A method for removing bismuth by vacuum distillation depth of high bismuth coarse tin alloy
A high-bismuth crude tin and alloy technology, applied in the field of non-ferrous metallurgy, can solve the problems of serious metal backlog, low element recovery rate, long process, etc., achieve low production cost, increase element recovery rate, and short turnover period.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
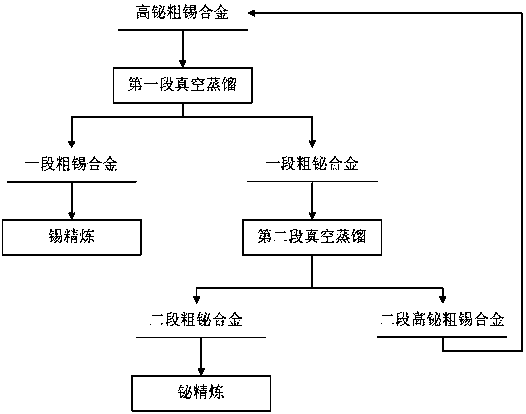
[0014] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, the method for removing bismuth by vacuum distillation depth of the high-bismuth thick tin alloy is as follows: First, the high-bismuth thick tin alloy raw materials (composition: Sn67.5%, Bi30.5%, Sb1.2%, Cu0.8%) into the melting pot to melt, start the first distillation process, the melting temperature is 450°C-500°C, the vacuum degree in the control equipment is 0.01-0.1Pa, the heating control temperature is 1150-1250°C, and the feeding system is turned on Continuously inject high-bismuth coarse tin melt into the vacuum equipment for 24 hours, and the injection rate is 420kg / h. The difference in vapor pressure of each element in the material is used to achieve distillation separation, and the distillation process continuously produces residue products and volatile products. After the test, a total of 100 tons of raw materials were input. The obtained residue is a section of crude tin alloy, totaling 64.5 tons, and its composition...
Embodiment 2
[0015] Embodiment 2: as figure 1 As shown, the method for the deep removal of bismuth by vacuum distillation of the high-bismuth thick tin alloy is as follows: first, the high-bismuth thick tin alloy raw material (composition is: Sn49.8%, Bi48.7%, Pb0.8%, Cu0.6%) into the melting pot to melt, start the first distillation process, the melting temperature is 450°C-500°C, the vacuum degree in the control equipment is 0.01-0.1Pa, the heating control temperature is 1150-1250°C, and the feeding system is turned on Continuously inject high-bismuth coarse tin melt into the vacuum equipment for 24 hours, and the injection rate is 380kg / h. The difference in vapor pressure of each element in the material is used to achieve distillation separation, and the distillation process continuously produces residue products and volatile products. After the test, a total of 100 tons of raw materials were input. The obtained residue is a section of crude tin alloy, totaling 45.5 tons, and its comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com