, humidity 80%, light intensity 15W, L:D=14h:10h (ratio of light time and dark treatment time in one day), place 30 larvae in e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com